home
 Management Management
 Management - Vikhansky OS Management - Vikhansky OS
|
Management - Vikhansky OS
2.2. Maintaining organizational culture
Typically, the organization is growing by attracting new members coming from organizations with a different culture. New members of the organization, whether they like it or not, are entered into it "virus" different culture. Which of Cultures "will survive", largely depends on its strength, since the latter affects the intensity of certain patterns of behavior.
The strength of the culture of the organization is determined by three factors:
• «thickness» Culture;
• the degree of separability culture of the organization members;
• clarity of cultural priorities.
"Thickness" organizational culture is defined by the number of important assumptions, shared by employees. Culture with many levels of faith and values have a strong influence on the behavior of the organization.
In some cultures, the shared beliefs and values clearly ranked. Their relative importance of and the relationship between them does not diminish the role of each of them. In other cultures, the relative priorities and the link between shared values is not so clear. In the first case, it achieved a greater effect in terms of impact on people's behavior, as they are developing confidence in what value should prevail in case of conflict of interest.
Thus, a strong culture of "thicker", it divides a large number of employees and more clearly identifies priorities, and accordingly, has a profound impact on the behavior of the organization.
A strong culture creates not only the benefits for the organization. It will be appreciated that the culture is strong at the same time a serious obstacle to making changes in the organization. "New" in the culture of the beginning is always weaker. Therefore it is considered better to have a moderately strong culture in the organization.
There are methods of maintaining an organizational culture that can not be reduced only to hiring the right people and the dismissal unnecessary (Fig. 10.5). The main groups are the following methods.
The objects and objects of attention, evaluation, management control. This is one of the most powerful methods of maintaining the culture in the organization, since their repeated actions Manager enables employees to know what is important and what is expected of them.
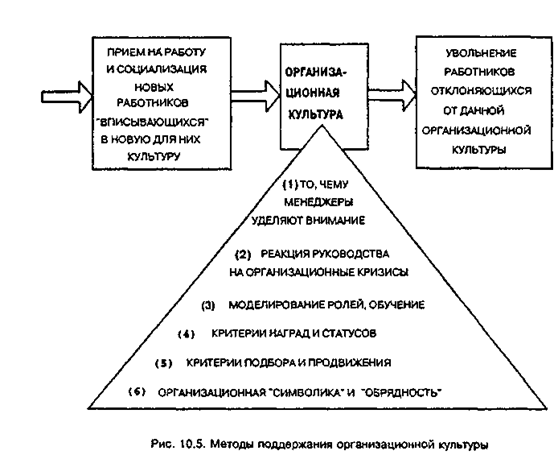
Management response to critical situations and organizational crises. In these situations, managers and their subordinates reveal for themselves the organizational culture to such an extent in which they are currently not represented her. The depth and breadth of the crisis may require the organization or enhance the existing culture, or the introduction of new values and norms, changing it to a certain extent. For example, in the case of a sharp reduction in demand for manufactured products the organization has two alternatives: SVR-pouring of the employees or in part to reduce working hours npi-the same number of employees. In organizations where the person claimed to be the value of "number one", apparently, will be the second option. Such an act of leadership will become over time in organizing folklore, which will undoubtedly strengthen this aspect of the culture in the company.
Modeling of roles, training and exercise. Aspects of organizational culture are assimilated through subordinates how they should perform their role. Managers can embed a specially important "cultural" signals in training and in daily assistance to subordinates at work. For example, an educational film can focus on clean workplace. The manager himself may also demonstrate a subordinate, for example, a certain attitude to the customers or the ability to listen to others. Constantly concentrating on these points account manager helps to keep certain aspects of the organizational culture.
Criteria for determining remuneration and status. Culture in the organization can be studied through the rewards and benefits system. The latter are usually tied to certain patterns of behavior and, thus, are arranged for the employees of the priorities and point to values that are more important for individual managers and the organization as a whole. In the same direction the system works in the organization of status positions. For example, the distribution of benefits (good office, secretary, car, etc.) points to the role and behavior of a valued organization. However, experience shows that this method is often not used fully and systematically.
Criteria for recruitment, promotion and dismissal. This is one of the main ways of maintaining the culture in the organization. That from which comes the organization and its management, handling the whole process of human resources, it becomes quickly known to its members on the movement of staff within the organization. The criteria for personnel decisions can help, or may prevent the consolidation of the existing culture in the organization. Thus, inherent in assembly-line production staff turnover on the assembly lines has prompted many companies to move to a team approach to work, or to move to "Wagon" assembly in the integrated brigades.
Organizational symbols and rituals. Many of the beliefs and values underlying organizational culture, expressed not only through legends and sagas that become part of the organizational folklore, but also through the various rituals, rites, traditions and ceremonies. By the standard rites are repetitive and collective activities carried out at the specified time and on a special occasion to influence the behavior and understanding of the organizational environment of the employees. Rituals are rituals system. Even certain management decisions can become organizational rituals that employees interpreted as part of the organizational culture. Such rites act as organized and planned actions, which have important "cultural" value. Observance of rituals, rites and ceremonies strengthens the self-determination of employees (tab. 10.3).


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.