home
 Finance Finance
 Books Books
 Finance and Statistics - Ковалева А.М. Finance and Statistics - Ковалева А.М.
|
Finance and Statistics - Ковалева А.М.
5. COMPANY PROFIT. ITS PLANNING AND DISTRIBUTION
5.1 THE ROLE OF PROFITS IN THE CONDITIONS OF ENTERPRISE DEVELOPMENT
Profit is the monetary expression of the main part of the monetary savings created by enterprises of any form of ownership. As an economic category, it characterizes the financial result of the entrepreneurial activity of the enterprise. Profit is the indicator most fully reflecting the efficiency of production, the volume and quality of the products produced, the state of labor productivity, the level of cost. At the same time, profit has a stimulating effect on the strengthening of commercial calculation, intensification of production under any form of ownership.
Profit is one of the main financial indicators of the plan and an assessment of the economic activity of enterprises. Due to profit, financing of measures for scientific, technical and socio-economic development of enterprises is carried out, an increase in the payroll of their employees.
It is not only a source of ensuring the intraeconomic needs of enterprises, but is gaining increasing importance in the formation of budgetary resources, extrabudgetary and charitable foundations.
The multidimensional value of profits is strengthened with the transition of the state economy to the foundations of a market economy. The fact is that a joint-stock, leased, private or other form of ownership enterprise, having obtained financial independence and independence, has the right to decide for what purposes and in what amounts to direct the profits left after payment of taxes to the budget and other obligatory payments and deductions.
The Law of the Russian Federation of December 25, 1990 "On Enterprises and Entrepreneurship" stipulated that entrepreneurial activity means enterprising independence of enterprises aimed at making a profit. At the same time, the enterprise as an economic entity, independently carrying out its activities, disposes of the products manufactured and the net profit remaining at its disposal. At the same time, the entrepreneurial activity of enterprises in a variety of forms of ownership means not only the distribution of property owners' rights, but also the increase of responsibility for rational management of it, the formation and effective use of financial resources, including profits.
Profit as the final financial result of the activities of enterprises is the difference between the total amount of revenues and the costs of production and sales of products, taking into account the losses from various business transactions. Thus, profit is formed as a result of the interaction of many components with both a positive and a negative sign. For details on the composition of the gross profit of the enterprise, see 5.3.
The leading value of profit as a financial indicator of entrepreneurial activity of an enterprise does not mean, however, its uniqueness. An analysis of the incentive role of profits shows that in individual economic entities the desire to extract high profits predominates in order to increase the wage fund at the expense of the production and social development of the collective. Moreover, the facts of obtaining "unearned" profit, that is, Formed not as a result of effective economic activity, but by changing, for example, the structure of products is not in the interests of consumers. Instead of producing low-profitable but highly demanded products, enterprises increase production of more profitable and more expensive profitable products for them.
In some cases, profit growth is due to an unjustified increase in product prices.
The desire to get high profits by any means with the purpose of increasing the wage fund leads to an increase in the volume of de-
"Has ceased to be effective since January 1, 1995, except articles 34 and 35.
A gentle mass in circulation, not provided with commodity resources, Hence - the further rise in prices, inflation, and consequently, the emission of money.
Thus, the absolute increase in the profit of an enterprise does not always objectively reflect the increase in the efficiency of production as a result of the labor achievements of the collective.
For a real assessment of the profitability level of an enterprise, you can use the methods of integrated profit analysis for technical and economic factors. These methods can be in the arsenal of tax authorities, credit and financial institutions, control bodies, arbitration and others, i.e. Those links that interact with this economic entity.
Complex analysis of profits is recommended to be carried out in a certain sequence. First of all, gross profit is analyzed by its constituent elements, the main one being the profit from sales of commodity output. Then, the enlarged factors of profit change from output of commodity output are analyzed. Important in this system will be an analysis of technical and economic factors of reducing (increasing) the costs of the monetary unit of commodity output. In addition, changes in the volume and structure of sales, changes in the level of prices for products sold, as well as purchased raw materials, materials, fuel, energy and other costs are analyzed. The level of material costs and labor costs is compared.
The change in profit is also determined as a result of a violation of economic discipline. Along with this, the analysis of changes in profit in the remainder of finished products from other sales and non-sales operations is carried out.
In addition to the mentioned methods of factorial analysis of profit, profitability indicators are used in the number of economic indicators of the effectiveness of entrepreneurial activity.
If the profit is expressed in an absolute amount, then the profitability is a relative indicator of the intensity of production. It reflects the level of profitability relative to a certain base.
The enterprise is profitable if the proceeds from the sale of products are sufficient not only to cover the costs of production and sales, but also to generate profit.
Profitability can be calculated in different ways. Over the past 25 years, profitability has been widely used, calculated as the ratio of profit to the amount of production assets (fixed productive assets and material working capital).
Given that this indicator under the previous conditions of management was planned, it was assumed that it had to influence the increase in output with the least amount of production assets, i.е. Stimulate better use of the latter.
However, as the past period showed, the set goal was not achieved. Nevertheless, this indicator of profitability, calculated as the ratio of profit to the value of production assets, continues to be applied in the practice of entrepreneurial activity for a general assessment of the level of profitability, profitability of the enterprise. At the same time, they argue as follows: since both the means of labor and the objects of labor take part in the production process, the more the "profit" is taken from each ruble of production assets, the better and more efficiently the enterprise operates, and vice versa.
This indicator of profitability is calculated by the formula

Such a high level of profitability can be explained by an increase in the volume of production, and mainly - by inflationary growth in prices for products sold, which led to the receipt of large amounts of profit with relatively low amounts of fixed productive assets and material working capital.
In addition to the profitability of production, in the process of analyzing the entrepreneurial activity of enterprises, the profitability index of products is widely used, calculated as the ratio of the profit from the sale of production to the total cost of production.
The application of this profitability indicator is most rational for on-farm analytical calculations, for monitoring the profitability (loss) of certain types of products, for introducing new types of products into production and for removing inefficient products.
Taking into account that profit is connected both with the cost of the product and with the price at which it is realized, the profitability of the products can be calculated as the ratio of profit to the value of sold products at free or regulated prices.
These indicators of product profitability are interrelated and characterize the change in current costs for the production and sale of both products and individual types. In this regard, when planning the range of products, it is taken into account how the profitability of certain types of products will affect the profitability of all products. Therefore, it is important to form a product structure depending on the change in the specific gravity of products with greater or less profitability, so as to improve overall production efficiency and obtain additional opportunities for increasing profits.
The profitability of products in its two varieties is calculated by the formulas:
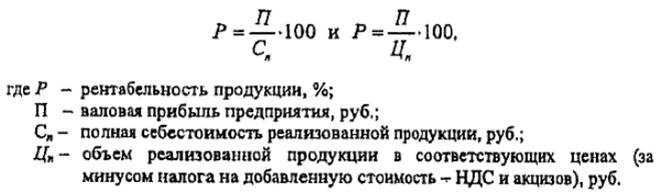
Let's trace, using the data of the given example, the ratio of the levels of profitability. For example, over the past year, products sold at full cost were sold at 1093.5 thousand rubles, and at current prices (minus VAT and excises) - by 1,485.5 thousand rubles,
The gross profit of the enterprise is 3 85.6 thousand rubles.

It is quite obvious that with this method, the level of profitability of products sold at appropriate prices will always be below the level of profitability of products calculated at full cost (except for unprofitable enterprises). Comparing the different profitability indicators, we can say that the profitability index of production (131.9%) is incommensurable with the profitability of products (35.3% and 25.9%). Nevertheless, the growth factors of any indicator of profitability depend on unified economic phenomena and processes. This is primarily:
- Improvement of the production management system in a market economy on the basis of overcoming the crisis in the financial and credit and monetary systems;
- Increasing the efficiency of the use of resources by enterprises on the basis of stabilization of mutual settlements and the system of settlement and payment relations;
- Indexation of working capital and a clear definition of the sources of their formation.
An important factor in the growth of profitability in the current conditions is the work of enterprises on resource-saving, which leads to a reduction in production costs, and, consequently, to a rise in profits. The fact is that the development of production through the savings of resources at this stage is much cheaper than the development of new deposits and the involvement of new resources in production.
The reduction in the cost price should become the main condition for the growth of profitability and profitability of production.


Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.