home
 Finance Finance
 Books Books
 Finance and Statistics - Ковалева А.М. Finance and Statistics - Ковалева А.М.
|
Finance and Statistics - Ковалева А.М.
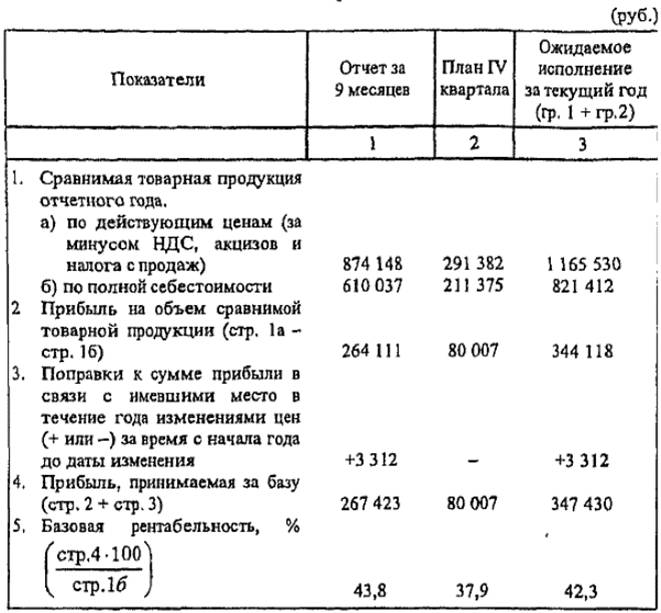
Calculation of basic profitability
Table 5.2 Calculation of basic profitability
Hence the increase in the cost of comparable commercial output is equal to 502,787 rubles. (1 406 340 - 903 553), which will lead to a decrease in the planned profit.
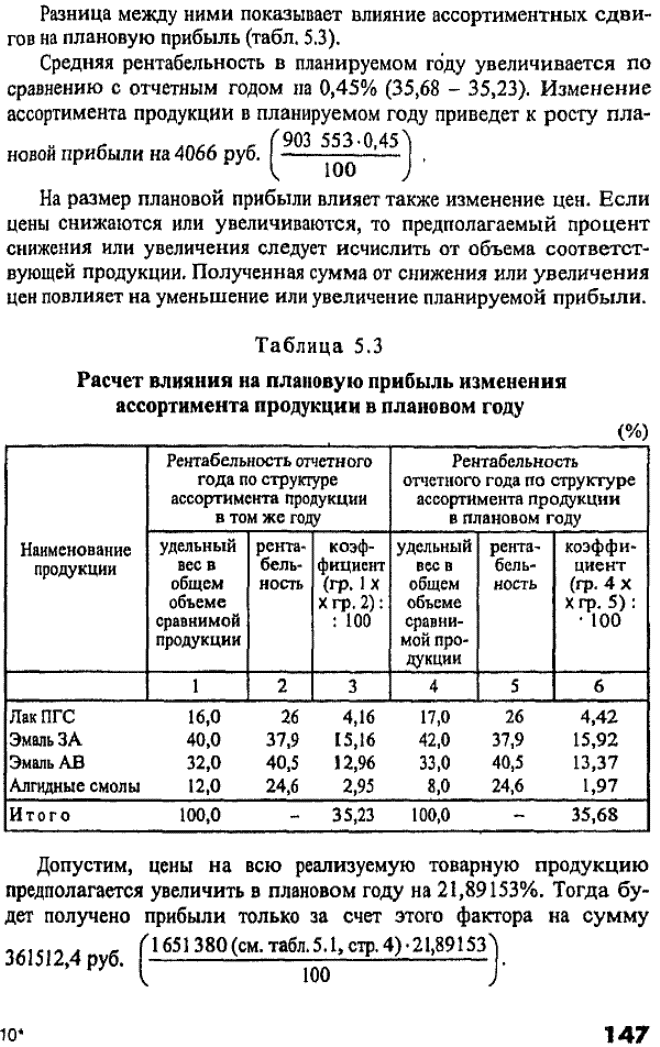
The planned change in the range of products causes an increase or decrease in the planned profit. In order to determine the effect of assortment shifts on profit, the specific weight of each product is calculated in the total volume of comparable products at full cost in the reporting and reporting year. Then the specific weight of each product in the reporting and planned year is multiplied by the reported profitability of this product (calculated as the ratio of profit to the total cost of the product) adopted at the level of expected performance. The amounts of the coefficients obtained reflect the average level of profitability in the reporting and planned year.

A significant increase in profit (by 361,112.4 rubles) is planned in connection with the expected increase in prices for products sold, which is also due to inflationary processes. In this regard, despite the increase in profit due to rising prices, this factor can not be regarded as positive.
In addition to the above reasons that affect the planned profit, it includes the amounts of profit for a comparable product through the basic profitability, as well as incomparable commodity products, put on production in the planned year. It also takes into account the profit in the leftovers of finished goods in the warehouse and in goods shipped at the beginning and end of the planned year.
In addition to profits from sales of commodity products in the gross profit, as noted earlier, profits from the sale of other products and services of a non-commodity nature, profits from the sale of fixed assets and other property, as well as planned non-operating income and expenses are taken into account.
The profit from other sales (products and services of subsidiary agriculture, auto-farms, non-industrial services - for capital construction, overhaul, etc.) is planned by direct account method. Only with a small share of this product (services), the profit from sales is determined on the basis of Its planned volume in the coming year and the profitability of the reporting year,
The result from the other implementation can be either positive or negative. Suppose, in our example, the profit from other sales is planned at 30 rubles, and the losses in the amount of 288 rubles.
The profit (losses) from traditional articles of non-operating income and expenses (fines, penalties, forfeits, etc.) is determined, as a rule, on the basis of the experience of the past. With respect to such items as income from equity participation in the activities of other enterprises, from leasing property, dividends, interest on shares, bonds and other securities owned by the enterprise, they are planned depending on forecasts in the development of the entrepreneurial activity of this economic entity .
For example, incomes from non-operating operations are planned in the amount of 2798 rubles, and expenses from these operations - in the amount of 9000 rubles.
So, in the considered example the total amount of profit will be 394866.7 rubles. (392038.7 + 30 + 2798), and losses - 9288 rubles. Therefore, the gross profit of the enterprise is determined in the amount of 385578.7 rubles. (394,866.7 - 9288).
In addition to the above methods of profit planning - the method of direct account and analytical - there is a METHOD OF COMBINED CALCULATION .
In this case, the elements of the first and second methods are applied. Thus, the value of commodity output in the prices of the coming year and at the cost of the reporting year is determined by the direct account method, and the impact on planned profit of factors such as changes in production costs, quality improvement, change in assortment, prices, etc. is revealed using the analytical method.
Calculation of the optimal amount of profit becomes an important element of planning business at the present stage of management. To forecast the maximum possible profit in the planned year, it is advisable, based on the experience of Western entrepreneurship, to compare the proceeds from the sale of products with the total amount of costs, divided into variables, fixed and mixed
Variable costs include the costs of raw materials, materials, electricity, transportation, etc. These costs vary in proportion to the change in output.
Constant costs are costs that do not change depending on the growth or decline in output. These include depreciation, payment of interest for a loan, rent, management personnel, administrative expenses, etc.
Mixed costs include variables and fixed costs. These, for example, are postal and telegraph costs, the costs of carrying out routine maintenance of equipment, etc.,
Due to the small share of mixed costs, we will focus on variables and constant costs and try to identify the effect of their changes on the amount of profit. The fact is that the increase in profits depends on the relative decrease in variable or fixed costs.
The calculations below allow us to determine the so-called "production lever effect" (a term taken from Western entrepreneurship practice). "The effect of the production lever" refers to this phenomenon when, with a change in revenue from the sale of products, there is a more intensive change in profits in one direction or another.


Proceeding from the strength of the impact of the production lever, we can conclude: the higher the share of fixed costs and, correspondingly, the lower the specific weight of variable costs with the same amount of revenue from sales of products, the stronger the impact of the production lever. However, this does not mean that it is possible to increase the fixed costs uncontrolled, since if the revenue from sales of products decreases, the enterprise will incur large losses in profits.
So, the given examples of profit maximization by changing the share of variables and fixed costs open the possibility for entrepreneurs to plan for the future the size of the profit increase depending on the economic successes in the production of competitive products and take appropriate measures in advance to change the variable and fixed costs in one direction or another. Approximate profit calculations are important not only for enterprises producing and selling products (services), but also for shareholders, investors, suppliers, creditors, banks related to the activities of this entrepreneur, participating in their own funds in the formation of its authorized capital. Therefore, planning the optimal size of profit in the current economic conditions is the most important factor for successful entrepreneurial activity.


Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.