home
 Finance Finance
 Books Books
 Finance and Statistics - Ковалева А.М. Finance and Statistics - Ковалева А.М.
|
Finance and Statistics - Ковалева А.М.
Balance sheet asset analysis
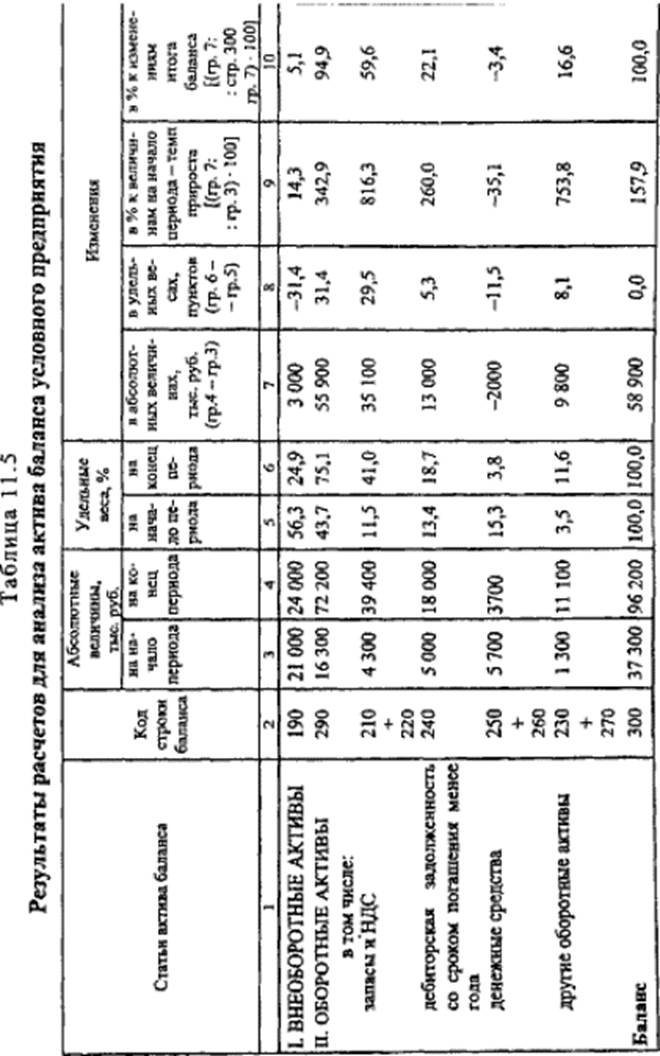
Analysis of the asset balance . To analyze the structure and dynamics of the balance sheet assets, we will perform preliminary calculations, the results of which will be summarized in Table. 11.5.
The analysis of assets for the period under review showed a slight increase (by 3000 thousand rubles) of the article "Non-current assets", however, the rate of their growth (14.3%) is much lower than the growth rate of the balance currency (157.9%). As a result, the share of the item "Non-current assets" in the assets of the enterprise decreased (from 56.3% at the beginning of the period to 24.9% at the end of the period). Accordingly, the shares of the articles "Stocks" and "VAT" on the acquired values increased (from 11.5 to 41.0%). The share of the item "Accounts receivable with maturity less than one year" (from 13.4 to 18.7%) sharply increased, which is caused by insolvency of consumers of the enterprise's products; Sharply decreased (from 15.3 to 3.8%) share of the article "Cash", the rate of its growth is negative (-35.1%). All this suggests a deterioration in the structure of balance assets. The share of the fixed assets of the enterprise creating the conditions for production of products decreased, and the share of the most liquid assets, which significantly reduced the ability of the enterprise to settle on its obligations in time.
Analysis of the balance sheet. Before analyzing the liabilities of the balance sheet, we make preliminary calculations, the results of which are presented in Table. 11.6.
The analysis of the balance sheet has shown a low growth rate (157.9%) of the company's own capital - "Capital and Reserves" (72.7%), with a sharp increase in accounts payable, which accounts for
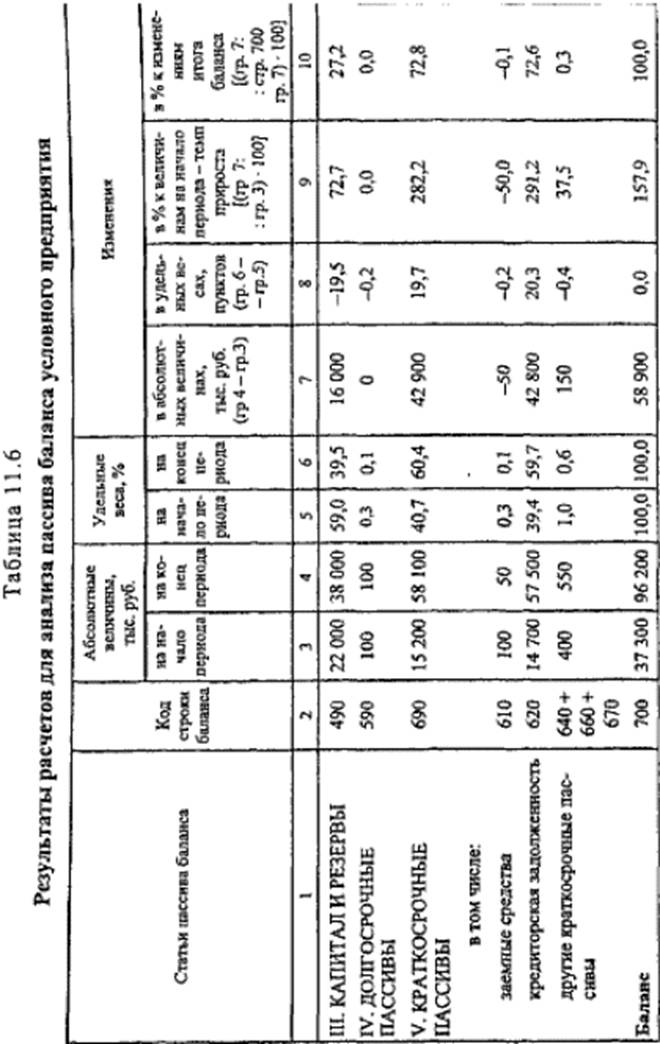
72.6% of changes in the currency of the balance for the analyzed period. The sharp increase in the share of accounts payable by 1.5 times (from 39.4 to 59.7%) is explained by the general crisis of non-payments in the country. The loans were practically not attracted: the share of the item "Long-term liabilities" decreased from 0.3 to 0.1%, as well as the share of the item "Short-term borrowed funds". The structure of liabilities worsened: "Accounts payable" - the most "urgent liabilities of the enterprise - is 59.7% of liabilities, the item" Capital and reserves "is less than 50% of liabilities at the end of the period, namely 39.5%, ie the enterprise in If all creditors submit their claims, they will not be able to satisfy them, even if they have sold all their property.
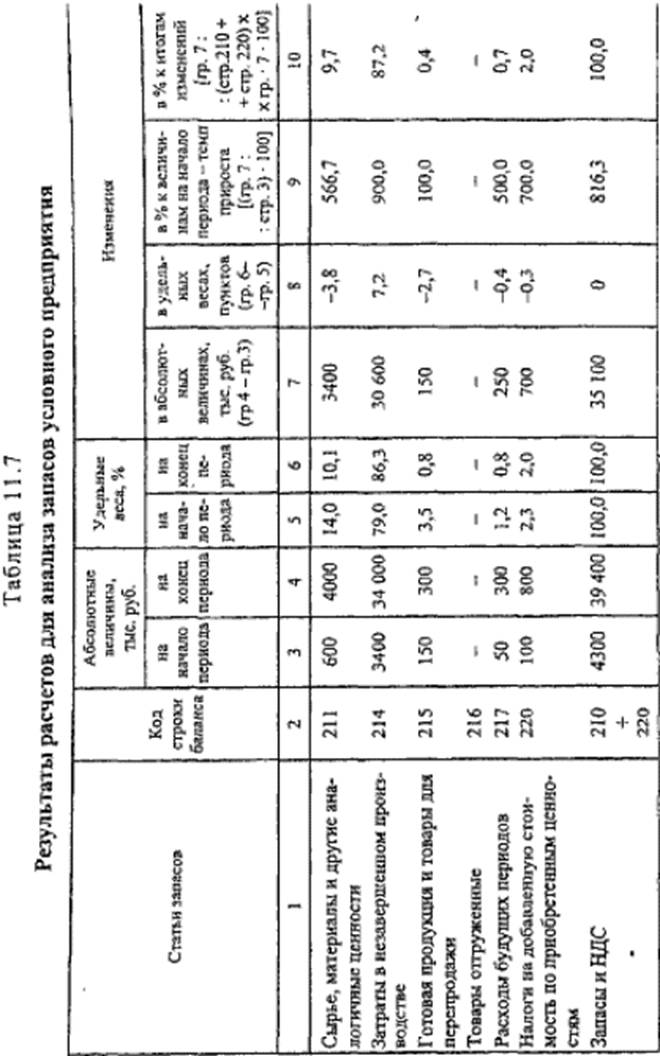
Analysis of reserves and costs. The results of preliminary calculations for the analysis of the structure of "Stocks" are presented in Table. 11.7.
In the structure of reserves and costs, there was a slight increase in the share of the item "Expenses in Work-in-Process" (from 79.0 to 86.3%), with a growth rate of 900% with a total growth rate of "Inventories and VAT" of 816.3%. Incomplete production is the bulk of the changes (87.2%). The structure of reserves and expenses deteriorated due to a long production cycle: there was an increase in "Costs in Work in Progress" (from 3,400 thousand rubles at the beginning of the year to 34,000 thousand rubles at the end of the year).
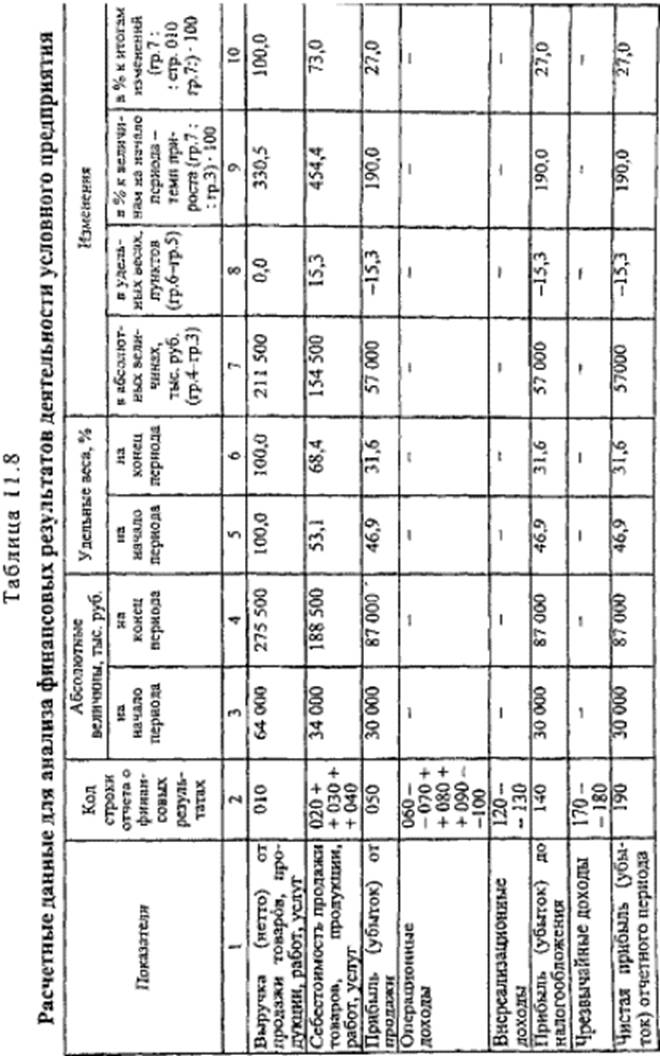
Analysis of financial performance of the enterprise. The analysis is preceded by preliminary calculations, the results of which are summarized in Table. P.8.
It follows from the table that the share of the item "Profit" in the "Revenues" item decreased by 15.3 points and is 31.6% at the end of the period due to the increase (from 53.1 to 68.4%) of the cost share. Such sources of profit as operating income, non-operating income and extraordinary incomes were not attracted. The growth rate of the article "Profit" is 190.0%, while the growth rate of the article "Revenues" is 330.5%. The fastest growing item is "Cost" (454.4%), the specific weight of changes which amounted to 73.0% in the change in the article "Revenue". Thus, we can talk about the decline in production efficiency (the growth rate of profit is lower than the growth rate of production costs).
The general financial analysis showed that the structure of the asset and liability of the contingent enterprise for the analyzed period deteriorated mainly due to an increase in accounts receivable and payable and an increase in the duration of the production cycle, which led to a decrease in the share of profits in the company's revenue.
Financial Stability Analysis
To determine the financial stability (the type of financial situation) of a conditional enterprise, we compile and review Table. 11.9.
Table 11.9
Calculation of indicators for determining the financial stability of a contingent enterprise
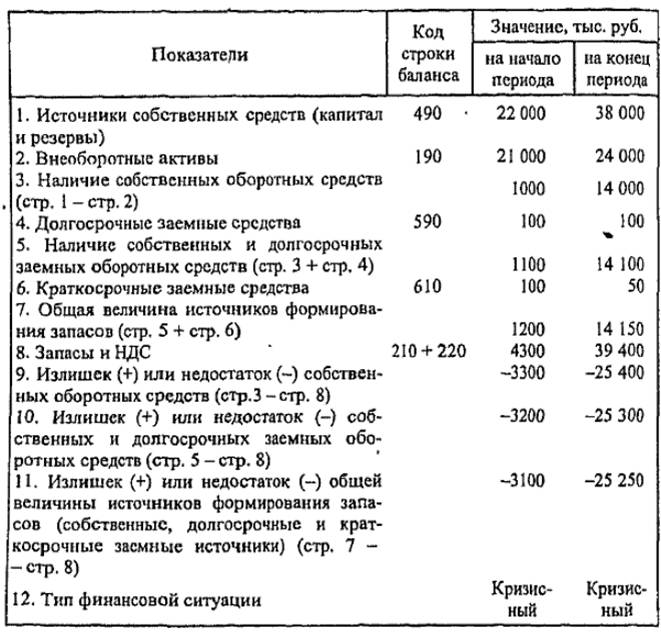
The financial condition of the enterprise under consideration at the beginning and the end of the analyzed period is a crisis one, since during the analysis there was a lack of own working capital (3300 thousand rubles at the beginning and 25,400 thousand rubles at the end of the period), own and long-term borrowed sources of formation of stocks and costs (3200 thousand rubles at the beginning and 25,300 thousand rubles at the end of the period), the total value of the main sources of formation

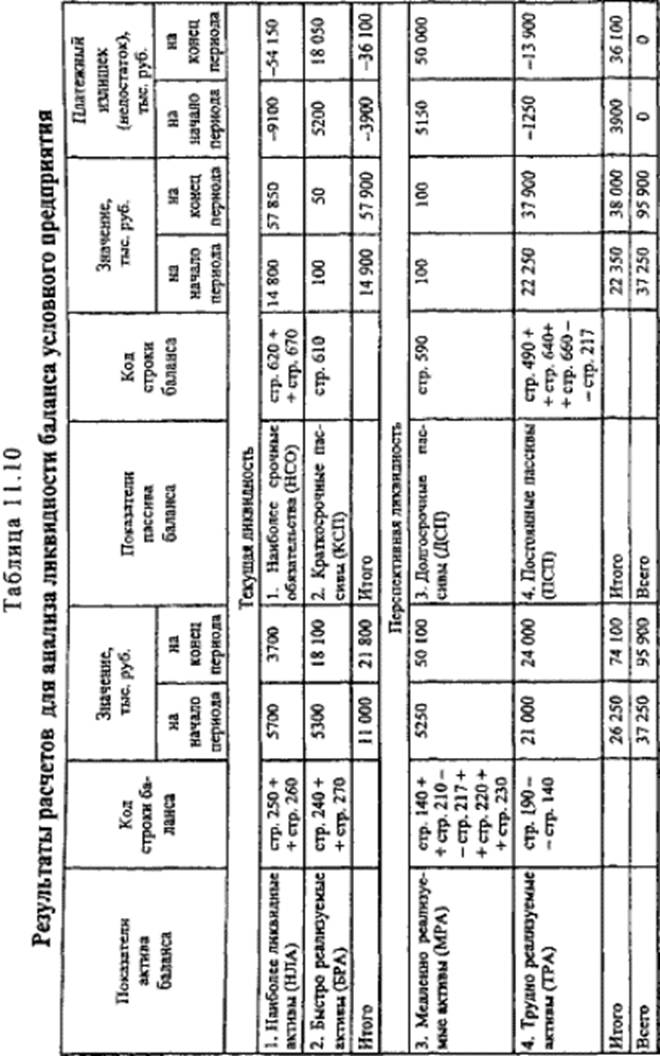
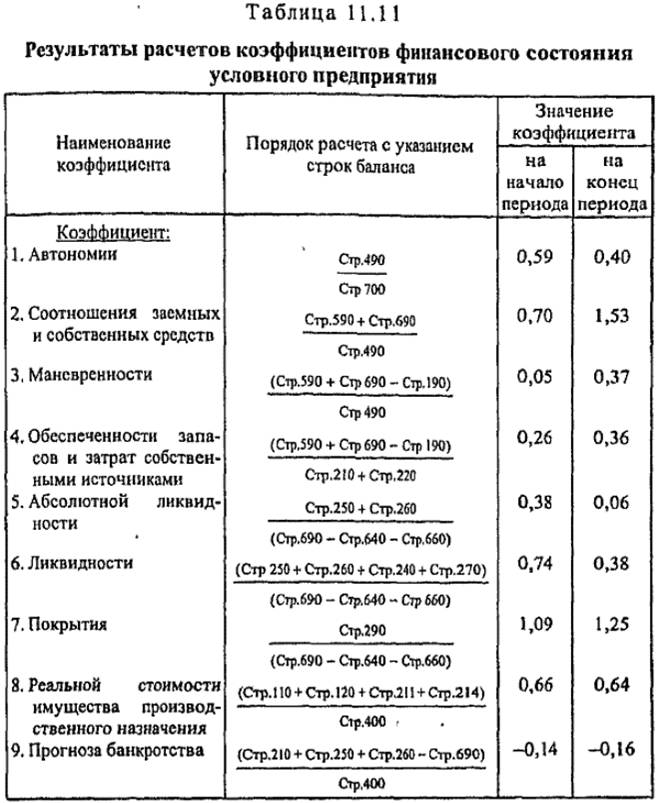
The ratio of debt to equity at the beginning of the analyzed period (0.70) corresponds to the normal limit (max 1.00), and at the end of the period it exceeds (1.53), which indicates that the enterprise's own funds are insufficient to cover its liabilities .
The coefficient of maneuverability increased from 0.05 to 0.37, which indicates an increase in the mobility of the company's own assets and the expansion of freedom in maneuvering these means.
Despite the fact that the coefficient of supply of reserves and costs by own sources of formation has slightly increased from 0.26 to 0.36, it is almost three times lower than the value of the normal constraint (1.00), which indicates insufficient supply of resources and expenses by own sources of formation.
The coefficient of absolute liquidity fell from 0.38 to 0.06 and became below the normal limit (0.20), which indicates the possibility of paying off only a small part of the company's short-term debt in the near future,
The liquidity ratio decreased from 0.74 to 0.38, which indicates a decrease in the projected payment capacity of the enterprise, provided timely settlements with debtors. With this value of the liquidity ratio, the enterprise can hardly hope for loans.
Not meeting the normal restrictions (2.00) at the beginning of the analyzed period, the coverage ratio increased by the end of the period from 1.09 to 1.25, which is due to the low payment capacity of the enterprise even if timely settlements with debtors and sales, if necessary, Material current assets. In such a situation it is difficult to find buyers of shares and bonds of the enterprise.
The coefficient of the real value of the production assets practically did not change (0.66 at the beginning of the period, 0.64 at the end of the period) due to the increase in costs in the work in process, therefore, despite the compliance of the values with the regulatory constraint (at least 0.5) On the deterioration of the structure of property.
The coefficient of the forecast of bankruptcy does not correspond to the normal restriction: for the analyzed period it decreased (from -0.14 to -0.16). This suggests that the lack of a share of enterprise funds in liquid form to pay off short-term liabilities in the property of the enterprise increased from 14 to 16%.
A joint analysis of financial ratios indicates a general deterioration in the financial position of the enterprise for the analyzed period.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.