home
 Finance Finance
 Books Books
 Finance and Statistics - Ковалева А.М. Finance and Statistics - Ковалева А.М.
|
Finance and Statistics - Ковалева А.М.
11.2 FINANCIAL STRATEGY OF THE ENTERPRISE
The financial strategy is a master plan of action to provide the enterprise with cash. It covers the theory and practice of forming finance, their planning and
Providing, solves problems that ensure financial stability of the enterprise in market conditions of management. The theory of financial strategy examines the objective laws of market conditions of management, develops ways and forms of survival in the new conditions of preparation and conduct of strategic financial operations.
The company's financial strategy covers all aspects of the enterprise's activities, including optimization of fixed and circulating assets, profit distribution, non-cash settlements, tax and pricing policies, and securities policy.
Comprehensively taking into account the financial capabilities of the enterprise, objectively considering the nature of internal and external factors, the financial strategy ensures that the financial and economic capabilities of the enterprise match the conditions prevailing in the product market. Otherwise, the enterprise may go bankrupt.
Distinguish the general financial strategy, operational financial strategy and strategy of performance of separate strategic tasks (achievement of private strategic goals).
The general financial strategy refers to the financial strategy that determines the activity of the enterprise (the relationship with budgets of all levels, the formation and use of the enterprise's income, the need for financial resources and the sources of their formation) for a year.
An operational financial strategy is a strategy of ongoing maneuvering of financial resources (a strategy for monitoring the expenditure of funds and mobilizing internal reserves, which is especially important in modern conditions of economic instability), is developed for a quarter, a month. The operational financial strategy covers gross revenues and receipts of funds (settlements with buyers for goods sold, proceeds from credit operations, income from securities) and gross expenses (payments to suppliers, wages, repayment of obligations to budgets of all levels and banks), which creates an opportunity Provide for all future turnover in the planned period for cash receipts and expenditures. A normal situation is the equality of costs and revenues or a slight excess of income over expenditure.
The operational financial strategy is developed within the framework of the general financial strategy, details it for a specific period of time.
The strategy for achieving private goals is to skillfully execute financial operations aimed at ensuring the implementation of the main strategic goal.
The main strategic goal of finance is to provide the company with necessary and sufficient financial resources.
The financial strategy of the enterprise in accordance with the main strategic goal provides:
- The formation of financial resources and their centralized strategic management;
- Identification of critical areas and focus on their implementation of efforts, maneuverability in the use of reserves by the financial management of the enterprise;
- Ranking and step-by-step achievement of tasks;
- Conformity of financial actions to an economic condition and material possibilities of the enterprise;
- Objective accounting of the financial and economic situation and the real financial situation of the enterprise in the year, quarter, month;
- Creation and preparation of strategic reserves;
- Accounting of economic and financial opportunities of the enterprise and its competitors;
- Determination of the main threat from competitors, mobilization of forces to eliminate it and skillful choice of directions for financial actions;
- Maneuvering and fighting for the initiative to achieve decisive superiority over competitors.
To achieve the main strategic goal in accordance with the requirements of the market and the possibilities of the enterprise, the general financial strategy of the enterprise is developed. In the general financial strategy, the tasks of forming finance by executors and directions of work are determined and distributed.
The objectives of the Financial Strategy :
• study of the nature and regularities of the formation of finance in market conditions of management;
• development of conditions for preparing possible options for the formation of financial resources of the enterprise and actions of financial management in the event of an unstable or crisis financial condition of the enterprise;
- Determination of financial relationships with suppliers and buyers, budgets of all levels, banks and other financial institutions;
- The identification of reserves and the mobilization of enterprise resources for the most rational use of production capacities, fixed assets and working capital;
- Providing the enterprise with the financial resources necessary for production and economic activities;
- Ensuring effective investment of temporarily free cash assets of an enterprise in order to obtain maximum profit;
- Determination of the methods of successful financial strategy and strategic use of financial possibilities, new types of products and comprehensive training of the company's personnel for work in market conditions of management, their organizational structure and technical equipment;
- Studying financial strategic views of possible competitors, their economic and financial capabilities, developing and implementing measures to ensure financial sustainability;
- The development of ways to prepare the way out of the crisis situation, the methods of personnel management in an unstable or crisis financial situation, and the coordination of the efforts of the whole team to overcome it.
Particular attention in the development of the financial strategy is paid to the completeness of the identification of money incomes, the mobilization of domestic resources, the maximum reduction in the cost of production, the proper distribution and use of profit, the definition of the need for working capital, rational use of the enterprise's capital. The financial strategy is developed taking into account the risk of non-payments, inflation spikes and other force majeure (unforeseen) circumstances. It should correspond to production tasks and, if necessary, be adjusted and changed. The control over the implementation of the financial strategy ensures the verification of revenue revenues, economical and rational use of them, since well-established, financial control helps identify internal reserves, improve the profitability of the economy, increasing cash accumulation.
An important part of the financial strategy is the development of internal regulations (through which, for example, the direction of profit distribution), successfully used in the practice of foreign companies.
Thus, the success of the company's financial strategy is guaranteed when the theory and practice of financial strategy are mutually balanced; If financial strategic goals are consistent with real economic and financial opportunities through strict centralization of financial management and the flexibility of its methods as the financial and economic situation changes.
The scheme for developing the company's financial strategy is shown in Fig. 11.2.
Proposals for the formation of the company's financial strategy are developed on the basis of the findings of the financial analysis of the enterprise on the objects and components of the general financial strategy in several options (at least three), with a mandatory quantitative evaluation of proposals and an assessment of their impact on the structure of the enterprise's balance sheet (construction of forecasts for the Balance Sheet and the Profit and Loss Report Losses).
Let's consider a fragment of development of a financial strategy of the enterprise, using results of the financial analysis of the conditional enterprise, stated in §11.1. In the course of the financial analysis it was revealed that the company in question was practically on the verge of bankruptcy. To overcome this situation, it is necessary to improve the financial condition of the enterprise on all analyzed indicators.
As an example, let's analyze the possibilities of improving the financial stability of this enterprise. Based on the analysis of financial stability, it is established that the enterprise is in crisis financial condition at the beginning and end of the period under review (Table 11.8).
The purpose of proposals for the formation of a financial strategy is to lead an enterprise out of a crisis financial state. Proposals for example the development of a financial strategy for the withdrawal of our contingent enterprise from a financial crisis are contained in Table. 11.13. They are formed according to the objects of the financial strategy with options for optimizing the components of the financial strategy.
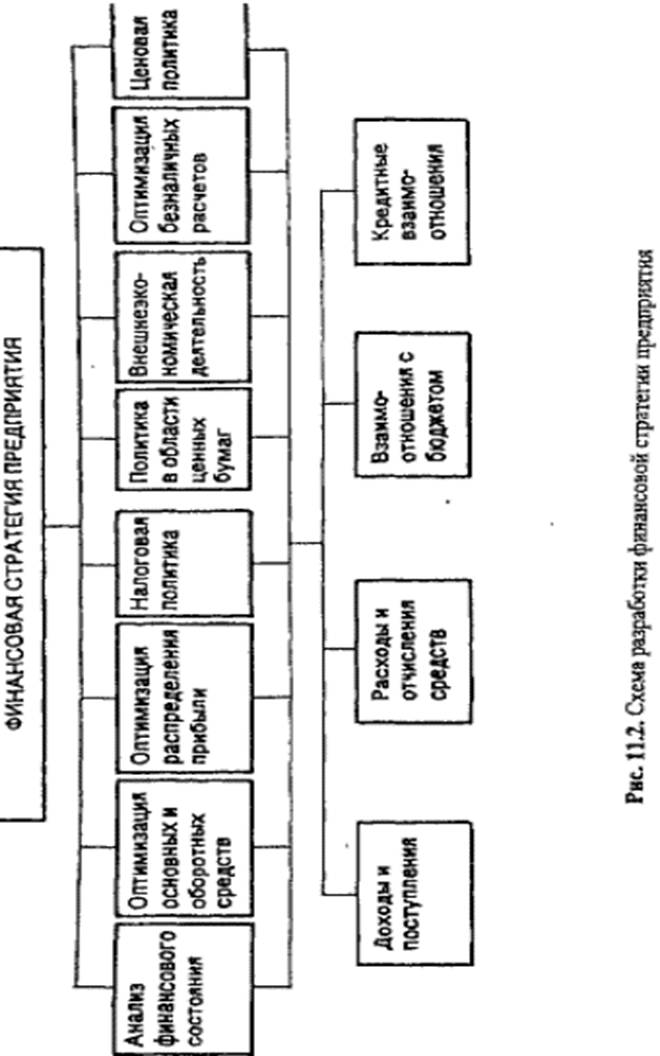
Table 11.13
Proposals for the formation of a financial strategy for a conditional enterprise to withdraw from a financial crisis
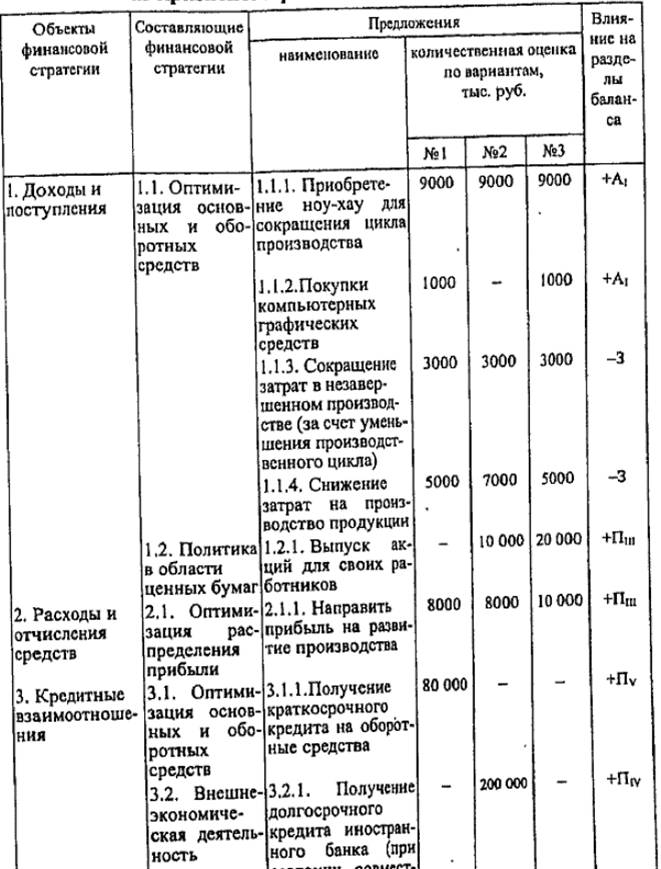
Table 11.14
The results of the calculation of proposals for the withdrawal of a conditional enterprise from a crisis state
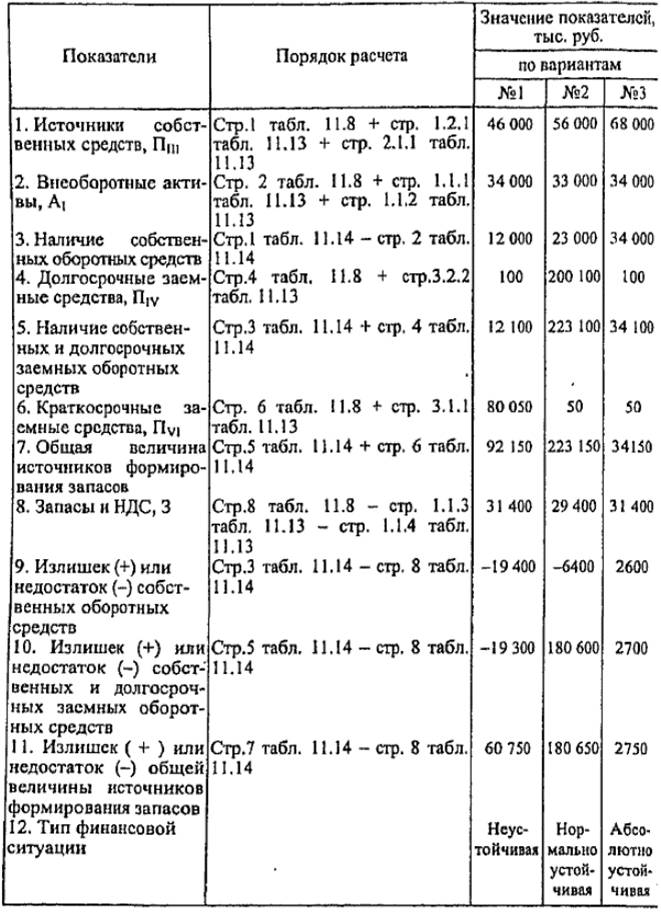
In the three proposed options for optimizing the components of the financial strategy, set out in Table. 11.13, we calculate the indicators of financial stability of the enterprise. The results of calculating the optimization of financial stability indicators are given in Table. 11.14. For the calculation, the row values of the tab. 11.8 at the end of the period.
Quantitative assessment of financial stability of the enterprise when implementing proposals for a financial strategy for all options indicates the possibility of removing the company from a financial crisis. When implementing proposals for the formation of a financial strategy for the first option, the enterprise provides reserves and costs, using all sources of formation of reserves and costs, i.e. Passes into an unstable financial condition; In the second variant, reserves and costs are provided by own and long-term borrowed sources - the enterprise passes into a normally stable financial state; By "the third option, reserves and costs are provided by own sources - the enterprise passes into an absolutely stable financial state. The implementation of this or that option depends on external conditions, in particular, whether the company will be able to sell its shares, get a short-term or long-term loan.
Depending on the external conditions (implementation of a particular version of the general financial strategy), an operational financial strategy is developed on a quarterly basis, taking into account the financial indicators achieved in the previous quarter. If necessary, a strategy can be developed to achieve private goals for the year and for the quarter.
Control questions
1. What are the differences between financial analysis and the economic analysis of an enterprise?
2. What is the procedure for conducting and the composition of the financial analysis of the enterprise?
3. What are the differences between the analysis of structure and the analysis of dynamics and analysis of structural dynamics?
4. How can the results of the enterprise's liabilities analysis be applied to an assessment of its creditworthiness?
5. What types of financial stability do you know?
6. What are the main sources of the formation of stocks and costs of the enterprise.
7. What assets of the enterprise are related to quick-selling assets?
8. Which liabilities of the enterprise are included in the most urgent obligations?
9. Describe the liquidity of the enterprise.
10. List the coefficients that characterize the financial independence of the company.
11. Explain the economic essence of the normative values of financial ratios.
12. What financial ratios are used to assess the creditworthiness of an enterprise?
13. Explain the economic meaning of the coefficients of profitability.
14. What is the difference between the terms "revenue from the sale of goods", "sales profit", "net profit (loss) of the reporting period"?
15. What is the normal ratio of turnover ratios of accounts payable and receivables?
16. In what way can borrow funds be optimized?
17. What are the components of the financial strategy of the enterprise?
18. Determine the place of the financial analysis in the financial management of the enterprise.
19. Make your own version of optimizing the liquidity of the balance sheet.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.