home
 Management Management
 Organization of production - Kurochkin A.S. Organization of production - Kurochkin A.S.
|
Organization of production - Kurochkin A.S.
6.3. Organization of operational and production planning system
Inter shop and intra-shop OPP
The main tasks of the inter-shop OPF are:
• determination of initial data for job calculation;
• compilation of monthly tasks and production plans for workshops and the enterprise as a whole according to the nomenclature;
• compilation of summary inter-shop schedules for the production and completion of products.
When compiling an OTP program, the following data is used:
• annual and quarterly programs;
• a portfolio of orders and contracts for the supply of products;
• calendar-planned standards - the size of batches and the frequency of their launch, the duration of the production cycle, etc .;
• Labor intensity standards;
• results of calculation of loading and productivity of equipment and production areas;
• results of the technical and economic analysis of the work of the workshops for the previous period of time.
An important role in the PPP system is played by the calculation of the optimum utilization of equipment and production areas. Very often this problem is considered in a truncated form - the conformity of the operational task of the shop's capacity is checked. Another important task - justifying the best load of equipment - requires multivariate calculations, and it is difficult to solve without the use of computer technology.
In the process of in-house planning, operational plans for plots, shifts and work teams are compiled: for a month, a decade, a week, a shift, etc.
The main tasks of the internal OCP are:
• checking the compliance of the monthly plan - tasks for production of production capacity, allocated resources, the capabilities of suppliers of semi-finished products;
• development of nomenclature plans for plots, shifts, work teams for a month;
• development of production schedules for production in workshops and on sites for the forthcoming planning period;
• development of shift-daily assignments to sections, teams of workers for the nomenclature for short planning periods - a decade, a shift, etc.;
• organization of control and accounting of the fulfillment of tasks by shops, sections, brigades.
Various schedules (linear, cyclic, network, etc.) are widely used for inter-shop planning and control over the fulfillment of plans and planned tasks for different time intervals at enterprises of all branches of the national economy.
General procedure for the development of operational plans
The enlarged sequence of the definition of the nomenclature and the development of production programs for the workshops (processing, procurement, assembly) is shown in Fig. 42. Naturally, in any enterprise there are specific features of the development of operational plans (type of production, level of specialization and cooperation, etc.), however their main stages and the sequence of development are preserved.
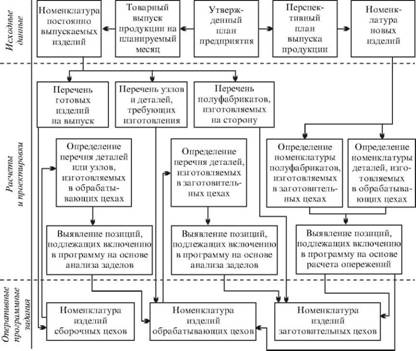
Fig. 42. Sequence of the stages of establishing the nomenclature of products to be included in the operational programs of workshops
In the process of preparing for the development of plans for the CPR, the frequency of issuing these plans to the workshops for execution is of great importance. This periodicity is largely due to the degree of reliability of production within the enterprise (Table 23).
Table 23
OPTIONS FOR THE PERIODICITY OF ISSUING THE MACHINES OF PRODUCTION PROGRAMS
| Characteristics of production | Periodicity of issuing tasks |
Manufacture of products is completely mastered from the qualitative and quantitative side; Production is rhythmic in shops |
Quarterly |
The production process is not well established or is characterized by significant changes in the production program by months |
Quarterly by month |
The production process is unstable: the demand for products can vary significantly |
Monthly breakdown by decade |
The program for the next month is compiled and issued between the 20th and the 25th, which allows you to quickly prepare for its implementation. The plans are adjusted in the period from the 2nd to the 4th of the planned month after the final results of the assignments for the previous month are clarified.
The question of who should draw up, formalize, approve and transfer to the plans of the plans of the OPP, is decided at the enterprise, depending on its organizational structure. Widely used variants of compilation of operational production programs are presented in Table. 24.
System of operational and production planning
At enterprises of mass production, the main form of the movement of objects of labor is the flow. Such enterprises (shops, sections) are characterized by a high level of specialization of workplaces, constant fixation of certain operations, parts, and parts at workplaces and sites, which allows planning the launch and release for each item name in accordance with their needs for the uninterrupted provision of the assembly process On the conveyor. Since blanks, parts and knots are transferred from operation to operation, from one production line to another, the movement of parts in accordance with the technological process must be strictly regulated in time, determined by the rhythm of the flow.
Table 24
DISTRIBUTION OF FUNCTIONS ON THE COMPOSITION OF OPERATIVE PRODUCTION PROGRAMS
| Stage of programs | Total task |
Detailed Task |
||
Volume of output |
Production Schedule |
Program in the nomenclature |
Calendar schedule Output |
|
Development and design of a general plant program |
Paeo |
Paeo |
Paeo |
Pdo |
|
Statement General program |
Head Enterprises |
|||
Development and design of workshop programs |
Paeo |
Pdo |
Pdo |
Pdo |
Approval of the workshop programs |
Head of the enterprise |
Chief Engineer Business enterprises |
||
Issuing tasks to workshops |
Paeo |
Pdo |
Pdo |
Pdo |
Adjusting the plan |
Paeo |
Pdo |
Pdo |
Pdv |
Note. PEO - planning and economic department; PDO - production and dispatching department; PDB - planning and dispatching bureau of the shop (or site).
In enterprises with a serial production type, the product range is more or less stable, the products are produced fairly evenly. At each workplace, as a rule, details of several basic names are processed. In these conditions, one of the most important factors in the rhythm of production and in raising labor productivity is the party organization of production.
In enterprises with a single type of production, the fixing of parts behind sections and workshops is constantly changing, which considerably complicates both inter-shop and intra-shop planning, leading to uneven loading of equipment by types of work. Under these conditions, a consistent type of movement of the parts is usually used, which causes their long-term interoperational and inter-shop clearance. One of the basic requirements for operational and production planning in a single production is the rational organization of the movement of labor objects in the process of manufacturing a certain product.
The system of OPP, presented in Table. 25, with minor modifications applied at most enterprises. The system for detailed planning involves the creation of hard hours and daily schedules for loading workplaces, releasing parts and feeding them to the next operation. The system of complete planning provides for the manufacture and delivery of sets of parts necessary for assembling the assembly or product. In this case, the parts are grouped in the node sets from the calculation of the supply of sets to the beginning of the assembly of the corresponding nodes.
Table 25
MAIN OPERATIONAL-PRODUCTION PLANNING SYSTEMS
Index |
Production |
||||
Massive |
Large-scale |
Mid-term |
Small-scale |
Single |
|
|
Applicable Systems Planning |
Understanding |
Mashinokomplekt, continuous and detailed planning |
Mashinokomplekt, network planning |
Mashinokomplekt, complete-nodal, network planning |
|
Scheduled accounting units |
Detail |
Mashinocomplekt, conditional product, part |
Mashinekomplekt |
Mashinekomplekt, the nodal kit |
|
Planning and accounting period |
Hour, shift |
Change, day |
Day, decade, month |
Decade |
Month |
|
The calendar- Planned Standards |
Start-release cycle |
Start-release cycle, Sizes of batches, periodicity Repetition And duration Production Cycle |
The sizes of batches, periodicity Repetition and Duration Production Cycle |
The duration of the production cycle, the timing specification of the lead |
|
The basis for compiling shift-daily assignments |
Production line schedule |
The schedule of the work of the production line, the standard plan for the work of the section |
Decade, Monthly tasks |
Decade task |
Monthly assignment |
In the system of OPP under consideration, with many of its advantages, there is one significant drawback: it is very laborious, even taking into account the use of computer technology, the operation to link the work of all the main shops in order to ensure their rhythmic production.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.