home
 Economy Economy
 Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF
|
Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF
Chapter 8. Investment Resources
Key concepts and terms
Investments; Industrial investments; Financial investment; Structure of industrial investments (capital investments); Sources of investment financing; Shares; bonds; Dividends; cash flow; Discount rate (capitalization); Net present value; Payback period of investments (capital investments); Internal rate of return on investment; investment project; Index of return on investment .
8.1. Concept, structure and structure of investments
Characteristics of investments . As calculations for a fairly long period show, on average about one third of the financial assets of enterprises in different sectors of the Ukrainian economy are investments (one-time capital expenditures).
Investments are long-term investments of capital (money) in entrepreneurial activities (for profit).
The one who has capital and invests it in this or that commercial business is called an investor , and the process of investing capital is invested (long-term financing). In any business activity, investors can be both legal entities and individuals, that is, both enterprises and individual owners of capital.
To characterize the investments, it is of considerable theoretical and practical importance to determine the types of investments by individual characteristics, that is, their functional-element composition (Fig. 8.1).
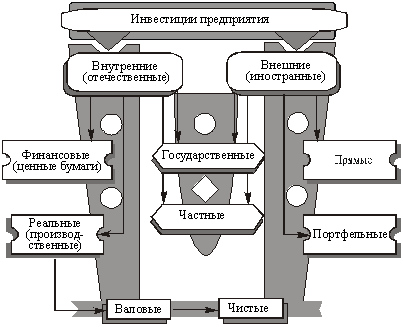
Fig. 8.1. Functional elemental investment of the enterprise
Depending on where the capital is invested (within the country or abroad), internal (domestic) and foreign (foreign) investments are allocated. In turn, domestic investment is divided into financial and real , and external - on direct and portfolio .
Financial investments mean the use of cash capital for the acquisition (purchase) of shares, bonds and other securities issued by enterprises and the state. With this investment, there is a transfer of titles of property, which gives the right to receive unearned income. In the literature on political economy, capital in the form of securities is called stock, or fictitious, because it is not real wealth and has no real value (unlike capital invested in various spheres and branches of social production).
Real investment is the investment of capital in various spheres and branches of the national economy (social production) with the purpose of updating existing and creating new "capital" (material) benefits, and as a result - a much larger profit. Such real investments are also called production ; But in the practice of management behind them, another name - capital investments - was fixed .
External direct investment is the investment of capital abroad, and the amount of investment should be at least 10% of the cost of a particular project. Foreign investment, which is less than 10% of the value of the capital project carried out with their help, is called portfolio investment. Periodic analysis of the ratio of direct and portfolio investments is of practical importance for establishing the general scale of participation of foreign capital in the sphere of development and increasing the efficiency of production, and other areas of activity of business entities.
The effectiveness of long-term financing of modernization of existing and construction of new production and non-production facilities depends to a large extent on the proportions between public and private investments. Naturally, with the acceleration of denationalization and privatization of property, the incorporation of state-owned enterprises, the share of private capital in the total volume of investments will increasingly increase, contributing to the increase in the efficiency level of both domestic and foreign investments.
Varieties and structure of capital investments . According to the commonly used definition, capital investments are periodic long-term investments of capital into the reproduction of fixed assets and objects of the social infrastructure of the enterprise.
On a functional orientation, there are gross and net capital investments. Gross capital investments are the total amount of non-recurrent expenditures of capital for simple and expanded reproduction of fixed assets and objects of the social infrastructure of the enterprise, and net investments are expenditures only for expanded reproduction. The value of net capital investments is not difficult to calculate. To do this, out of the total volume of capital investments, it is necessary to exclude the amount of depreciation deductions, which are known to be used, for simple reproduction of fixed assets and other property of the enterprise.
The planning and accounting systems in enterprises in the structure of capital investments include: 1) the cost of construction and installation works; 2) the cost of all types of production equipment, as well as tools and inventory included in the fixed assets; 3) other capital works and costs. The latter include: the cost of land; Work on deep exploratory drilling for oil, gas and thermal water; Design and research; The cost of acquired patents and licenses; The costs of training operational personnel for enterprises under construction; The cost of non-title temporary structures associated with the construction of production facilities, etc.
The ratio between the allocated types of capital expenditures characterizes the elemental technological structure of capital investments. A positive trend in the dynamics of this structure is a gradual increase in the cost of equipment, tools and inventory with a relative decrease in the specific weight of the cost of construction and installation work.
In the investment policy of enterprises and their voluntary associations it is very important to make informed decisions regarding the reproductive structure of capital investments , which reflects the ratio of long-term costs for simple and extended (technical re-equipment, reconstruction, expansion of existing enterprises, new construction) reproduction of fixed assets. The main tendency of changes in the reproductive structure of capital investments in recent years is a significant increase in the share of costs for the technical re-equipment and reconstruction of existing enterprises in most industries.
According to the results of special studies and expert evaluation, the ratio of expenses for simple and extended reproduction of fixed assets, corresponding to 35 and 65% of the total volume of gross capital investments, can be considered optimal (or close to it). It is in this proportion that the reproduction structure of gross capital investments in enterprises of various spheres and branches of the Ukrainian economy is changing now. The ratio of individual parts of the total amount of net capital investments is on the average technical re-equipment and reconstruction of existing industrial enterprises - 50-60; Expansion of enterprises - 15-20; New construction - 20-35%.
The priority direction of capital investments for the technical re-equipment, reconstruction and expansion of enterprises will continue in the short term development of the national economy of Ukraine.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.