home
 Economy Economy
 Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF
|
Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF
9.4. Evaluation of the effectiveness of technical and organizational innovations
Efficiency of technical innovations. The groups of technical innovations and innovations for which economic efficiency and its other types are determined and evaluated include the creation, production and use of new or modernization (improvement of operational characteristics) of existing means of labor (machinery, equipment, buildings, structures, gears), objects Labor (raw materials, materials, fuel, energy) and consumption (products to directly meet the needs of the population), technological processes, including inventions and rationalization proposals.
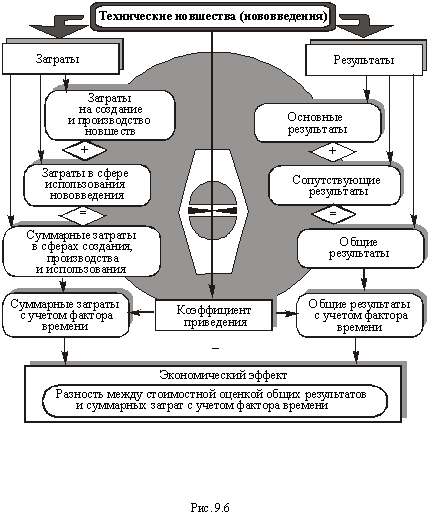
A single generalizing indicator of the economic efficiency of any group of technical innovations is the economic effect that characterizes the absolute value of the excess of the value of the expected (actual) results over the total resource costs for a certain billing period. Depending on the tasks assigned, the magnitude of the economic effect should be calculated in one of two forms-the economic (general effect from the use of innovations) and the intraeconomic (the effect obtained separately by the developer, producer and consumer of technical innovations or innovations).
The economic economic effect is determined by comparing the results from the application of technical innovations and all the costs of their development, production and consumption; It reflects the effectiveness of a group of technical innovations from the perspective of their impact on the final indicators of the country's economic development.
The intraeconomic (commercial) economic effect, calculated at the individual stages of the cycle "science-production-exploitation (consumption)," makes it possible to evaluate the effectiveness of certain technical innovations and innovations from the point of view of market economic interests of research organizations (design and engineering), producer enterprises And consumer enterprises. The first form of the economic effect as an evaluation indicator is used at the stages of justifying the expediency of developing and subsequently implementing new technical solutions and choosing the best option, and the second, in the process of implementing innovations (innovations), when prices for new scientific and technical products and the volume of its production are already known . Despite the differences between the two forms of expressing the effect 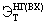 (Economic - the index of "NG", on-farm - index "BX"), the methods of their calculation are identical; They are defined as the difference between the results (output, work, services in the valuation) and the costs of achieving those for a certain period T:
(Economic - the index of "NG", on-farm - index "BX"), the methods of their calculation are identical; They are defined as the difference between the results (output, work, services in the valuation) and the costs of achieving those for a certain period T:
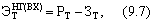
Where PT - the results for the period,
ZT - costs for the same period.
The algorithm for calculating the economic economic efficiency of technical innovations is shown in Fig. 9.6.
Since the calculation period has a significant duration, the results and costs for each year should be determined taking into account the time factor, i.e., lead to one point in time - the settlement year with the help of a special reduction factor a t , calculated by the formula:
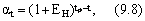
Where Ен - the standard of reduction of different costs and results (Ен = 0,1);
Tp is the calculated year;
T is the year for which costs and results are shown in the calculation year.
Absolute values of the coefficients a t calculated from formula (9.8) are given in Table. 9.1.
Taking into account the time factor, the economic economic effect of technical innovations equals:
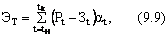
Where P t , З t - valuation of actual results and costs in the t-th year of the settlement period;
Tn, tk are the initial and final years of the calculation period, respectively.
The initial (first) year of the billing period is the year of the beginning of financing the development of technical innovations, including scientific research. The final year of the accounting period is considered to be the completion of the whole life cycle of a technical innovation covering development, production development and use in the national economy. It can be determined by the normative (expected) terms of renewal of products or means of labor, taking into account their technical and economic aging.
Table 9.1
ABSOLUTE VALUES OF COEFFICIENT COEFFICIENTS FOR THE CORRESPONDING YEARS OF THE CALCULATED PERIOD
| Number of years preceding the calculation year | The value of the coefficient |
Number of years following the settlement year |
The value of the coefficient |
10 |
2.5937 |
1 |
0.9091 |
9 |
2,3579 |
2 |
0,8264 |
8 |
2.1436 |
3 |
0,7513 |
7th |
1,9487 |
4 |
0 6830 |
6th |
1,7716 |
5 |
0,6209 |
5 |
1,6105 |
6th |
0.5645 |
4 |
1.4641 |
7th |
0.5132 |
3 |
1,3310 |
8 |
0.4665 |
2 |
1,2100 |
9 |
0,4241 |
1 |
1,1000 |
10 |
0.3855 |
0 |
10000 |
15 |
0.2394 |
The total result of practical innovations is defined as the sum of the main ( 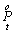 ) And accompanying (
) And accompanying ( 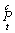 ) Of the results:
) Of the results:
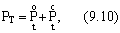
The main results are calculated by the formulas:
- For long-term use
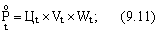
- For new objects of labor
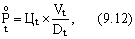
Where Ц t - the cycle of a unit of production (taking into account the effectiveness of its application), manufactured with the help of new means or objects of labor in the t- th year;
V t - the volume of application of new means of labor or objects of labor in the t- th year;
Wt - labor productivity in the t- th year;
Dt - expenditure of labor items per unit of production produced using these items in the t- th year;
The accompanying results include additional economic results in various sectors of the economy (for example, the introduction of new types of vehicles can contribute to additional savings in warehouses and reloading bases due to a reduction in cargo reserves, and the use of new automation tools - to reduce in-process production, etc.) As well as an economic assessment of the social and environmental consequences of the implementation of technical innovations. A value estimate of the latter can be determined using the formula
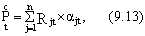
Where 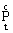 - valuation of social and ecological results of using technical innovations in the year t ;
- valuation of social and ecological results of using technical innovations in the year t ;
Rjt is the value of a single result (in natural meters), taking into account the scale of its implementation in year t ;
A jt - the value of the unit of a single result in the year t ;
N - the number of indicators considered when determining the impact of technical innovation on the social sphere and the environment.
The total costs for the implementation of the technical innovation for the billing period include the costs of production and use of the product,
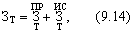
At the same time, the costs for both production and use of products (without taking into account the costs of its acquisition) are calculated in the same way:
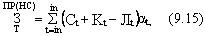
Where C t - current costs for production (use) of products in the year t without taking into account depreciation charges for renovation;
Kt - simultaneous costs for production (use) of products in the year t ;
L t - residual value (liquidation balance) of fixed assets retiring in the year t .
The current includes costs that are taken into account in accordance with the current order of calculation of the cost of production at the enterprises, while simultaneous - capital investments and other costs of a one-stage nature. In particular, they include the costs of: research, design and technological and design work; Development of production and development of prototypes of products; Purchase of equipment, its transportation, installation and commissioning; Construction of new and reconstruction of existing buildings and other elements of real estate fixed assets and social infrastructure facilities; Replenishment of working capital, which is associated with the implementation of technical innovation; Means necessary to prevent negative social, environmental and other consequences of the innovation.
The existence of a national economic effect from one or another technical innovation does not always indicate the expediency of its use. This can happen when a new technical solution that is economically profitable for the national economy as a whole leads to a deterioration in certain economic indicators of the activity of individual scientific organizations or enterprises involved in the reproductive cycle "science - production - exploitation (consumption)." Therefore, it is always necessary to determine not only the overall magnitude of the economic effect, but also its share, which each participant in the process of creating and implementing a technical innovation receives, that is, to calculate the intraeconomic (commercial) economic effect.
In the conditions of functioning of market economic relations between production contractors, an indicator of profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise (scientific organization) can be used to assess the intraeconomic (commercial) economic effect from the technical innovations and innovations used; It is calculated by the formula
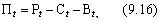
Where П t - profit at the disposal of the enterprise (scientific organization) in the t- th year;
P t - proceeds from the sale of scientific, technical or production and technical products in the year t at market (other applicable prices);
C t - production cost in year t ;
B t - total amount of payments from the balance profit of the enterprise (scientific organization) and taxes in the year t .
For the purpose of a deeper economic analysis of the effectiveness of technical innovations (innovations), it is advisable to calculate and evaluate also other production meters - the efficiency factor of simultaneous costs (internal efficiency rate), the payback period,
In modern conditions of forming a socially oriented economy, a fundamentally new approach to determining the effectiveness of innovations and innovations becomes possible and necessary. Its essence consists in recognizing the unconditional priority of the criteria of social efficiency and environmental safety of objects of technical innovations and innovations, in comparison with the criterion of economic efficiency. The procedural mechanism for comparing and selecting the best possible variant of technical innovations (innovations) is carried out in such a sequence.
- First, the purpose of developing production and the use of objects of technical innovation is ranked; To the highest rank include social goals and environmental safety requirements, to the lowest - the maximization of economic efficiency.
- Secondly, possible variants of technical innovations of the same and functional purpose are tested for compliance with social goals and environmental safety requirements, fixed in state and international standards, as well as in targeted social standards; If innovations do not meet such goals and requirements, then they should be rejected regardless of their level of economic efficiency.
- Thirdly, at the final stage of the process of comparison and selection, only social and environmentally acceptable (in this sense - effective) variants of technical innovations or innovations should be considered; The best of them is determined by the economic criterion.
Features of an estimation of efficiency of organizational innovations. Based on the characteristics of the effectiveness evaluation, the whole set of new organizational solutions can be conditionally divided into two groups: the first - organizational innovations, the implementation of which requires certain (often substantial) additional certain costs (capital investments); The second is innovations that do not require investment.
Determination and assessment of the economic efficiency of organizational innovations related to the first group (for example, the organization of new specialized or combined production facilities, the concentration of production at an operating enterprise, which necessitates its expansion (reconstruction, technical re-equipment), are carried out exactly as well as new technical solutions. It is necessary to take into account a very important circumstance - in the current costs, it is necessary to include additional transportation costs, as well as losses of raw materials (materials) and finished products in the process of their transportation and storage.
The effectiveness of cost-free new organizational solutions (in particular, the introduction of a brigade or other form of organization of labor remuneration, the improvement of individual elements of the economic mechanism - organizational management structures, planning and financing systems, the creation of new market structures) determine in most cases, based on the calculation of current cost savings, Implementation of such innovations. In each specific case, it is necessary to accurately delineate a set of indicators to assess the effectiveness of a group without costly organizational decisions.
Questions for self-study in depth
- Essence and content characteristic and interaction of various types of innovation processes (innovations, innovations).
- Analytical assessment of the impact of organizational, technical and other innovations on economic and socio-environmental performance indicators of Ukrainian enterprises.
- Selection and methodology of calculating indicators to determine the impact of innovation on the economy of the enterprise.
- Essential characteristics of scientific and technological progress (various approaches to interpretation).
- Concepts and fundamental features of the modern scientific and technological revolution.
- Current current and priority directions of scientific and technical progress in certain sectors of the national economy of Ukraine.
- Directions and tendencies of modern organizational progress at enterprises and other links in the management of social production.
- Technique of determining the effectiveness of technical innovations and the possibility of improving it.
- Methodical approaches to determining the effectiveness of organizational and other innovations.
- Innovative model of development of diversified enterprises: objective necessity, substantial characteristics and directions of practical implementation.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.