home
 Economy Economy
 Business Economics - Pokropivny SF Business Economics - Pokropivny SF
|
Business Economics - Pokropivny SF
13.4. Development Strategy predpriyatiyay business planning
Strategic planning
The constant variability of the market environment calls for a strategic approach to the management system of the company.
Strategy - a general comprehensive program of activities, determine the priority issues for the company, its mission, main objectives and the allocation of resources to achieve them. The content of the strategy is a long term planning document, the result of strategic planning.
Strategic planning - the implementation of the set of systematic and mutually works with the definition of long-term (for a certain period) the goals and directions of activity of the enterprise
Its basic steps are shown in Fig. 13.11.
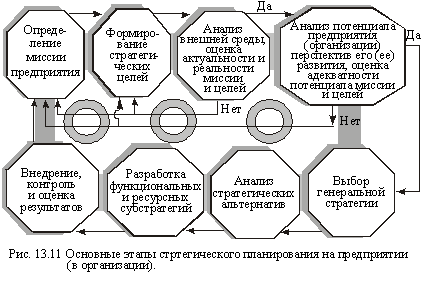
Strategic planning first, most important and decisive choice of targets is considered one way or another business entity. The main goal of the company is called mission. Selection of the company's mission is carried out taking into account the action of environmental factors. Proceeding from the overall mission of the enterprise, formed its other strategic goals. The reality and effectiveness of company strategy provided if the strategic objectives are:
- specific and measurable;
- clearly focused in time (when and what targets to be achieved);
- Achievable, balanced, resource provision;
- unidirectional and Harmonies.
It is desirable to set goals for each direction of the company.
After determining the mission and goals begin the diagnostic phase of strategic planning. The first important step is the study of the environment. Analysis of the external environment - it is a continuous process of observation, study and control external to the enterprise factors for timely exhaustive definition of the possible positive effects or risks to the business entity, ie the definition of positive and negative impact of external factors -.. Political, economic, scientific-technical, social , international, and so on. n.
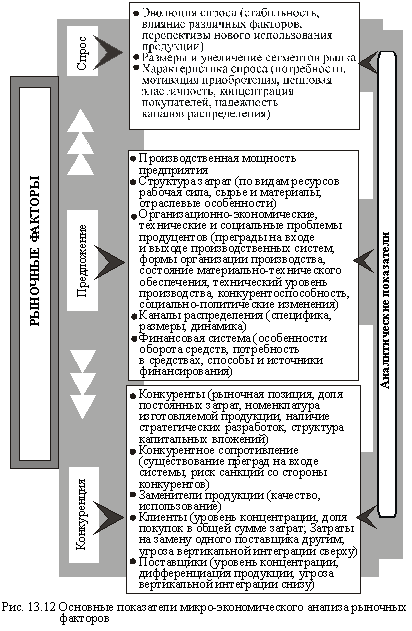
To develop and implement the strategy of great importance is the analysis of market factors, which, because of its constant and high volatility can directly affect the success or enterprise crisis. We are talking primarily about the microeconomic analysis of demand, supply and the level of competition for a particular scorecard (Fig. 13.12).
Methods of selection of the grand strategy can be divided into two groups: the first - methods of single-commodity analysis; second - methods "portfolio" of analysis (matrix). Each of these groups comprises several specific techniques (Fig. 13.13).
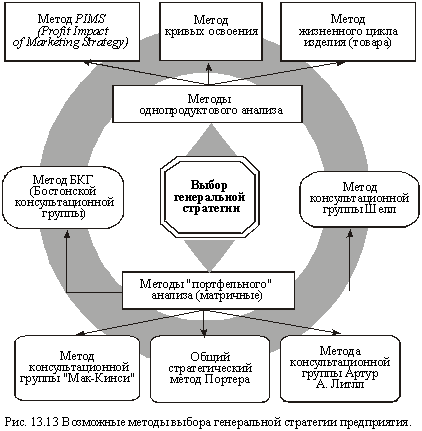
Among the methods of single-commodity analysis of the most scientifically valid method is the PIMS (Profit Imprakt of Marketig Strategu), first implemented by "General Motors" with the participation of the Harvard Business School in the early 70's .. The basis of the method laid PIMS modeling of strategic factors in the performance indicators businesses (in particular, the profitability of investments, gross profit).
If PIMS method and its models take into account the effects of both external and internal factors, the learning curve method, which is based on the dependence of the size of the cost of production from its scope, reflecting the impact of external factors. The basis of the method is a well-known pattern: the increase in the scale of production saves certain costs, the size of which does not depend, or little affected by changes in the number of production units. Moreover, in the production process we have the repetition operations, the formation of a dynamic skills or stereotype, which also leads to a reduction of labor costs.
Logically related to the method of learning curve is yet another method of development strategy of the enterprise - the method of product life cycle (product). During the period of its existence, the product passes, usually four stages: introduction (development), growth, maturity, decline.
Strategic decision-making on a particular product is preceded by the identification stage of its life cycle. In the process of identifying a single step is distinguished from the other by means of indicators such as the percentage of sales volume growth (production), the number of competitors, the pace of technological change, the frequency of modification of the product, etc.
For each stage identifies priority strategic directions and actions. In particular, such a trend is the growth stage of marketing activities (advertising offensive and active tovaroprodvizhenie; improved product distribution, pricing, demand an appropriate response, etc...).
On the stage of maturity the foreground performance indicators of production and commercial activities (optimal use of production capacity, standardization of business processes, a gradual decrease in the cost of research on this product). In order to best take into account external factors matrix is built, and one of the indicators of its generators, is characteristic of the competitive position of the product (tab. 13.1).
Table 13.1
Selection of basic strategy depending on STADIIZHIZNENNOGO CYCLE AND COMPETITIVE POSITION PRODUCTS
Almost all methods of portfolio analysis and the choice of enterprise strategy in a diversified production are matrix. Using these methods, there is the same pattern: as a rule, constructed a matrix on one axis which houses assessment of prospects for development of the market, on the other - an estimation of competitiveness of the so-called strategic management center (STSH). Define the mission and goals of each such center, the grand strategy and its sub-strategies. Strategic plans are assessed each STSH central office management and identifies the key indicators of the company strategy as a whole.
The main difference between the different methods of matrix consists of various indicators used to assess the market attractiveness and competitive position STSH. The simplest (and most common) is the method proposed by the Boston Consulting Group (the company) - BCG. The indicators forming the evaluation matrix by this method, the growth rate is controlled by the enterprise and of the market.
Among the matrix methods well known method of consulting group "McKinsey", where performance indicators are the competitive position STSH (weak, medium, strong) and the attractiveness of the market (similar to three estimates). specific action in each market a certain set of factors studied and analyzed by this method. These include: the capacity and the market growth rate; dynamics of the price level; controlled entity of the market; cyclical demand; the number of competitors in the trend changes; competitive advantages of industry leaders; growth leaders arrived; the state of the labor force.
Among other matrix determine the general policies of methods known to the following (in brackets are the figures that form the matrix):
- Porter's overall strategic approach (strategic benefits / strategic objectives);
- method of consulting group "Arthur D. Litll" (step life cycle / competitive position);
- method of consulting group "Shell" (the potential market / capacity of the enterprise).
The basic strategy as the general direction is the core of the company's strategic plan. In accordance with the company's development cycle, you can choose one of these basic strategies:
- growth strategy - describes the intention of the company to increase sales volumes, profits, capital investment, etc .;.
- strategy of stabilization - in the case of the company with tangible instability sales and profits;
- survival strategy - a purely defensive strategy applied during a deep crisis of the enterprise.
Within the framework of the relevant basic strategy, you can select one of several possible actions, which are called strategic alternatives (tab. 13.2, Fig. 13.4).
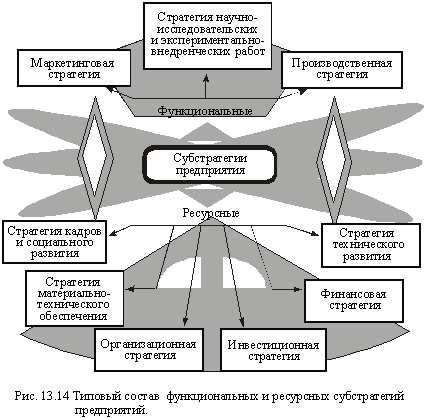
Each substrategies usually comprises:
- objectives, conditions and main directions of activity in one or another sphere, the final results to ensure the implementation of resource strategies;
- the order and sequence (in space and in time) solution of qualitative and quantitative problems of long-term plans; a number of measures that are adequate to purpose sub-strategies that ensures the achievement of this goal.
The business plans of enterprises (organizations)
Business Plan (BP) of the enterprise or organization - is a written document that sets out the nature, direction and ways to implement business ideas, characterized by market, industrial, institutional and financial aspects of future business, and especially its management. This document is a permissive basis of attracting investments for the development and implementation of business ideas, any innovation investment projects.
In a market system of managing BP has two functions: external (to introduce interested people to the essence and effectiveness of the implementation of new business ideas) and internal (working out the implementation of enterprise project management system).
The specific objectives of the development of PD as a multifunctional document are:
- establishing business relationships between employers and employees, as well as between enterprises and future suppliers, or vendors;
- designing prospective business management system in a particular area of activity;
- the timely prediction of possible obstacles and challenges to the success of one's own business;
- the formation and development of management as an entrepreneur;
- check the viability of business ideas even before its implementation.
The general methodology for developing PD covers three stages: primary, preparatory and basic (razrabotochnuyu). The initial step is required for starting a new business; It includes the development of the concept of future business. At the preparatory stage of forming an information field, evaluated the strengths and weaknesses of the firm, formed its mission and specific goals, develop strategies and possible strategic alternatives. On the main stage is carried out direct development of a particular PSU.
On the specific content and structure of the BP significantly affect: PSU development goals; audience, which calculated the PSU; the scope and size of the business; Business product characteristics; financial entrepreneur opportunities. Typical power supply structure shown in Fig. 13.15.
Common logic training companies BP (organization) provides for certain steps in the process, developed in sequence (Fig. 13.16).


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.