home
 Economy Economy
 Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF
|
Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF
19.3 Sanitation (financial recovery) of business entities
general characteristics
The word sanation comes from the Latin "sanare" , which means healing or recovery. From the "financial and credit" point of view, this concept should be interpreted as a system of measures to prevent the bankruptcy of industrial, commercial, banking enterprises and institutions and the revival aimed at their future.
In economic literature, there is also a broader interpretation of the concept of "sanitation" - as the sum of all the organizational, industrial, financial and social measures designed for strategic perspective, used, on the one hand, to overcome illiquidity and eliminate capital losses, and on the other hand, to restore Or achieve profitability, productivity, or innovation, ensuring the profitability and viability of the enterprise in the long run.
Consequently, sanitation is a complex of consecutive interrelated measures of financial, economic, production, technical, organizational and social nature aimed at removing the business entity from the crisis and restoring its profitability and competitiveness.
Structural elements of sanation (financial recovery)
The public model of the financial recovery of the enterprise provides for the consistent implementation of the corresponding measures, as shown in Fig. 19.7.
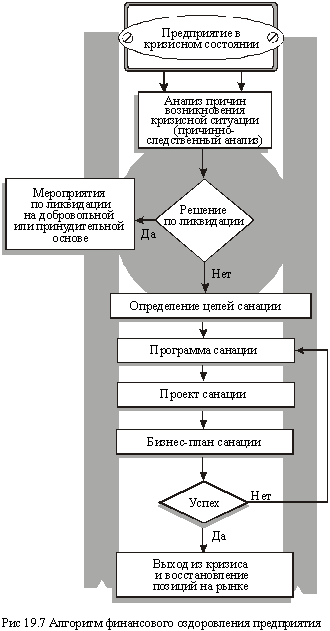
In this regard, an important practical significance is the content characteristic of the individual stages of the financial improvement algorithm of the business entity.
- Based on the identification and analysis of the causes of the financial crisis of the enterprise (organization), it is concluded that it is expedient to carry out its sanation. The decision on the expediency of reorganization is accepted only if the enterprise: has a real opportunity to restore solvency, liquidity and profitability; Has sufficiently trained management personnel and commodity markets, and the products produced meet the standards and are competitive. If the production potential of the enterprise is destroyed, the capital is lost, the balance structure is unsatisfactory, then a decision is made to preserve and liquidate the economic entity.
- A separate and very important analytical block in the classical model is the formation of strategic goals and tactics of the reorganization. The ultimate strategic goal of the rehabilitation should consist in the achievement of the enterprise long-term competitive advantages by choosing the best option for its development and optimizing the investment resources required for this, as well as a sufficiently high level of profitability of production. At the same time, it should be taken into account that the successful operation of the enterprise by approximately 70% depends on the correct strategy for its long-term development, approximately 20% on the effectiveness of operational management and 10% on the quality of current tasks. In other words, the success of sanation is affected by: the quality of strategic analysis; The reality of strategic planning; Quality of implementation of planned activities.
- In accordance with the chosen strategy, a sanation program is being developed - a system of interrelated measures aimed at getting the enterprise out of the crisis. It is formed on the basis of a comprehensive study of the causes of the financial crisis, the analysis of internal reserves, the strategic objectives of sanitation and conclusions about the possibilities of attracting capital.
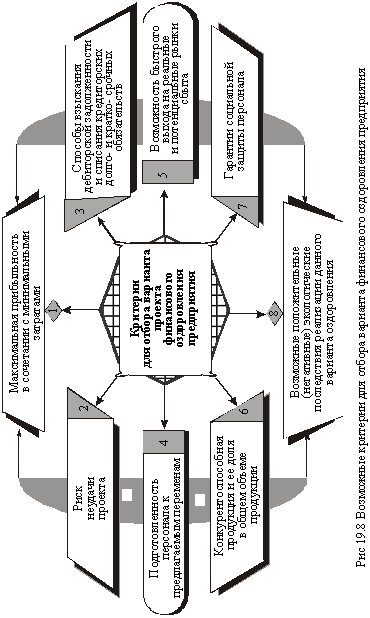
- The next element of the classical model of recovery is the rehabilitation project, which is developed on the basis of the rehabilitation program and contains a feasibility study for the rehabilitation, calculation of the financial resources needed to achieve the strategic goals, specific schedules and methods for mobilizing financial capital, the timing of investment development and their payback, Sanation measures, as well as projected results of the project. The project of financial recovery is recommended to be made in several variants. To select an effective option, you can suggest using criteria ranked by importance (Figure 19.8).
An important component of the sanation process is the coordination and quality control of the implementation of planned activities. Supervisory authorities should promptly identify and use new sanation reserves, as well as take objective, qualified decisions regarding remedial measures. Effective sanation control uniting information and control functions can provide effective assistance here. The task of sanation control is the identification of operational results and preparation of draft decisions on the use of identified reserves and overcoming additional obstacles.
The rationale for the sanation process for each individual business entity can be made in the form of a financial recovery plan, a business plan, a feasibility study. The standard form and structure of such a plan does not exist, but any form of it requires the availability of reliable basic information. For most cases, the rehabilitation project can have this structure:
- General characteristics of the enterprise (actual financial condition by such indicators as actual volume of sold products, profit, debt, solvency and liquidity ratio); Analysis of the reasons why the company was in a difficult financial situation; Prospects for overcoming the crisis;
- The financial rehabilitation plan (the production program for the coming years, the balance of cash incomes and expenses, the calculation of the effectiveness of measures aimed at improving the enterprise);
- Prediction of the final results of the rehabilitation project.
- The financial rehabilitation plan for the enterprise (organization) is submitted in the form of a business plan, and the sections highlighted in Fig. 19.9
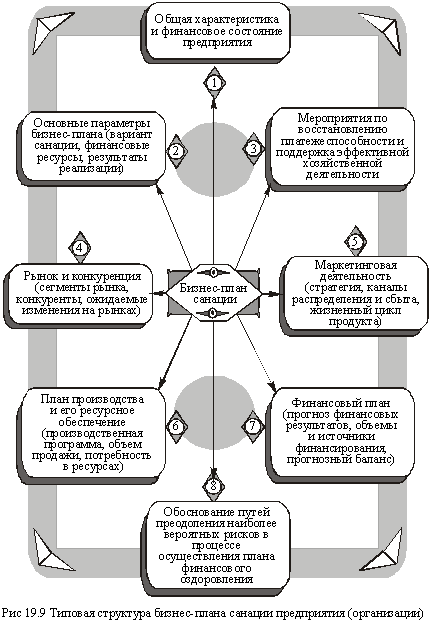
The first section "General characteristics of the enterprise and its financial status" contains such information: the name of the enterprise; Data on registration, subordination, mission and activities; Organizational and legal status; type of ownership; organizational structure; Financial ratios of liquidity, solvency, financial stability, capital turnover, level of accounts receivable, profitability, profitability.
In the second section "Basic parameters of the business plan project", the net present value, the internal rate of return and the payback period of the project are indicated to characterize the financial results of the plan implementation.
Among the many different activities that are recommended for implementation in order to restore solvency and constitute the main content of the third section of the business plan for the rehabilitation, the following are highlighted:
- Changing the composition of the company's managers and management style;
- Inventory of the company's assets;
- Optimization of the size and structure of accounts receivable, reduction of production costs;
- Sale of subsidiaries and stakes in the capital of other enterprises; Sale of unfinished construction;
- Substantiation of the required number of staff by category;
- Sale of surplus equipment, materials and leftovers of finished products;
- Restructuring of debts by converting short-term debt into a long-term loan or mortgage;
- Introduction of advanced technology, mechanization and automation of production;
- Improving the organization of work;
- Carrying out major repairs, modernization and replacement of obsolete equipment and vehicles.
When preparing the fourth section "Market and competition", you need to pay special attention to a detailed description of the survival strategy, and the seventh "Financial Plan" - to take into account that this section of the plan has a decisive role in the process of choosing a particular financial rehabilitation option for a particular enterprise.
Finally, it is very important to correctly substantiate a possible scenario for overcoming likely risks in the process of financial recovery of an enterprise. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the fact that the consequences of implementing too risky projects are in most cases negative; So this problem requires careful discussion and making the right decisions. For small businesses, risks can depend primarily on the microsphere and internal difficulties. For large enterprises that have started the reorganization project, the risks most often come from the macro environment (changes in the legislative base, state policy, etc.).
Sanitation projects are usually subjected to state expertise to assess their quality and identify enterprises that require government financial support. Selection of enterprises (organizations), which economically expedient to provide state support , is carried out according to certain criteria (Figure 19.10).
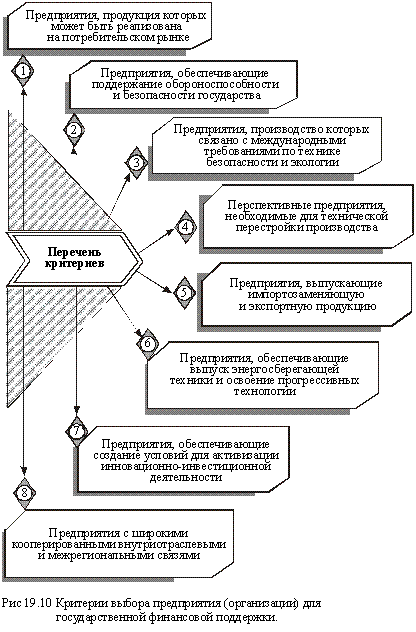
It is quite clear that when selecting enterprises for financial recovery, it is necessary to carefully weigh the negative social consequences of the shutdown and subsequent liquidation of a particular enterprise. First of all, we mean enterprises that are located in large industrial centers with a high level of interconnected production, as well as in small towns where these enterprises are almost the only place for possible employment of the population.
In the process of substantiating the list of enterprises that need state sanation facilities, diagnostics of their financial and property status is carried out. As the accumulated experience shows, such an analysis should cover the main aspects of the enterprise's functioning, but differently:
- Characterization of the form of ownership and distribution of the authorized capital (organizational structure of the enterprise, charter, organizational form, state ownership share, specific weight of foreign capital);
- Financial condition of the enterprise (profit and structure of its distribution, profitability of products, cost of capital);
- Indicators of the cost price of commodity output, accounts receivable and accounts payable, inventories of inventories, volume of circulating assets, loans, subsidies, subsidies, etc.;
- Assessment of the production potential (fixed assets and level of their wear and tear, level of use of production capacities, resource availability, volumes and product range);
- Cooperated communications and product failure (volumes and objectives of implementation, the main suppliers of raw materials, consumers of products, sales markets, leftovers of finished products);
- Characteristics of staff, remuneration;
- The characteristics of the social infrastructure of the enterprise (organization);
- Feasibility study of the rehabilitation of the enterprise and other business entities.
An indispensable condition for obtaining state support is the availability of a feasibility study (feasibility study) for the rehabilitation of the enterprise. The feasibility study may have a diverse structure, but, as a rule, consists of the following sections:
- General provisions;
- The characteristic of the enterprise;
- Demand for products and market analysis;
- The availability of resources and the sources of their replenishment;
- The main technical solutions in the field of enterprise re-profiling;
- Personnel and labor productivity;
- Estimate of construction costs (reconstruction, technical re-equipment);
- Cost of production;
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of measures for the rehabilitation of the enterprise;
- The main technical and economic indicators of the enterprise, which are subject to reorganization;
- Financial and economic evaluation of sanation;
- Conclusions and recommendations.
When developing a feasibility study, a fairly wide range of various indicators is used, which are considered in the basic and prospective periods (after reorganization) periods. These include:
- Profitability of products and production;
- The payback period (as the ratio of the discounted amount of cash flows to the discounted amount of sanation costs);
- breakeven point;
- The total amount of investments for the rehabilitation, their nature and distribution by the investment terms;
- Volume of products sold;
- profit;
- Costs for production and sales of products;
- Terms and conditions for repayment of loans;
- number of staff;
- Level of use of production capacities.
Particular attention should be given to indicators of financial sustainability of the sanation project, the nature of use and timing of investment return, as well as correctly assess the dynamics of profitability in the prospective period, the volume and structure of profit distribution, sources of lower production costs, turnover of working capital.
The volume of sanation facilities (Іс) for improvement of financial condition of the insolvent enterprise can be determined by the formula
Ic = 3c - (Pg - Πφ), (19.1)
Where Зс - necessary total sum of expenses for realization of sanation measures, providing profitable work of the insolvent enterprise;
Рв - the volume of internal reserves of the enterprise, which can be used for its financial recovery;
Pf - the amount of financial assistance from other enterprises interested in the cost-effective operation of an insolvent enterprise.
The mobilization of internal reserves can be achieved by: selling products at lower prices; Reduction of accounts receivable; Sale of surplus equipment, other inventory items; Leasing of premises, equipment, etc. Financial assistance can be provided by partners in cooperative relations, enterprises (holdings) that own a controlling stake in an insolvent enterprise, as well as creditors who are confident of the positive consequences of financial rehabilitation of such an enterprise.
The expediency (efficiency) of the sanation programs for the development of the subject of farming is usually determined by the indices given in Table. 19.1.
Table 19.1.
INDICATORS FOR EVALUATION OF THE SANATORY PROGRAMS OF ENTERPRISE DEVELOPMENT
| Index | Criteria level |
||
optimal |
acceptable |
Unpromising |
|
|
Production and profits
|
Exceeds or is equal to one |
Less than one, but more than the industry average |
Less than the industry average |
|
Less inflation index |
Equals the inflation index |
More inflation index |
|
> 1.0 |
1.0 |
<1.0 |
|
<1.0 |
1.0 |
> 1.0 |
|
> 1.0 |
1.0 |
<1.0 |
|
> 1.0 |
1.0 |
<1.0 |
|
> 1.0 |
1.0 |
<1.0 |
|
Competitiveness in the internal and external markets
|
> 1.0 |
> 0 |
0 |
|
> 1.0 |
1.0 |
<1.0 |
|
> 1.0 |
> 0 |
0 |
Questions for self-study in depth
- Essential content of the restructuring of enterprises (organizations).
- The main forms and types of restructuring of enterprises (organizations) carried out in certain sectors of the national economy of Ukraine.
- Analytical assessment of the technical and economic and financial situation in the process of substantiating the forms, types and depth of restructuring of business entities.
- Practice of implementation and effectiveness of restructuring of enterprises (organizations) and structural reorganization of certain sectors of the national economy of Ukraine.
- The essence of sanation (financial recovery) of business entities.
- Classical model of the process of financial recovery of enterprises and organizations.
- Programs and projects for the rehabilitation of business entities.
- Business plan for financial recovery of an enterprise (organization) and its model sections.
- The structure of the feasibility study (feasibility study) for the rehabilitation of the enterprise (organization).
- Economic efficiency of the implementation of sanation programs for the development of enterprises and organizations.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.