home
 Economy Economy
 Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF
|
Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF
20.3. Elimination of bankrupt enterprises (organizations)
The procedure for the liquidation of bankrupt business entities
The reasons for the liquidation (termination of activities) of enterprises and organizations may be different. The main ones are the following:
- Property continues to depreciate and any opportunity is used to restore its value;
- No legal or natural person has applied to the relevant body with a request to restructure or sanitize the debtor;
- None of the restructuring or reorganization plans submitted was approved by creditors;
- The proposed plans for the withdrawal of an enterprise (organization) from a crisis state for one reason or another can not be realized.
Each of these reasons can be a sufficient basis for taking a court decision on the liquidation of the debtor: on his own initiative or at the request of the property administrator, creditors, meeting or creditors' committee. After acceptance by the arbitration court of the resolution on recognition of the debtor bankrupt, this decision is sent to all those who are involved in this process: the founder of a bankrupt legal entity; To the owner of the property of the bankrupt or authorized body; Bank, whose client is bankrupt; The body that registered the bankrupt as a subject of entrepreneurial activity; All creditors; To all participants of agreements in which the debtor took part; To all participants in the arbitration process; State employment service; Relevant trade union bodies. The same resolution appoints liquidators from representatives of meetings of creditors, banks, financial bodies, as well as from the State Property Fund, if a state enterprise or organization is declared bankrupt.
The liquidators appointed by the arbitration court become members of a liquidation commission with broad powers. To this commission goes the right to dispose of property, bankruptcy and all of its property rights and obligations. Liquidation commission: controls the property of the bankrupt; Produces inventory and property evaluation; Determines the liquidation mass and disposes of it; Takes measures to recover accounts receivable; Realizes the property of a bankrupt enterprise (organization) and carries out other activities aimed at satisfying the claims of creditors.
The liquidation mass is the property assets of the bankrupt, to which, with the purpose of paying off the debt, recovery may be directed at the request of creditors, that is, virtually all the property of the debtor, which belongs to it by right of ownership or full economic management. If the subject of bankruptcy is the founder or a participant of the economic company and, accordingly, the owner of a share in the company's statutory fund, this share is subject to withdrawal (exclusion) from the statutory fund by the way of its reduction. The funds received are included in the liquidation mass. Leased property is excluded from the liquidation mass.
The valuation of the liquidation value of a bankrupt enterprise has certain peculiarities due to the unusual nature of the situation. The main feature is that this is an active type of evaluation, on the basis of which certain managerial decisions are made, concrete practical actions are carried out. In addition, the assessment of the liquidation value of an enterprise directly affects the interests of a third party (other than customers and appraisers), namely creditors, investors, judicial bodies.
Liquidation value is a net monetary sum that the owner of an enterprise can receive upon the liquidation of an enterprise and the sale of its assets.
In the world practice, the concepts of orderly and coercive liquidation are distinguished, and also the terms "ordered liquidation value" and "forced liquidation value", respectively. With the orderly liquidation of an enterprise, the sale of assets is carried out within a certain (reasonable) time in order to obtain the highest price for them. For the most illiquid assets this period can be up to two years. Forced liquidation provides for immediate sale of assets, usually all at the same time (at one auction).
The value of the disposal value of the sale of assets, cleared of related costs, is discounted at the valuation date at a discount rate that takes into account the risk associated with this sale. It is better to sell assets separately than the whole enterprise. In this case, the amount of revenue is usually more.
The practice of management identifies certain stages of the technological sequence of the process of calculating the orderly liquidation value of an enterprise:
- The first stage is the development of a calendar schedule for the liquidation of the assets of the enterprise;
- The second stage is the estimation of the current value of assets, taking into account the costs of their liquidation;
- The third stage is the specification of the scope of the enterprise's liabilities;
- The fourth stage is the determination of the difference between the current (adjusted) value of assets and the value of the enterprise's liabilities.
To determine the liquidation value of assets, the company's balance sheet data is used, the market value of land plots and other assets is calculated by different valuation methods (asset accumulation, comparative or market, income). The calculation of the liquidation mass is made for the purpose of selling the assets of the bankrupt and, if necessary, other persons responsible for its obligations, to distribute the proceeds between the creditors.
Consequences of liquidation and forms of sale of bankruptcy property
Recognition in due course of the debtor bankrupt has certain legal consequences:
- First, the entrepreneurial activity of the debtor (enterprise, organization) is terminated;
- Secondly, the right to dispose of the property of the bankrupt, all his property rights and obligations passes to the liquidation commission;
- Thirdly, the terms of all bankruptcy debts are considered expired;
- Fourth, accrual of penalties and interest on all types of debts of the enterprise (organization) - bankruptcy - ceases.
The decision to sell the property of the bankrupt in consultation with the meeting (committee) of creditors is taken by the liquidation commission, which determines the procedure for the sale of this property (composition, conditions and terms of acquisition of property). The sale of the bankrupt's property assets is carried out by redemption in the event of receipt of only one offer; If there are several proposals, a contest or auction is to be held.
In the world practice, generally accepted methods of selling assets are: a) sale to one or more buyers; B) sale at auction or by tender; C) leasing out to one or several persons all or part of the property assets of a bankrupt with the further distribution of funds received from the lease, among creditors; D) transfer of pledged property to the pledgee; E) leaving the debtor unprofitable property or one that has insignificant value and does not affect the increase of property assets. You can use other ways of selling assets, approved in court.
In the event that the subject of bankruptcy is a unitary state enterprise or an economic company in whose statutory fund the majority share of the property belongs to the state, the auction (competition) is carried out by the privatization body. If the subject of bankruptcy is a legal entity based on a non-state form of ownership, the liquidation commission may itself conduct the auction, or entrust it to a specialized enterprise (institution).
All forms of sale of bankruptcy property are formalized by purchase and sale contracts, which is concluded between the liquidation commission on behalf of the bankrupt enterprise and the buyer. The liquidation commission, in agreement with the meeting (committee) of creditors, determines the sequence of sale of the objects of the liquidation mass and the criteria for their selection for sale, since it is permitted to sell both integral property complexes and individual individually defined property, unfinished construction objects or preserved facilities.
Priority for the satisfaction of claims of creditors
The funds received from the sale of bankruptcy are directed to the satisfaction of creditors' claims (Figure 20.4).
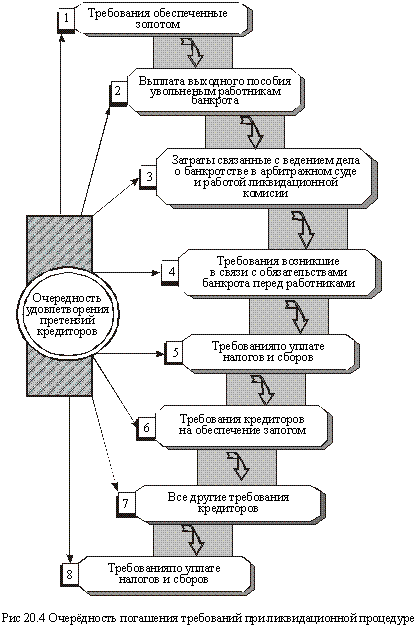
The requirements of each next stage are met only after the requirements of the previous one are fully satisfied. In the absence of property to fully satisfy all the requirements of one stage, claims are satisfied proportionally to the amount of time each creditor has.
Requirements that are not satisfied due to lack of property are considered to be extinguished. The claims submitted after the deadline for submission of claims are not considered and are considered to be canceled. Property (other than the funds of state-owned enterprises that are bankrupt), which remains after the satisfaction of the claims of creditors and members of the labor collective, is transferred to the owner or the appropriate privatization body for sale if the arbitration court has adopted a resolution on the liquidation of the debtor enterprise.
The funds remaining after the state enterprise-bankrupt satisfy the requirements of creditors and members of the work collective are credited to the corresponding extra-budgetary privatization fund.
After the completion of the sale of property objects and distribution of proceeds between creditors, the liquidation commission shall prepare and submit to the arbitration court the liquidation balance sheet . This is considered the final stage of the liquidation procedure for bankruptcy.
The arbitration court considers the liquidation balance sheet and passes a resolution on its approval or on refusal to approve. The second case may take place if any of the liquidation procedures are performed unsatisfactorily or the creditors have objected. In this case, the court may raise a demand for correction of errors (if possible) or decide on the appointment of new liquidators. The new liquidation commission is obliged to carry out all stages of liquidation of the enterprise (organization) - bankrupt anew.
If the liquidation balance is approved by the Arbitration Court, the latter:
- Issue a resolution on the liquidation of a legal person-bankrupt;
- Publishes this resolution in relevant publications of an operational nature;
- Exempts liquidators from performing their duties.
Thus, the bankruptcy case can be considered closed only after the approval of the restructuring plan (sanation) of the debtor's property or after approval of the liquidation balance sheet. If the bankrupt's estate was sufficient to satisfy the claims of creditors, it is considered to be free from debts and can continue its business activities or organize a new one (of course, if the remaining part of the property is sufficient for this).
Questions for self-study in depth
- Essential multi-aspect characteristic of bankruptcy of the enterprise (organization).
- System of signs of bankruptcy of an enterprise (organization) as an economic phenomenon.
- Identification and analysis of the causes (factors) of bankruptcy of business entities.
- Consecutive stages of filing a bankruptcy case of an enterprise (organization).
- Common methods in the world practice of managing methods of determining the possibility of bankruptcy of an enterprise (organization).
- Organizational aspects of the process of initiating the bankruptcy case of certain economic entities.
- Possible consequences of bankruptcy recognition of certain legal entities.
- The procedure for the liquidation (termination) of bankrupt enterprises and organizations.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.