home
 Marketing Marketing
 Basics of Marketing - Kotler Philip Basics of Marketing - Kotler Philip
|
Basics of Marketing - Kotler Philip
Advertising
In 1981, advertising costs in the United States amounted to 61.3 billion dollars. We define advertising as follows:
Advertising is a non-linear form of communication, carried out through paid means of dissemination of information, with a clearly indicated source of funding.
Among those who spend money on advertising are not only commercial firms, but also museums, foundations and various public organizations seeking to advertise their goals to different target audiences. By the way, the twenty-fourth among the largest advertisers is a non-profit organization - the US government.
Table 19. Ten largest national, advertisers of the USA 1981
A place |
Firm |
Total advertising costs, mln. |
Total sales, mln. |
Advertising costs,% to sales volume |
1 |
Procter & Gamble |
671.7 |
11,944 |
5.6 |
2 |
Sears, Robak and Co |
544.1 |
27,360 |
2.0 |
3 |
General Foods |
456.8 |
8.351 |
5.5 |
4 |
Philip Morris |
432.9 |
10.885 |
4.0 |
5 |
General Motors |
401.0 |
62,698 |
0.6 |
6th |
"K-Mart" |
349.6 |
16,527 |
2.1 |
7th |
Nabisco Brands |
340.9 |
5,819 |
5.9 |
8 |
"R. J. Reynolds Industries » |
321.2 |
11,691 |
2.7 |
9 |
ATT |
297.0 |
58,214 |
0.5 |
10 |
"Mobile" |
293.1 |
68,587 |
4.3 |
In the commercial sector, a quarter of all advertising in the country falls to the share of hundreds of leading nationwide advertisers2. In Table. 19 shows the list of the top ten advertisers in 1981. Spent the most on advertising for the corporation "Procter and Gamble" - almost $ 672 million, or 5.6% of total sales of $ 1.9 billion. The remaining leading advertisers are in Automotive and food industries, retail and communications, and the tobacco industry. In the automotive industry, the share of advertising accounts for a small percentage of the cost of sales, in the food and pharmaceutical industry, this percentage is high. The biggest of all is the percentage of costs for advertisers dealing with medicines, toiletries and cosmetics. Behind them go advertisers offering chewing gum, confectionery and soap. The record percentage of advertising costs from the amount of sales from the corporation "Knoxell" - 22.2%.
Advertising dollars come in a variety of means of information dissemination: magazines and newspapers, radio and television, outdoor displays (billboards, posters, signs, inscriptions in the sky), "direct mail", souvenirs (matchboxes, notebooks, calendars), transport tablets (In trains, buses), catalogs, reference books, circulars. In advertising, many applications are used to form a long-term image of the organization (prestigious advertising), for the long-term allocation of a particular branded product (brand advertisement ), for the dissemination of information about a sale, service or event (classified advertisement ), for the announcement of a sale at reduced prices ( advertising Sales) and to defend a specific idea (promotional and promotional advertising).
The roots of advertising go to gray antiquity (see box 34). Although its main users are private enterprises, advertising is used all over the world, including in the socialist countries. Advertising is a cost-effective way to distribute appeals, whether they are designed to create a worldwide preference for the Coca-Cola brand, to motivate consumers to consume milk or to apply methods of birth control.
Organizations approach advertising in different ways. In small firms, advertising is usually handled by one of the sales staff, who occasionally comes into contact with an advertising agency. Large firms establish their own advertising departments. The manager of this department reports to the vice president of marketing. The functions of the advertising department include the development of a general advertising budget, the approval of announcements and campaigns submitted by the agency, the conduct of activities for direct mail advertising, the establishment of advertising for dealerships and the implementation of other forms of advertising that advertising agencies usually do not. Most firms use the services of third-party advertising agencies, since this organization of work offers a number of advantages (see box 35).
In the process of developing the program of promotional activities, the management of the marketing department needs to make five fundamentally important decisions. They are listed in the diagram in Fig. 79 and are discussed in the following sections of this chapter.
Box 34. Historical Milestones of Advertising
On the advertising practice it is already in the very first documents of written history. During the excavations in the Mediterranean countries, archaeologists found signs informing about various events and proposals. The Romans painted the walls with announcements of gladiatorial battles, and the Phoenicians painted the rocks along the routes of various kinds of processions, extolling their products in every way. All these are the precursors of modern outdoor advertising. One of the wall paintings in Pompeii praised the politician and urged people to give his votes for him.
Another early version of advertising personified the city herald. The "Golden Age" of Ancient Greece saw the heralds, who walked the streets of Athens, proclaiming the sale of slaves, livestock and other goods. Here is how the "advertising song" meant for the ancient inhabitant of Athens sounded: "To make your eyes shine so that cheeks are glowing, to preserve the girl's beauty for a long time, a sensible woman will buy cosmetics at reasonable prices from Exlintos."
Another early version of advertising was the brand that artisans put on their products, such as pottery. As the rumor spread information about the reputation of the artisan, buyers began to search for goods with its brand. Today, for these purposes, use trademarks and brand names. For example, the canvas from Osnabrück was carefully checked for quality and assigned to it a price 20% higher than the Westphalian canvas that was sold without the vintage names. As the centralization of production and the removal of markets, the value of the stigma grew steadily.
The turning point in the history of advertising was 1450, the year Gutenberg invented the printing press. The advertiser did not need to manually create additional copies of his notifications. The first printed announcement in English appeared in 1478.
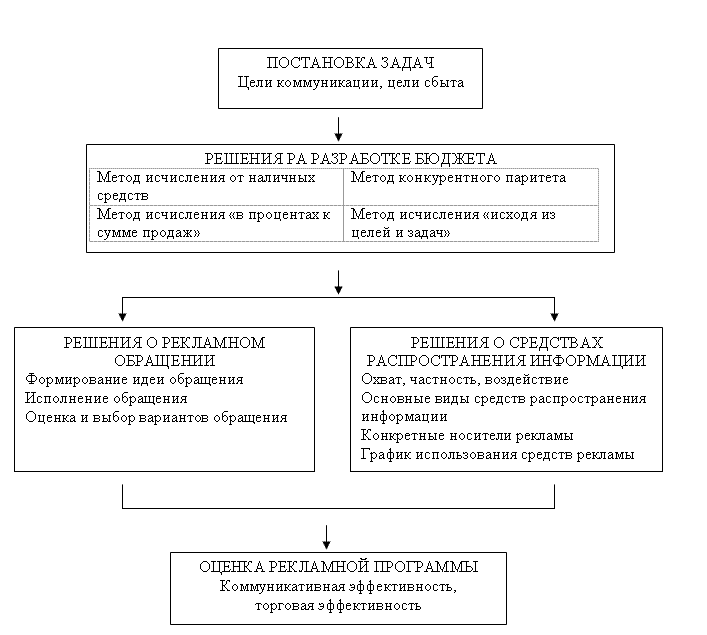
Fig. 79. The main decisions in the field of advertising
In 1622, advertising received a powerful stimulus in the form of the first English-language newspaper that was launched, which was called the Weekly News. Later, Addison and Steel began to publish the newspaper "Tatler", becoming loyal advocates of advertising. Addison printed the following advice to the drafters of advertising texts: "The great art of writing an advertisement is to find the right approach in order to grab the attention of the reader, without which the good news can go unnoticed or get lost among the bankruptcy notices." In the issue of "Tatler" for September 14, 1710, advertisements for razor straps, patented medicines and other consumer goods were published.
The greatest prosperity of advertising has reached in the United States. The father of American advertising is called Benjamin Franklin. His Gazette, which appeared in 1729, achieved the largest circulation and the largest volume of advertising publications among all the newspapers of colonial America. The transformation of America into the cradle of advertising contributed to several factors. First, the American industry was leading in the process of introducing mechanization into the production, thanks to which there was an excess of goods and there was a need to convince consumers to buy more. Secondly, the creation of an excellent network of waterways, highways and ordinary roads made a real delivery of goods and means of advertising to rural areas. Thirdly, the introduction in 1813 of compulsory primary education raised the level of literacy and contributed to the growth of newspapers and magazines. The invention of radio, and later of television, meant the emergence of two remarkable means of advertising distribution.
Box 35. How does the advertising agency work?
Madison Avenue, USA - this phrase, familiar to most Americans, refers to a street in the center of New York, which houses the headquarters of several major advertising agencies. About 30 thousand people work in these headquarters. And the vast majority of the 6,000 advertising agencies in the country are outside of New York. In the US, there are not so many cities where there would not be at least one advertising agency, even if it is an enterprise with only one employee. In 1978, the seven largest advertising agencies in the United States in terms of turnover on accounts on a global scale were: "J. Walter Thompson, McCann-Erickson, Young & Rubikam, Ogilvy and Meiter, BBDO, Ted Bates and Leo Burnett. The world's largest advertising agency is in Japan and is called "Denzu".
The services of advertising agencies are resorted to even by firms with strong own advertising departments. The agencies employ creative and technical specialists, who are often able to perform advertising functions better and more efficiently than regular employees of the firm. In addition, the agencies bring the view from outside to the problems facing the firm, as well as a rich variety of experience working with different clients and in different situations. Payment for the services of agencies occurs at the expense of commission discounts received by them from the means of advertising, and therefore they cost firms inexpensively. And since the firm can at any time break the contract, agencies have a powerful incentive to work effectively.
Typically, the basis of the advertising agency is four departments: the creative department engaged in the development and production of ads; Department of means of advertising , responsible for the choice of means of advertising and placement of ads; A research department studying the characteristics and needs of the audience, and a commercial department dealing with the commercial side of the agency's activities. Work on the orders of each individual client is managed by a responsible executor, and employees of specialized departments are entrusted with servicing orders of one or several clients.
Often, agencies attract new customers because of their reputation or their size. However, as a rule, the client offers several agencies to conduct competitive presentations, according to which they make their choice.
Advertising agencies receive compensation in the form of commission and sometimes fees, Usually, the agency receives a 15% discount from the cost of the media it purchases. Suppose that it buys a place for a client in a magazine worth $ 60,000. The magazine issues an account to the agency for $ 51,000 (60,000 minus 15%), and the agency receives a full amount of $ 60,000 from the client, A commission of 9 thousand dollars in their favor. If the customer bought the same place directly from the magazine, he would also pay $ 60,000 to the magazine, since commission discounts are granted only to accredited advertising agencies.
And advertisers and agencies are increasingly dissatisfied with the system of commission discounts. Large advertisers complain that they pay more for the same services than small advertisers, simply because they place more advertising. Advertisers also believe that the commission system distracts the attention of agencies from inexpensive means of advertising and short-term advertising campaigns. Agencies complain that they provide additional services to the client, without receiving any additional compensation for this. Today, more and more tend to the system of compensation, either on the basis of direct fees, or on the basis of a combination of fees and fees.
On the foundations of the activities of agencies, some tendencies of our days are also adversely affected. Full-service agencies face increasing competition from agencies with a limited cycle of services, which specialize either in the purchase of advertising media, in the creation of advertising texts, or in the production of promotional materials. Commercial managers are gaining more and more power in advertising agencies and are increasingly demanding from the creative staff more focus on making profit. Some advertisers have opened their own in-house advertising agencies, thus ending a long-term relationship with their previous advertising agencies. Finally, the Federal Trade Commission wants advertising agencies to be held responsible for false advertising on an equal basis with customers. All these trends will undoubtedly cause a number of changes in this area of activity, but agencies that do their job well will survive.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.