home
 Other disciplines Other disciplines
 Books Books
 Mathematics programmers - Nakonechny S.I. Mathematics programmers - Nakonechny S.I.
|
Mathematics programmers - Nakonechny S.I.
2.8.3 Optimal rozvyazok. Criterion of optimality for the plan
Simppleksny method umozhilju directions of perebіr of basic planіv, тобто перехід від one plan to іншого, який є хоча б not гіршим від переднього за значенням функціонала. Otzhe, okremim pitannyam stae vibri vektora, yakii neobhidno enter into the basis for zdіysnennі іteratsіyno procedures simplex method.
The problem of linear programming (2.36) - (2.38) is rozglyanemo.
It is permissible, but it is impossible for them to survive, they can not survive. Rozglyanemo pochatkivy support plan (2.40):
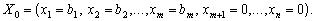
Such a plan is due to the development of the base vectors
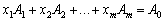 (2.45)
(2.45)
The value of the function:
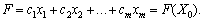 (2.46)
(2.46)
Кожен з векторів 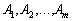 It is possible to distribute vectors behind the vectors, to the prichem at єdyniy sposib:
It is possible to distribute vectors behind the vectors, to the prichem at єdyniy sposib:
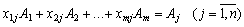 , (2.47)
, (2.47)
To such a retail connection in the course of the year and in the year the value of the functional:
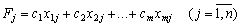 . (2.48)
. (2.48)
Significantly through 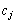 Koefіtsієн functііонала, що відповідає vector
Koefіtsієн functііонала, що відповідає vector 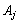 , That
, That 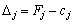 (Їх називають оцінками відповідних vectorsів the plan)
(Їх називають оцінками відповідних vectorsів the plan) 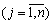 . Todi is fair є tak tverdzhennya (in order to optimize the plan for the tasks of the linear programming): yakshto for the active plan
. Todi is fair є tak tverdzhennya (in order to optimize the plan for the tasks of the linear programming): yakshto for the active plan 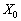 Rozklad vseh vektoriv
Rozklad vseh vektoriv 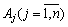 I give the basis to the given dowry:
I give the basis to the given dowry:
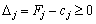 , (2.49)
, (2.49)
The plan 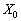 - the optimal rozvyazykom tasks lennyi programvannya (2.36) - (2.38).
- the optimal rozvyazykom tasks lennyi programvannya (2.36) - (2.38).
Analogously to formulate the principle of optimality in the plan of tasks for the solution of the minimum value of the functional: for the active plan 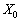 Rozklad vseh vektoriv
Rozklad vseh vektoriv 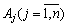 I give a basis to a dull smile
I give a basis to a dull smile
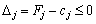 , (2.50)
, (2.50)
Then the plan X 0 is optimal for the problems of linear programming.
Separate, in order that the plan of problems of linear programming is optimal, necessary and sufficient, that the yogo otsinki 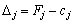 Bulls are insignificant for tasks at the maximum and underdelivers for tasks at the minimum.
Bulls are insignificant for tasks at the maximum and underdelivers for tasks at the minimum.
Umovi optimality plans for the problems of linear programming is done by two theorems. Skorstavshis introductions in danogo paragra admitted by that cognition, formulated theorems, and takozh navelemo їх доведення.
THEOREM 2.6. Yakshto for the active vector 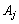 Vikonuetsya umova
Vikonuetsya umova 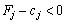 , The plan
, The plan 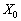 Not å optimal і mozhna vidshukati such a plan X , for yakogo vikonuvatimetsya nervіnnist
Not å optimal і mozhna vidshukati such a plan X , for yakogo vikonuvatimetsya nervіnnist 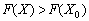 .
.
Beforehand . Multiply (2.47) and (2.48) by 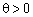 І Віднimмемо the result is in turn from (2.45) and (2.46). Отримаємо:
І Віднimмемо the result is in turn from (2.45) and (2.46). Отримаємо:
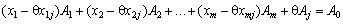 ; (2.51)
; (2.51)
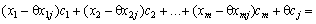
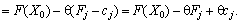 (2.52)
(2.52)
At the level (2.52) to the particles, the quantity 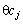 for
for 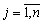 . We have (2.51)
. We have (2.51) 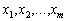 Dodatny, that zavzhdi can know taka
Dodatny, that zavzhdi can know taka 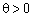 , That is, all vectors for vectors
, That is, all vectors for vectors 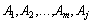 Buli b nevіd'єmnimi, іnakshe kazuchi, otrimati novy plan of tasks and mind:
Buli b nevіd'єmnimi, іnakshe kazuchi, otrimati novy plan of tasks and mind:
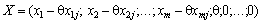 , Yakomu zgіdno з (2.52) відповідає так значення функціонала:
, Yakomu zgіdno з (2.52) відповідає так значення функціонала:
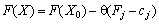 . (2.53)
. (2.53)
Oskilki for the sake of theorizing 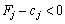 I
I 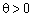 , Then
, Then 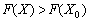 , But it would be necessary to bring it up.
, But it would be necessary to bring it up.
Yaksho rozglyadaetsya problem on the problem of the minimum value of the function, then formulate such a theorem.
THEOREM 2.7. Yakshto for the active vector 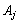 Vikonuetsya umova
Vikonuetsya umova 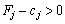 , The plan
, The plan 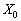 Not å optimal і mozhna poduduvati such a plan X , for a vikonuvatimetsya nerіvnnist
Not å optimal і mozhna poduduvati such a plan X , for a vikonuvatimetsya nerіvnnist 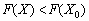 .
.
Follow the analogue to the alternate.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.