home
 Finance Finance
 books books
 Pricing - Erukhimovich IL Pricing - Erukhimovich IL
|
Pricing - Erukhimovich IL
7.2. Determination on the basis of the analysis of break-even price and ensure profit target
As already mentioned, the profit is a function of the volume of production, production costs and prices. In real life, in a market economy, the volume of production is not always identical to the volume of sales. Therefore, to ensure that the target profit should not only provide profits per unit of output. In the context of the elasticity of demand price increase causes an increase in profit per unit of product, but it leads to a decrease in sales and a decrease in the size of the total profit. Under the conditions of inelastic demand reduction in the unit price leads to an increase in sales.
Thus, the maximum profit you can get the optional when setting a maximum price for the goods. And here arises the problem of price optimization, t. E. You need to find the price of the goods (in determining the scope of its sales), in which profit is maximized (or target).
To calculate the optimal price is necessary to determine the dependence of the cost of production of the volume of production and revenue from the volume
sales. In general terms, this relationship at a constant low as shown in Fig. eleven.
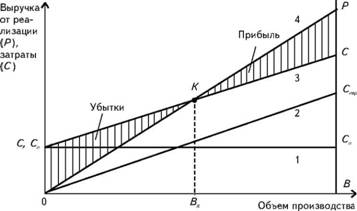
Fig. 11. Dependence of production costs, sales revenue and profit from the volume of production in natural measurement
Line 1 in Fig. 11 reflects the fixed costs of the company (C), which do not depend on the production volume (V). Line 2 represents the change in variable costs (Spur), proportional to the volume of production. The increase in total costs (C = C + Spur) with an increase in the volume of output is characterized by a line of 3, and an increase in revenue from the sale of (R) - 4 line.
At a certain volume of production (Bx) proceeds from the sale of products only commodity producers reimburse the cost of its production (point K), t. E. There is no profit and no loss. Thus, the output of the I is the minimum required volume of sales, in which revenue equals expenses. Increasing the I output provides earnings (P -> 0), whereas the decrease - loss (P - C <0).
Bx point is called the critical volume is measured in real terms (that is, pcs., M, m 2, and so on. D.). Point K is called the break-even point, and is measured in monetary terms.
This graph corresponds to a price under certain costs of production and sales volumes. Increasing the price causes a large angle of the line 4 and moving the breakeven point to the left.
In general, the costs of production and sales revenue described by the equations

where C - unit price.
Then, provided that the break-even production of a particular type of product the minimum volume of production - the breakeven point - can be calculated by the formula

and the break-even threshold - according to the formula
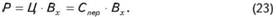
When setting prices according to this method, provided straightforward dynamics of costs and revenues (elastic demand) its level is calculated according to the formula

For example, in the production process fixed costs (C) per unit of up to 150 thousand UAH, and the variables -.. 250 UAH. The market unit price - 400 UAH.
Then, in accordance with formula (22) the minimum output
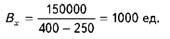
This means that if it is produced and sold 1000 units. production, the commodity producer only recovers its costs.
breakeven threshold of 400 thousand. UAH. (400 UAH. • 1000 150000 or + 250 • 1000).
If you develop a new product and a constant source data (Cn, Spur) will be revealed demand of 1000 units. products, the level of the selling price, calculated by the formula (24), will be
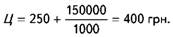
However, each commodity producer is planning its operations, it expects to certain (specified, the target) profit.
In this case the proceeds from the sale of (C * B) is required to reimburse the costs (C + Spur * B) and provide a predetermined amount of profit (Poise):
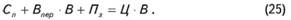
Then the unit price and the required volume of production are determined by the formulas, respectively
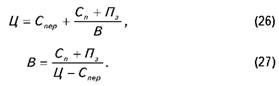
This pricing method allows to analyze the various options for the ratio of the volume of production and prices, that will provide a given (target) profit and will protect the enterprise (company) against losses.
7.3. Determination on the basis of the prices perceived value
In a market economy, many producers in the justification, calculating and setting prices are based on the perceived value of their products.
The main factor in pricing in this case the production costs are not acting, and purchasing perception. To identify consumer evaluations using non-price methods of exposure: Special polls, surveys and other market research, allowing to form in the minds of consumers ideas about the value of the goods.
Using this method of pricing requires an objective approach to setting prices: if the price is greater than the value recognized by buyer significance of the goods, selling products will be lower than estimated; in the case of unjustified underpricing the risk of not getting the estimated amount of profit.
For example, the company specializes in the production of household appliances. Among the products - washing machines. The company has set the price on them 400 conv. den. u At rival machine price with similar properties is 320 conv. den. u
When asked about the reason of buyers increase in car prices by 80 conv. den. u The answer: the price for a car similar to competitor products - 320 conv. den. units, the margin for increased durability -. 50 conv. den. units for improved reliability -. 25 conv. den. units, for an increased level of service -. 10 conv. den. units, the cost of a long-term guarantee -. 15 conv. den. u Thus, the price of the complex value indices - 420 conv. den. u However, the company gives the customer a discount of 20 conv. den. u Therefore, the final price of a washing machine - 400 conv. den. u


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.