home
 Management Management
 Management - Vikhansky OS Management - Vikhansky OS
|
Management - Vikhansky OS
3.3. Rotation of work
Rotation of the model design work is to move an employee from one job to another and thus enable it to perform more diverse functions. In this sense the rotation of the work is very closely linked with the considered model of expansion of scale of operation, since it is based on the addition of a variety of tasks in order to increase interest in the work. In the case where all the work in the organization uninteresting, their rotation is a little something to help. For example, moving the worker on the assembly line with the tightening of bolts on the bumper on screwing bolts on wheels, the head is unlikely to achieve a noticeable effect. Typically, the rotation of the work brings success, if it appears part of a major re-engineering work under models such as the enrichment of work and socio-technical system, dealing with qualitative parameters of the (complexity and relationships). Rotation of work also has the effect of a method of teaching and training of personnel, especially those in managerial positions.
3.4. Enrichment work
Enrichment of the work in practice means the addition to the work performed by the individual functions or tasks that enhance the responsibility of the Executive for planning, organizing, monitoring and evaluation of their own work. Enrichment refers to such operating parameters as its complexity and the relationship to work, together constituting the concept of the organization of work. It is believed that the first time the model design work was used in the 40-ies. the company IBM. In 50 - 60-ies. dramatically increased interest in this model, in particular, after the well-known experiments in the AT & T and "Tek-Tools SAS." A strong impetus to the development of design models of work-related parameters such as its complexity, given the theory of the two motivators of Herzberg (see. Chap. 2). According to this theory, the work of a high degree of responsibility must be characterized and importance, a great opportunity to achieve a result.
Methods enrichment work is very specific and depends on the specific work that is subject to change. However, the following key elements that make up the essence of this model:
• establishing a relationship with the consumer;
• Planning the individual their own work;
• the employee performs the work by the owner of the process;
• the employee is informed of the results of (feedback);
• the work includes the study of the new;
• Work contains unique elements.
Establishing a relationship with those for whom the products are intended employee is the most important point in this model. An employee is usually more interested in the reaction of his boss, than those whom he directly transmits your product for future use. Thus, for example, behaves worker typing pool, if it does not have direct contact with the customer. Model enrichment work suggests that the worker must be in direct contact with the consumer directly to him to solve all the problems.
The model also provides that the employee must be able to plan their work. The manager can set the extreme timing and objectives, but within them the worker should have the right to set their own schedule and your own pace of work. Known system of flexible working hours, are widely used in a number of companies, especially in the field of office work. Under this system, the employee may, within certain limits itself to set the time of arrival and departure from work, depending on their needs and desires. This system forces the individual planning of the work of the advent of personal computers and their inclusion in the network allows today to perform the work at home, without disrupting the working rhythm.
The degree of proximity to the completion of the work product produced by the organization / service determines how the employee identifies himself with the final product and the process takes himself the owner. For example, if the team at the company "Volvo" is given the opportunity to "Wagon" way to collect the car from start to finish, it significantly helps all its members aware of their responsibilities and the importance to the work performed.
Direct and may prompt the individual to inform about the results of his work is a must to use enrichment work model. Reports on the progress should come to the table the performer, not only on the table, his boss. The employee must be given the opportunity to inspect the work, so that in time to make adjustments to it. Direct communication with other staff members increases the effectiveness of feedback, making it more accurate and timely.
Learning a new enrichment work as the element creates in man a sense of growth. Effectively designed work should provide the opportunity for professional growth.
Finally, an important element of the model is to make the enrichment operation work and some unique specificity.
The use of this model in the framework of the management of the work involves a focus on professional development and consulting employees and are not focused on the strengthening of control and administration. Enrichment of the work due to changes in working methods, with the delegation of implementing the rights and enable them to set goals and evaluate performance.
Widespread enrichment work model has features designed J. G. Hackmann and Oldham (Fig. 6.8)
The model focuses on strengthening the work of the five major features shown in Fig. 6.8. According to the model, these characteristics can be changed or improved under the influence of the psychological state of the corresponding employee. In turn, the employee's condition can lead to certain positive results for the individual and for work.
According to the theories of motivation (see. Chap. 2), an employee may experience positive emotions in relation to the operation depending on how quickly he gets feedback on the results of the work, the degree of his responsibility to work and how much of the feel the importance of its work. The presence of these three psychological self-reproducing individual states creates positive motivation to work, based on self-formed remuneration. In this case, the potential motivation can reach its maximum.

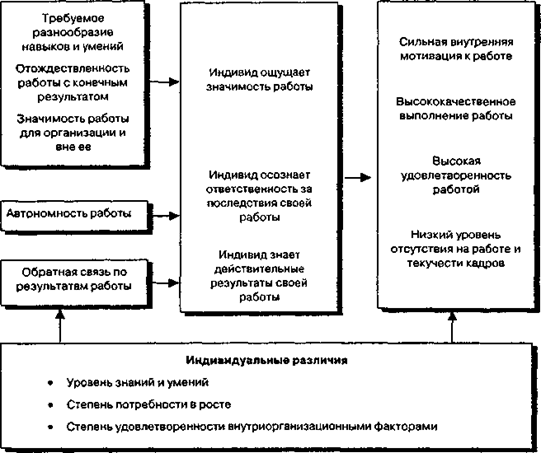
Figure 6 August Model enrichment work performance
The model considers the characteristics of the enrichment operation barely-1 following five main characteristics of the work. A variety of skills reflects the level of personal competence and abilities) that the work required from the contractor. Otodzhestvlyaemost work with a finite or solid result reflects the degree to which the work is included as part of in whole, or the distance at which the work is separated from the beginning and the end of the total product (service) | organization. The significance of the work reflects the extent to which it is perceived as an employee has a significant impact on the lives of others within or outside the organization. Avtonomnost - is the degree to which the job provides freedom and independence in planning work, in choosing the means for its implementation. Feedback on the results of the work reflects the extent to which performance of the individual work provides a direct and clear information on the impact of its efforts.
According to this model, three important individual differences may affect how the employee will respond to the enrichment of his work. These differences are: the level of knowledge and skills, the extent of the need for growth, the extent of intra-satisfaction factors. These differences largely determine the relationship between the characteristics of the work and the consequences of its performance for the individual and the work itself. They have carefully studied the design and redesign work.
Having the necessary level of knowledge and skills to perform the rich operation, the worker usually experiencing positive emotions in relation to the latter. Lack of knowledge and skills, as a rule, it is disappointing, stress and dissatisfaction. The intensity of these feelings particularly increases when an employee wants to do a good job, but realizes that the lack of knowledge and skills does not allow him that. It is therefore important to determine the level of existing knowledge and skills, before making a job change. And if the work is enriched, it is necessary to accompany it with appropriate programs and refresher training.
The extent of the growth of demand is determined by the employee's desire to be able to make decisions, learn from experience and to achieve specific achievements in the work. People with a strong need to increase positively inclined to accept the program of enrichment work, they get more satisfaction from work, internally and more motivated as a result, if their work is enriched, work more efficiently. People with poor growth in demand often indifferent to the enrichment operation, but the latter does not cause their dissatisfaction.
The degree to which employees are satisfied with intra-organizational factors of work, affecting their willingness or ability to respond positively to the enrichment operation. Noticeable influence factors such as organization management, technical management, salary policy, interpersonal relations, working conditions (lighting, heating, safety equipment, etc.). It is noted that the workers, much unmet these factors are less likely positively related to enrichment work. Other intra-organizational factors, such as organizational culture, power and influence, the group forms, etc., also have an impact on employee work related to enrichment.
In addition to the study of human capacity to deal adequately with rich work is necessary to study or carry out a diagnosis of the work itself from the viewpoint of whether it is necessary to enrich and, if necessary, bring whether this model of design work success. There are two methods of such a diagnosis: the method of structural solutions and method of inspection.
The method of structural solutions associated with the identification of those intra components, which reflect the drawbacks in the design work. An analysis of five specific structural components makes it possible to determine the existence of problems in the work itself and the level of desirability for its employee enrichment.
• Inspectors and auditors. When the content of the work is checked strangers, it reduces the level of its characteristics, such as autonomy and immediacy of feedback.
• resolver problems. If your organization, there are special people who are engaged only in resolution of problems arising in the different works, it means that from the works seized a number of important characteristics, such as excitement in its development, and the challenge that it poses to the performer. In this case, the lost sense of responsibility for the consequences of its implementation, as well as weaken the completeness, autonomy, and feedback in the work.
• Communication and relationship with the consumer. Implementation of communication and communication with the consumer through a special structural unit removes an employee from the consumer of the results of its work and thereby adversely affect the feedback effect and identification with the end result.
• Integrated Brigade. Connecting disparate works performers in enclosed structural units are often motivated by a desire to increase the effectiveness and the ability to cope with the changing workload. However, such "clustering" of work can affect the employee a sense of ownership in the process of work and reduces the finished work.
• Narrow the scope of control. The head, which has a small number of employees, has a tendency to interfere with their daily work. This situation leads to the centralization of decision-making and overcontrol the actions of subordinates. As a result, it suffers from the autonomy of work.
survey method is based on the extensive use of tests, questionnaires and questionnaires via which the diagnostic work can be carried out. One of these questionnaires, created by J.. Hackmann and G. Oldham, called "diagnostic evaluation work" (DOR). With the help of this questionnaire can be measured performance characteristics shown in Fig. 6.8, and the results of its redesign.
The following five questions are taken from the simplified version of the questionnaire. They allow you to measure the perceived employee autonomy (question 1), completeness (question 2), diversity (question 3), importance (question 4) and feedback (question 5). The full version of the questionnaire several questions used to measure the characteristics of each work.
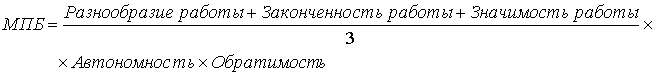
Using a seven-point scale for each job characteristics, we can calculate the total score of the rich content of the work, which is called "motivating potential score" (BCH):
Below are statements that may describe your work. It should be noted how each statement describes your work by choosing to assess each issue one of the seven points located on the scale.
1. What is the degree of autonomy of your work? E., The degree to which your work gives you the opportunity to decide for themselves how to do the job?
1



Very little Moderately A lot of diverse

Not very significant average importance Very significant

Very little Moderately Very much
Let us consider the effect of the connection technology for the design work (see. Fig. 6.6) and the enrichment operation characteristics (see. Fig. 6.8). In order to change the characteristics of the five work normally required to produce a change in one or more process variables affecting the design work.
One can cite as an example of the design work in the following circumstances. Suppose that the manager decided during the design work to use a combination of delegation of its powers to the formation of a working corpses, selected on the basis of logic, clear to the participants.
Delegation of authority to the enrichment operation in the following ways:
• employees within certain limits granted the right to plan the work, to determine the methods of its implementation, to decide when and how to check its quality;
• employees are allowed to make decisions about the beginning and end of the work, take breaks, and on the choice of priorities for work;
• Employees are encouraged to find their own solutions to problems or for the problems with the help of boards of other group members, rather than by an immediate appeal to the leader for help to solve the problem.
This state of affairs during the redesign of work changes its process variables - when and where the work should be carried out in the direction of greater uncertainty. Delegation of authority can also affect the third variable - the relationship work. The greater the powers delegated, the more the situation shifted in the direction of the emerging interdependence and the more reduced sequence and interaction of interdependence in the work.
During the formation of the working group the individual work together in formal divisions (brigades, sections, divisions and offices) that meet several criteria.
• Territory. For example, for the service centers of personal computers manufactured by normally fixed reachable within the required time (usually 24 hours) regions or areas.
• Type of business. For example, certain groups of workers serve individual clients by types of business in the insurance company: trade, industry, agriculture, etc.
• Communication with specific units. For example, typing pool in a certain group of workers can be assigned to the materials coming from the accounting department.
• Alphabetic or numbering sequence. For example, the registration of voting ballots of the polling station staff are divided into "alphabet" of the group (from A to B, from B to D, etc.).
• The type of consumer. For example, bank employees are divided, as a rule, those who serve the organization, and those who serve individual investors.
Formation of the working groups on these criteria has a direct impact on the relationship work.
Fig. 6.9 shows how the technological changes associated with the program redesign work, including the delegation of authority and the formation of a working group. These changes ultimately result in changes in the characteristics of the work.



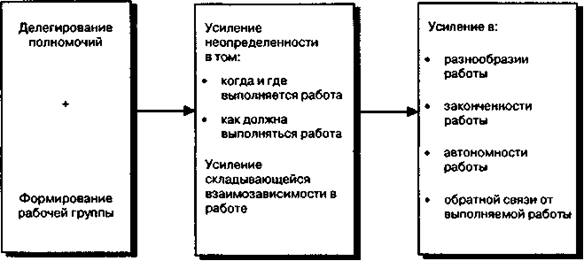
Fig. 6.9. Ожидаемая связь между технологией работы, характеристиками работы и программой ее перепроектирования


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.