home
 Management Management
 Theory and practice of personnel management - Shchekin GV Theory and practice of personnel management - Shchekin GV
|
Theory and practice of personnel management - Shchekin GV
8.1. The subject, tasks and content of personnel management
Personnel management as a scientific and practical direction is an integral part of the general science of production management. To study management means to study the relations between people in the course of a purposeful influence on the production processes, to reveal the laws of the formation of management relations so that on their basis the principles of managerial activity, the forms and methods of its implementation can be established.
The main element of any management system is the frames, which at the same time can be both an object and a subject of management. Employees of the enterprise (organization) act as an object, because they are the productive force, the main component of any production process. Therefore, the planning, formation, redistribution and rational use of human resources in production constitute the main content of personnel management, and from this point of view they are treated analogously to management as material-material elements of production. At the same time, personnel are primarily people characterized by a complex set of individual-typical qualities and properties, among which socio-psychological play a dominant role. The ability of personnel to act simultaneously as an object and subject of management is the main specific feature of personnel management in the workplace.
Proceeding from this, human resources management is understood as the process of planning, selection, preparation, evaluation and continuous education of personnel, aimed at rational use of it, increasing production efficiency and, ultimately, improving the living conditions of workers. The subject of personnel management as a scientific and practical area is the study of the relations of workers in the production process from the point of view of the most complete and effective use of their potential in the conditions of the functioning of production systems. The main purpose of personnel work in modern conditions is to form a new person who has a high responsibility for the task entrusted with modern economic thinking, high qualification, and a developed sense of professional dignity.
Personnel management is a complex system, the elements of which are the main directions, stages, principles, types and forms of personnel work. Let's consider each element separately.
First of all, it is necessary to understand what the content of the concept of "cadres" is. Personnel represent a permanent staff of skilled workers of enterprises, institutions, organizations and are divided into two large groups: management personnel (employees) and workers.
Workers include workers who are directly engaged in the creation of wealth or work to provide various production services and the movement of goods. Workers are conditionally divided into main and auxiliary ones. Their ratio is an important analytical indicator of production efficiency, as the role of the latter increases significantly as automation and mechanization of production processes increase.
Management personnel include employees who perform or contribute to the performance of specific managerial functions. They are divided into three main groups: a) leaders directing, coordinating and stimulating the activities of the participants in production (so-called line managers - factory directors, shop managers, masters, etc.); B) Specialists who provide expert assistance to managers in analyzing and resolving questions of production development (engineers, economists, psychologists) or independently guiding engineering, technical, economic, social and other functional services (so-called functional managers - department heads, chief specialists , Heads of bureaus, groups, sectors, etc.); C) auxiliary workers who provide technical and information services to the management apparatus - collection, primary processing, storage and transfer of information (draftsmen, archivists, clerks, etc.).
In terms of management level, managers are divided into grass-roots leaders (masters, heads of plots, bureaus, groups at the enterprise), secondary (heads of shops and departments, their deputies) and top management (heads of enterprises and associations, their deputies).
Personnel management is carried out in the course of performance of certain purposeful actions and assumes performance of the following basic functions: definition of the purposes and the basic directions of work with the staff, constant perfection of the system of personnel work at the production; Determination of means, forms and methods of achieving the set goals, organization of work on the implementation of decisions taken, coordination and monitoring of the implementation of the planned activities.
The totality of goals, directions, forms and methods of personnel management is a single system of personnel work, the main subsystems of which are:
A) subsystem of analysis, planning and forecasting of personnel. Its main tasks are the formation of objects and management structures, the calculation of the need for personnel in the required professions, specialties and qualifications. In other words, the solution of the tasks of this subsystem should give an answer to the question: "Who is needed and in what quantity?";
B) subsystem of selection, arrangement, evaluation and continuous training of personnel. Its main tasks are to provide quality support for the formed objects and structures of management of the necessary personnel, as well as to organize effective stimulation of their activities;
C) subsystem of rational use of personnel. The solution of the tasks facing this subsystem envisages the implementation of a set of measures to create high-performance stable teams.
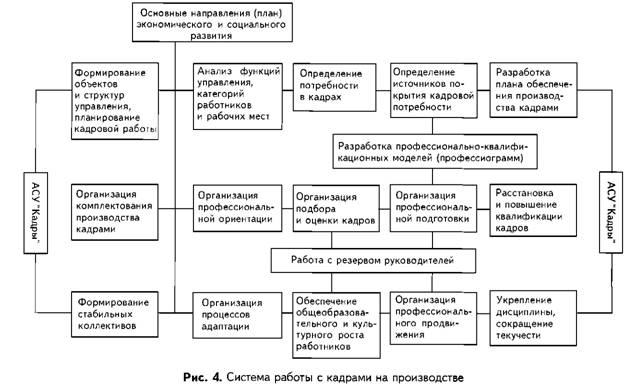
The system of work with personnel in production is shown in Fig. 4.
The complexity and multifacetedness of personnel management presupposes a multiplicity of aspects in the approach to this important problem. There are such aspects of personnel management:
• technical and technological (reflects the level of development of a particular production, the features of the machinery and technology used in it, production conditions, etc.);
• organizational and economic (contains issues related to planning the number and composition of employees, moral and material incentives, use of working time, organization of records management, etc.);
• legal (includes issues of compliance with labor legislation in personnel work);
• socio-psychological (reflects the issues of socio-psychological support for human resources management, the introduction of various sociological and psychological procedures in the practice of personnel work);
• pedagogical (it presupposes the solution of issues related to the training and education of cadres, mentoring, etc.). The basis of the personnel management system is personnel policy, which is a long-term line for the improvement of cadres, a general direction in personnel work, which is determined by the combination of the most important, principled positions and attitudes. The means of implementing the personnel policy is the personnel work , which is subordinated to the solution of the tasks put forward by it in economic activity.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.