home
 Management Management
 The organization of production - AS Kurochkin The organization of production - AS Kurochkin
|
The organization of production - Kurochkin AS
1. GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF INDUSTRIAL ENTERPRISES
1.1 Industrial as a production system
The concept of enterprise, task and its main features
For business activities and achieve its objectives in the presence of physical, biological, psychological, and other restrictions, people are forced to join forces. Such joint efforts, provided a specific organization in most cases, be more productive and requires less power consumption, time and other resources. This "organization effect" - the most valuable asset of humanity.
The organization as a form of joint activity of people has distinctive features. Thus, the basis of any organization is composed of people united in a group (minimum - two people). Groups are created to achieve certain goals. People in groups intentionally work together to achieve a common goal. The activities of people in these groups are coordinated in a certain way.
Thus, the organization - a joint coordinated activity of a group of people to achieve their common goal (s).
This definition is valid only for the formal organization - formally established and fixed structure and functioning of its parts. Such a formal organization, the main objective (s) of which lies in the economic field, is called now. In accordance with the Law of Ukraine "On Enterprises in Ukraine", the company is the primary organizational element of the economy of Ukraine. This is the main primary economic unit in the economic system of the country, which is manufacturing and implementing products and services that achieves its goal tseley.Glavnaya enterprise - to maximize profits in the long run. Note that the profit is not always the main motivating moment of creation and functioning of the enterprise. They may be the desire for public recognition, the possession of a strong position on the market, the preservation of the business started. This will require not to receive short-term profits, TE main goal is not to maximize profits, and maximizing the overall situation, where profit is the only one of the most important komponentovDlya achieve the main goal, the company decides to a large number of tasks, the center of which is a complete and the timely satisfaction of customer needs. In this regard, the company should ensure that:
• the competitiveness of products and services;
• development and improvement of production efficiency;
• acceleration of scientific and technological progress;
• favorable conditions for highly productive labor, and so on. D.
Industrial enterprises are characterized by production-technological, organizational and economic unity and economic independence.
Industrial and technological unity is the close relationship of all components of the business units, which is defined by common purpose products manufactured by them, and the process. The technological relationship is supplemented by auxiliary and service units (farms).
Organizational-economic unity is characterized by:
• uniform government;
• single production team;
• administrative isolation;
• the relationship of the production plan to ensure its implementation material, labor, technical and financial resources;
• organization of activities on the basis of commercial calculation. Note that the above defines the unity of the economic independence of enterprises, which provides:
• self-sufficiency in basic needs and working capital for production activities and the provision of services;
• separate sales of manufactured products;
• availability of a complete self-reporting and balance sheet.
As noted, the main task of Industrial Production Company - output. A variety of businesses
types of products (products) requires classification according to their applicability. This classification is shown in Fig. 1.
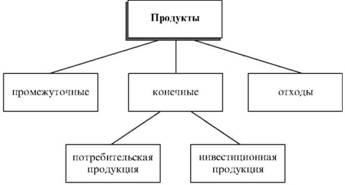
Fig. 1. The integrated product classification
The end product is considered, which is produced by the company and transferred to other economic entities. At the same time it can take the form of both consumer and investment (industrial) goods. Consumer products (eg, ice cream, cigarettes, furniture) is used directly. Investment sake (products), such as machine tools, production lines, are used in order to use them to produce other products. Thus, the application of certain of the final product is the criterion for its classification as a consumer or investment goods. for example, to plant bulbs, are investment products and household - the consumer.
Intermediates in the production of multi-step processes are used in the subsequent production of both factors. Legs for chairs and tables at a furniture factory is an intermediate product. This feature shows them that strictly divide the goods (products) on products and production factors is difficult and decisive for the classification of goods is the place (of products) in the manufacturing process.
Waste - are products that remain in the production of goods (products) or their use and can no longer be used as a consumer or industrial goods (eg, empty matchboxes or cutting tissue in the manufacture of clothing). Waste may again be sent for processing, but it requires a new manufacturing process.
Properties of industrial systems
In a broad sense, the system refers to a certain set of elements forming a unit (composed of parts), which has a new quality, the missing elements in the system.
The company is considered as a production system, because it has all the features characteristic of the system. business units (shops, sites, departments, etc.) are subsystems consisting of elements of varying complexity (employees, items and tools, and so on. d.).
Production systems - a special class of systems, including staff, tools, work items, and other items necessary for the functioning of the system, during which creates products and services.
At the primary level, the production system can be considered as a group of mechanisms (machines, devices, and so on. P.), Served by the employee (operator, driver, and so on. D.). Each mechanism and support its employee represent the system "man - machine", consisting of two interacting and interrelated elements.
More conceptual apparatus of the enterprise as a system, as well as the principles of the organization of production systems are described in [12, 14]. *
If you go along the path of integration of primary systems "man - machine", we arrive at the production site - a complex system consisting of the basic and auxiliary workers, main and auxiliary equipment, with a complex system of interrelations complex relationships and interests, which has a complex structure and organization.
Production systems and higher levels of order are shops, housing and so on. N. In this case, each unit of the system, sub-system at any level reflects the most essential features of the system of higher level (about), to which they belong.
Thus, in the industrial production of a hierarchy of systems interconnected unity and functioning of the enterprise. Next we consider the relatively small system: the workplace, the site shop company.
The characteristic features of functioning of the enterprise as a production system include:
• focus, ie, the ability to develop new products to provide services (such as the systems are designed to meet the specific needs)..;
• Polystructural, ie, the simultaneous existence of the company (as a system) intertwined subsystems (departments, sections, departments, etc...), Where almost every element of the system at the same time is part of several subsystems and functions in accordance with their requirements, goals..;
• openness, manifested in close interaction with the external environment of the enterprise - in material, energy, information, financial and other forms of exchange with the external environment;
• the complexity caused by such a basic element of the system, as migrant and Polystructural, stochastic changes in the state of elements of the system and the impact of the external environment. It is a huge number of elements of the system with multiple and complex, as a rule, alternative connections, a large number of the processes.
The company is a dynamic system able to change, to move from one qualitative state to another, while at the same time due to certain system properties. Here are the main ones:
• effectiveness - the ability to create products or provide services. It provides the organization of the production system;
• reliability - stable functioning, the ability to localize in relatively small parts of the system the negative effects of stochastic disturbances occurring within the system and in the external environment. System reliability is enhanced by limiting the quantities and frequency of stochastic perturbations, as well as due to the increase of intra reserves and provided a control system;
• Flexibility - the ability to adapt production systems to changing environmental conditions, primarily to increase the level of competition, changes in market demand, etc .;
• Manageability - characteristics of the enterprise management process as a system. The system is controllable, if time reaches a predetermined control target and fits in with the resource constraints. unmanageable system if you do not reach the goal; poorly controllable, if it reaches the intended target is not exactly, but approximately, or out-of resource constraints.
Normal (normal) state of the enterprise as a production system - functioning. the production process is carried out in each production system. This process changes the elements of the production system. Some of these elements (material) is consumed, transformed into a work in progress, semi-finished products, and finally, in the finished product, which leaves the system. Other items, such as tools, machines, and gradually wear down as the wear are replaced by new, not always identical. Thus, the production systems are mobile (dynamic) equilibrium - system preserved under continuous change. This feature is provided by the system structure, ie. E. Its organization. Therefore, at any given time the state of the system is not determined initial state (although the latter affects the state in the next time the system), and system parameters. The above properties of production systems determine their inertia: the established structure of the system, including the ratio of the elements and their relationship is maintained as long as it will not change significantly as a result of the accumulation of small internal and external changes or due to purposeful improvement organization.
After considering the characteristics of the enterprise as a production system, we note that all of its elements function in order to output, providing adequate quality of services, the volume and mix. Using the methodology of the system approach, will present the company as a production system having an input, output and feedback (Fig. 2).
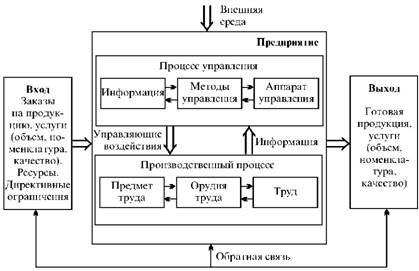
Fig. 2. The enterprise as a production system

Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.