home
 Management Management
 Organization of production - Kurochkin A.S. Organization of production - Kurochkin A.S.
|
Organization of production - Kurochkin A.S.
1.4. Production capacity of the enterprise
The essence of the concept of production capacity
In modern conditions, the program of output of any enterprise is determined on the basis of:
• aggregate demand for the products it produces;
• its production capacity.
The production capacity of the enterprise (shop, site) is potentially the maximum possible annual (quarterly, monthly, daily, shift) volume of output of products, works, services (or extraction, processing of raw materials) of the required quality for given nomenclature and assortment on the basis of progressive norms for the use of equipment And production areas, taking into account the implementation of measures for advanced technology, advanced organization of labor and production.
When planning and analyzing the activities of an enterprise, there are three main types of production capacity: perspective, project and operational.
The prospective production capacity reflects the expected changes in technology and production organization, the nomenclature of the main products laid down in the company's long-term plans.
The projected production capacity is the possible output of a conditional nomenclature output per unit of time specified in the design or reconstruction of an enterprise, shop, or section. This volume is fixed, since it is designed for a constant conditional product nomenclature and a constant mode of operation. However, over time, as a result of the reconstruction and technical re-equipment, the introduction of new advanced machinery and the best practices of organizing labor and production, the initial design capacity will change, but will be fixed as a new design capacity. This is a very important indicator of the organization of production to achieve high performance. This is due to the fact that the project documentation, as a rule, is laid design solutions, the highest at the time of the development of the project.
The existing design capacity of the enterprise, shop, site reflects its potential ability to produce during the calendar period the maximum possible number of products provided for by the plan for the production of marketable products of a given range and quality. It has a dynamic character and changes in accordance with the organizational and technological development of production. Therefore, it is characterized by several indicators:
• capacity at the beginning of the planned period (input);
• capacity at the end of the planned period (output);
• average annual capacity.
The input production capacity of the enterprise (shop, site) is the capacity at the beginning of the planning period, usually at the beginning of the year. The output capacity is the capacity at the end of the planning period, which is defined as the algebraic sum of the input capacity that was in effect at the beginning of the year (as of January 1) and the new capacity introduced during the year and the capacity that was withdrawn in the same year. The average annual production capacity is the capacity available to the enterprise (workshop, site) on average for the year, taking into account the growth and retirement of available capacities.
The production capacity is measured in the same units as the production program (pieces, tonnes, meters, etc.). For example, the capacity of a tractor plant is determined by the number of tractors in pieces, the thickness of a coal mine is the amount of coal in tons. At the enterprise, where the quality of raw materials affects the volume of finished products, its capacity is measured in units of processed raw materials. Thus, the production capacity of the sugar factory is measured in tons of processed beet, the dairy plant - in tons of processed milk.
The production capacity of an enterprise is a variable. It changes with time, that is, it increases or, on the contrary, decreases. Many factors influence the change in production capacity. We list the main of them:
• structure of fixed production assets, specific weight of their active part;
• the level of progressivity of technology in the main production processes (the more advanced the production technology, the greater the production capacity);
• productivity of technological equipment (the more perfect the machines and equipment and the higher their productivity per unit of time, the greater the production capacity);
• level of specialization of the enterprise (increasing the level of specialization contributes to the increase of the production capacity of the enterprise);
• the level of organization of labor and production; This is a very important factor affecting the production capacity, that is, their direct dependence is observed;
• the level of qualification of the personnel of the main production divisions (the dependence is manifested in the fact that the higher the qualification of the employees, the less marriage, breakdowns, equipment downtime and higher its productivity);
• the quality of the objects of labor, i.e., the higher the quality of raw materials, materials and semi-finished products, the less labor and time required to process them, and therefore more products can be produced per unit of equipment operating time.
In addition to these factors, the level of production and labor organization in auxiliary and serviced divisions - instrumental, repair, energy, transport facilities - also has a significant influence on production capacity.
Calculation of production capacity
In conditions of transition to a market economy, it is impossible to organize production without first developing a business plan. One of the sections of such a strategic document is the production plan, which should contain the calculation of the production capacity of the enterprise divisions. Such calculations are an important component of business planning, in particular an industrial production plan. Calculations of production capacity allow objectively:
• plan the volume of output;
• identify possible reserves for the development of production;
• justify the economic feasibility of specialization of production and co-operation of enterprises;
• plan the development of the company's production capacity.
The production capacity of the enterprise is determined by the capacity of the leading shops, and the capacity of the workshop is the capacity of the leading sectors, units, leading groups of equipment. The leading groups include equipment that performs the bulk of the work - in complexity and labor. Under the leaders are understood such shops (plots):
• where most of the main production equipment is concentrated;
• occupying the largest share in the total labor input of manufacturing products.
When choosing the main leading link, it is necessary to take into account the specifics of the industrial enterprise. For example, in the mining industry, the capacity of a mine in an underground method of mining is determined by the possibilities of mine lifting. At metallurgical plants, these are blast furnaces, rolling mills.
The production capacity is calculated on the basis of:
• nomenclature, structure and quantity of products;
• the number of units of available equipment at the disposal of the enterprise;
• operating fund of equipment operating time;
• labor intensity of the products and its planned reduction;
• Progressive technically sound standards for equipment performance;
• reporting data on the implementation of production standards. The production capacity is calculated in series
From the lower link to the highest, ie, from the productivity (capacity) of groups of technically homogeneous equipment to the capacity of the site, from the site's power to the capacity of the shop, from the capacity of the shop to the capacity of the enterprise.
The production capacity of the workshop (section) equipped with the same type of equipment and producing the same products is determined by the formula
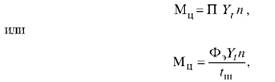
Where P is the normative annual output of one machine (unit); Vt is the average overfulfillment rate; N - average annual park of this type of equipment; Fe is an effective annual
Time fund of one machine (unit); T ш is the time norm for processing (manufacturing) a unit of production, h.
If the workshop (site) is equipped with different types of equipment, the production capacity is determined by the capacity (throughput) of the park of the leading groups of equipment that characterize the profile of this unit.
The production capacity of the enterprise (shop, site) is a dynamic category, changing during the planning period. These changes are caused by such factors:
• Wear and, therefore, write-off and culling of equipment;
• commissioning of new equipment instead of worn out equipment;
• modernization of equipment during the overhaul, which can change its performance;
• reconstruction and technical re-equipment of the whole enterprise or its individual production units, etc.
In order to plan production, it is necessary to monitor and update the actual capacity of the enterprise in a timely manner. This is done with the help of average annual production capacity - outgoing and input.
The annual average production capacity (Ms) is defined as the sum of the retiring production capacity (MF) multiplied by the number of months (ni) remaining from the retirement to the end of a certain year divided by 12:
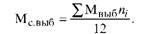
The production capacity of the average annual input (Ms input) is defined as the sum of new capacities (Mn) (in comparable units of natural or monetary expression) multiplied by the number of months of their use by the end of the year (m), divided by 12:
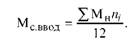
Taking into account the above-mentioned indicators, in addition to the production capacity, at the beginning of the year (input capacity MWh), its year-on-year increase or decrease in the i-th month (Mg-), as well as the output power (Mvh), ie, capacity at the end of the year:
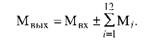
The unevenness of the change in power during the year makes it necessary to determine its annual average:
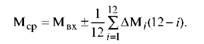
The average annual capacity is found by subtracting the average annual outgoing capacity available at the beginning of the year and adding an average annual capacity increase during the year.
Example. At the beginning of the planned period (year) Мвх = 1000 units. In March, the power output was 50 units, in July - 100 units. In April, capacity was put into operation by 150 units, in August - by 150 units.
Average annual production capacity
Mcg = 1000 + [150 (12 - 4) + 150 (12 - 8) - 50 (12 - 3) - 100 (12 - 7)] / 12 = 1000 + 850/12 "1071 units.
The output capacity of the enterprise at the end of the planned period (year)
Mw = 1000 + 150 + 150 - 50 - 100 = 1150 units. Average annual withdrawn (outgoing) production capacity
Msvyb = (50 • 9 + 100 • 5) / 12 = 950/12 "79 units. Average annual input capacity
Msvvod = (150 • 8 + 150 • 4) / 12 = 1800/12 = 150 units.
As noted, the average annual capacity of the enterprise is used to justify the production plan. The level of its use is determined by the utilization factor of the production capacity (qt), which is calculated by dividing the planned (or actual) volume of the production (works, services) produced by the enterprise (shop, site) or the volume of processed raw materials (VF) for a given year (month) by the average annual planned (Actual) or, respectively, the average monthly production capacity (Msr):
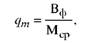
or
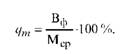
According to the calculations of production capacity, the reporting and planned balances of production capacities are compiled (Table 2).
table 2
BALANCE OF PRODUCTION CAPACITIES
(Conditional example)
| Index | Value |
Production capacity (project) |
1200 |
Production plan |
1050 |
Production capacity at the beginning of the year |
1000 |
Disposal of capacities for the planning period |
150 |
|
Increase of capacities for the planning period Including due to: - modernization of equipment - commissioning of new capacities |
300 200 500 |
Increase or decrease in capacity as a result of changes in the range and range of products |
|
Production capacity at the end of the year |
1150 |
Average annual capacity |
1071 |
Additional power demand |
- |
Coefficient of use of design capacity |
0.87 |
Average annual capacity utilization factor |
0.98 |
When compiling a balance sheet for the reporting year, capacity at the beginning of the reporting year is taken on the basis of the nomenclature and in the assortment of products of the year preceding the reporting year, and the capacity at the end of the year is based on the nomenclature and assortment of products of the reporting year.
When developing the balance for the planned period, the capacity at the beginning of the period is taken by the nomenclature and in the assortment of products of the reporting year, and the capacity at the end of the period (year) is based on the nomenclature and the range of products of the planned period (year).
As practice shows, it is very difficult to calculate the production capacity. The results of calculations often occupy 200300 pages of text, tables, graphs, they need more than 1000 person-hours. The calculated production capacity is one of its variants with a minimum amount of computing and computing work.
As noted, a large number of factors influence the production capacity. In this case, the nature of their influence is different and varies significantly. With regard to specific conditions, it is possible to calculate the n-th number of values of production capacity. The task is reduced to determining the optimum value of production capacity by examining the function for extremality. It is difficult to solve this task by usual methods. Therefore, linear programming methods are used to find the optimal production capacity of the site, shop, and enterprise.
When considering the factors influencing the production capacity, such a feature is revealed in their interrelation: they all determine the fund of working time, machine capacity, labor intensity of production and employment of equipment for the production of a certain quality and a certain type. The principal dependence of the production capacity (MDP) on these factors has the following principal form:
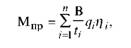
Where n is the number of product types; В - working time fund of the production unit (technological line, aggregate), h; Ti - time spent on manufacturing a unit of production of the i-th type in one cycle, h; Qi is the volume of output of the i-th type produced per unit of time (per one cycle), pieces; Ni is the specific weight of products of the i-th type in the total output of the product (per one cycle).
An analysis of this dependence shows that the production capacity is significantly influenced by the operating time fund of the production equipment, which depends on the operating mode of the enterprise. The concept of the operating mode of the enterprise includes the number of shifts, the length of the working day and the shift.
Depending on the time losses that are taken into account in calculating production capacity and planning, the equipment's operating time schedules are distinguished from the calendar, nominal (mode) and valid (working), or planned.
The calendar fund for operating time of equipment (FC) serves as the basis for calculating other types of fund for the use of equipment and is defined as the product of the number of days in the current calendar period (DK) by the number of hours per day:
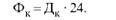
Nominal (regime) fund of equipment operating time
(Fr) depends on the number of calendar days (DK) and the number of non-working days per year (Dn), as well as on the adopted shift work schedule per day:
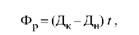
Where t is the average number of hours of operation of the equipment per day on working days according to the adopted shift regime and taking into account the shortening of the shift on public holidays, or
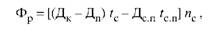
Where Дп - the number of days off and holidays in the planned period; T - duration of the working shift, h; Dsp - the number of pre-holiday (pre-holiday) days with a shorter working shift in the current period; Tсп - the time for which the duration of the working shift for the pre-holiday and pre-holiday days is shorter than on ordinary days (in this industry), h; Nс - the accepted mode of change of work of the enterprise.
In the continuous mode of operation without days off, the number of calendar days and 24 working hours per day is taken into account. The number of working days and the working time fund for equipment operating in seasonal conditions (agriculture, peat extraction) are taken based on the optimal duration of the season of work (in accordance with regulations and technical projects).
For enterprises with a continuous production process, the equipment runtime and production capacity are calculated on the basis of a three-shift (or four-shift) operating mode. If the main workshops of the enterprise work in two shifts (or less than two shifts), the equipment operating time and production capacity are calculated on the basis of a two-shift operating mode, and by unique and expensive equipment - from a three-shift operation mode.
The actual (working, regulatory) fund of the equipment operating time (Fd) is equal to the difference between the regime (nominal) fund in the current period (Fr) and the amount of time spent on repairs, adjustment, readjustment, change of the equipment workplace during the year (0, h:
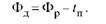
The time for repair, adjustment, adjustment and change of the workplace of the equipment is taken into account only when these operations are performed during working hours.
Показатели эффективности использования производственной мощности
Показатели использования производственной мощности составляют систему показателей, выражающих степень использования производственной мощности. Они позволяют выявить резервы производства и являются показателями его эффективности.
Рассмотрим два показателя, характеризующие производственную мощность (см. табл. 2):
• коэффициент использования среднегодовой мощности предприятия, равный 0,98. Он представляет собой отношение объема планового выпуска продукции (1050 ед.) и среднегодовой производственной мощности (1071 ед.);
• коэффициент использования проектной мощности предприятия, равный 0,87. Он представляет собой отношение фактического объема производственной продукции (1050 ед.) к проектной мощности предприятия (1200 ед.).
Сравнительный анализ приведенных коэффициентов свидетельствует о наличии на предприятии резерва производственной мощности. На первый взгляд, это может свидетельствовать о неудовлетворительной организации производства на предприятии.
Однако необходимо учитывать следующее. В условиях рыночных отношений для быстрого реагирования на изменения потребительского спроса предприятиям необходимо иметь резервную мощность. Это позволяет им на этих резервных производственных мощностях осваивать новые виды продукции. Такой подход дает возможность резко сократить время перехода производства на выпуск новых изделий.


Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.