home
 Management Management
 The organization of production - AS Kurochkin The organization of production - AS Kurochkin
|
The organization of production - AS Kurochkin
2. ORGANIZATION OF THE CORE
2.1. The manufacturing process and its organization in time
The nature and structure of the production process
The production process - a set of interrelated processes of labor and natural processes, which resulted in the original raw materials are converted into finished products.
The main production process is the process, which resulted in the change of shapes, sizes and properties of objects to be treated and labor formed finished products.
The production process at the enterprises (in particular mechanical engineering) involves three stages: the procurement, manufacturing and assembly.
Harvesting stage ensures the production of various preparations: castings, stampings, forgings, etc...
The processing step comprises the mechanical, thermal, chemical and other processing details.
On the stage of the assembly of parts and components assembly units are formed and finished products; their adjusted tested and packaged.
In the production process distinguishes main, auxiliary and service processes.
Under the main refers to the processes that result in changing the shape, dimensions, intrinsic properties of the object of labor, the condition of its surface, the relative positions of its parts. For example, obtaining the preform, its processing, assembling prefabricated components.
Auxiliary processes are not directly affecting the objects of labor, and designed to ensure the normal flow of basic processes (eg, production for own needs of the enterprise tools and equipment, repair of process equipment, and so on. N.).
Operating processes are designed to create the conditions for successful implementation of primary and secondary processes. These include internal and intershop transport operations, supply of materials and blanks for jobs, warehouse operations, and others.
The decisive role in the company play a major production processes, but their normal course impossible without a precise organization of support and service processes.
Each stage of the production process consists of partial processes, characterized by a certain completeness stage of production. Partial processes in turn are divided into process steps (Fig. 6).
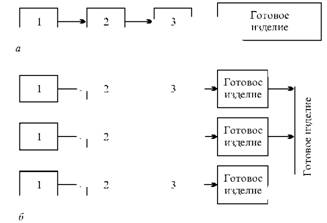
Fig. 6. Types of production processes:
and - simple; B - complex; 1-3 - operation
Operation - a partial manufacturing process performed at one workplace with one or more working on the same subject of labor. Basic (processing) operations are directly changing the geometric shapes, chemical composition, physical and mechanical properties of the objects of labor or parts of the product compounds. Auxiliary operations include transport, control, loading, labeling, commissioning, repair, and others.
By way of impact on the objects of labor operations are divided into hand-held, computer-hand, machine, automatic and hardware.
By the nature of the production processes for the production of the object are distinguished simple and complex (Fig. 6).
Simple production process - a sequence of operations, which result in the product *.
The complex production process involves the connection of several simple processes.
The principles of rational organization of the production process
Practice has developed the rational principles of organization of the production process, the main ones are the specialty, parallelism, proportionality, continuity, direct-flow and rhythm.
Specialization - the division of the production process into components and binding to each production unit (workshop, site, workplace) manufacture certain products (Subject specialization) or perform a certain operation (technological specialization). Specialization allows the use of high-performance equipment and advanced forms of production organization.
Parallelism - simultaneous performance parts (steps, operations) of the production process, ie the implementation of processes to "overlap"... This performance is determined by the duration of the process units, which is less than the duration of the cycle on the size of the "overlapping". The implementation of this principle is connected with a number of conditions, the main of which - sufficient volume of production at which the equipment is provided by full load. If the full parallelism of the manufacturing process to introduce inappropriate (for example, in the case of small batch production), it is possible to organize a partial parallel. *
The word "product" should be understood the item, unit, finished products.
The implementation of this principle makes it possible to significantly reduce the time of manufacturing products (cycle time) and as a result - reduce the need for working capital.
The principle of proportionality requires compliance with performance per unit of time of all the production units - the main, auxiliary and service departments, and within them - sites and lines, groups of equipment and workplaces. Achievement of proportionality based on the rules that determine the quantitative relationship of the elements of production, when the performance of the equipment on all technological operations is proportional to the complexity of processing of products in those operations and provides continuity of the production process, the most complete capacity utilization, eliminates "bottlenecks".
Example. Known initial capacity of jobs for the production of a kit of parts of the four operations (Fig. 7).
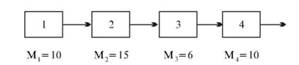
Fig. 7. The production process of manufacturing parts made of four operations
Replacement bandwidth (power) process chain M = 6 parts. Workplace 3 is a "narrow" place. Power workplace 2 is used by 40%, ie, (6 • 100%): 15 and jobs 1 and 4 - 60%, ie, (6 • 100%):.... 10. How to improve the proportionality of the process ?
There are four areas:
• Review design details in order to ensure the proportionality on the complexity of operations;
• revision process, the processing modes;
• Development and implementation of organizational measures for the equipment, the replacement of the redevelopment area;
• additional loading jobs other similar components. Replacement demand for these items - 10 units.
So, in the workplace 3 advisable to put another machine with the same capacity. Then the replacement capacity will reach 12 pieces. On 2 units. (About 80 minutes) is the workplace will need to download another piece. Workplace 2 is necessary to reload by 30%. If there are similar parts to reload jobs 2 and 3, the power line will respect the principle of proportionality. *
The proportionality is determined by the proportionality factor (CRC) formula
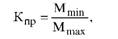
where Mm | n - minimum bandwidth or setting workplace in technological chain (eg, power, discharge papers, the scope of work, etc...); Mmax - the maximum capacity.
Example proportionality assessment process chain in the category of work and workers is given in Table. 3.
Table 3
EXAMPLE Assessment of proportional
| discharge Name | Discharges for jobs |
||||
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
||
discharge papers |
4 |
3 |
3 |
5 |
|
The discharge of the working |
3 |
3 |
4 |
3 |
|
Having analyzed in Table. 3 data, we see that in the workplace 1 digit operating below the required discharge papers on the technology, then the probability of marriage. In the workplace, 3, on the contrary, the discharge of the third worker performs a fourth discharge means there overruns wages as working to pay for his discharge. And in the workplace 4, most responsible, finishing the work of the fifth level worker performs the third category. The savings on salaries fraught with probability of marriage. *
On the proportionality principle to remember when dealing with any issues, as the "squadron rate is determined by the speed of the low speed of the ship."
According to the factual data the proportion of the technological chain at the most "narrow" place of (3 • 100%): 5 = 60%. Hence, it is necessary to develop and implement organizational measures to ensure the conformity of work and working places.
Continuity involves reducing or minimizing interruptions during production. Continuity is one of the most important conditions for the reduction of terms of manufacturing products, increasing production utilization levels, ensure uniform operation of the enterprise and product quality in a given rhythm.
Degree (ratio) continuity (Knepr) determined by the formula

where T is the servant - the duration of the process (the work) of the production cycle; TN - total duration of the process, including delays or prolezhivanie object of labor between jobs, workplaces, etc...
The principle of continuity is fully realized in continuous production at steel mills, chemical industry, food industry, and in engineering - to continuously production lines and automated production.
In-Line - the principle of the rational organization of the process is to provide the shortest path objects of labor in all stages of the production process and operations. It is characterized by the continuous-flow ratio (Kpryam), which is defined by the formula
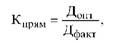
where Dopt - the optimal length of the path of the object of labor, excluding the extra links, returns to its original location; Dfakt - the actual length of the path of the object of labor.
Ramjet requires the exclusion of recurrent movements of objects of labor in the production process, reducing transport routes. This is achieved primarily rational location of production units in the territory of the enterprise, the technological equipment in the shops and on the sites in accordance with the process. The most fully realized when the continuous-flow in-line production.
The principle of rhythm of manufacture involves the release software in regular intervals of the same or equally increasing number of products at all stages and operations. This is an important indicator of the company, its work culture. Spasmodic working of the enterprise is usually performed in the first decade of the lowest percentage of the plan, and the third - sometimes 50% or more. This leads to downtime, the use of workers is not their specialty, an increase in unproductive expenditure. Timely detection, elimination of the causes of irregular - an important reserve of improving the economic activity of the enterprise. Rhythm production is analyzed on the basis of accounting data (monthly and quarterly - in the context of the year; on weekdays, five-day and ten-day periods - in the context of the month and quarter, by the clock - in the context of the day, day).
The organization of the production process in time (the production cycle)
One of the most important requirements for the organization of production, is to provide the lowest duration of manufacturing products, t. E. Production cycle. The production cycle - a calendar period from the start of raw materials to production to complete the manufacture of the finished product. Depending on the nature of the product and other conditions of the production cycle can be measured in minutes, hours, days and so on. D. The production cycle of manufacturing large products such as marine craft, power is measured even years.
The structure of the production cycle is shown in Fig. 8. Consider the content of its individual components.
Work during the manufacture of the product consists of a time process, transport and storage and control operations.
In turn, during manufacturing operations it consists of a set-piece and final time. Set-up time is spent at the beginning of the work shift for the preparation of the workplace, equipment debugging tools,
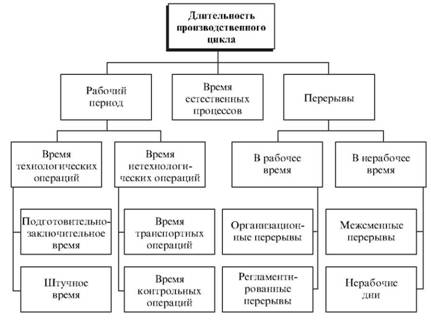
Fig. 8. Structure of the production cycle
installation tools and at the end of the work shift on the removal of appliances, tools and so on. n. This is the time spent on the game being processed during the shift of work items.
Breaks during working hours are divided into institutional (waiting for the release of the workplace, delayed delivery of components and so on. P.) And regulated (lunch breaks, holidays and so on. N.).
Separately allocated time for natural processes - drying of wood, normalization after the heat treatment, and other operations taking place without human intervention.
Enlargement is possible to imagine that the production cycle (Tc) is the duration of work operations (operating period) Tp and Tn breaks (widely known practice time will lie-tion):
T = T + T.
PIU
Conventionally, the production cycle of any product can be represented in Fig. 9.
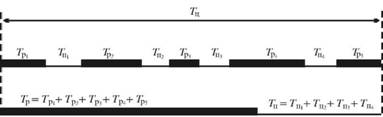
Fig. 9. The production cycle of any product
Thus, it is necessary to consider that the product in the production process can only be in two states: either it is processed, or it prolezhivaet.
It should also be borne in mind that the production process is involved is another element of production - machines (and all that is in it belongs: production facilities, appliances, tools, etc.), Which is in the process can only be in two states: either works or idle. (The third element of the production process - labor - is not considered here.)
The duration of the production cycle is of great economic significance as influences on the rate of turnover of working capital, the rate of output, the use of production space, equipment and other fixed assets.
The main factors reducing the length of the production process are as follows:
• simplification of the kinematic scheme of the product, its design ( "simple design - a measure of the designer of the mind");
• simplification of improvement of technological processes of manufacturing products;
• harmonization and standardization of components of the product, elements of technological processes, equipment, tooling, and production management;
• analysis and adherence to the principles of rational organization of production processes - proportionality, parallel, continuous, direct-flow, rhythm, etc .;
• mechanization and automation of time tracking, control, transport and storage operations;
• Reduction of inter-operational interruptions;
• increase the proportion of technically based norms of the time, service and consumption of resources. Incentives to save time and meet the requirements on quality, etc..


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.