home
 Management Management
 Organization of production - Kurochkin A.S. Organization of production - Kurochkin A.S.
|
Organization of production - Kurochkin A.S.
4.3. Design preparation of production
Stages and composition of work
Experimental design work (ROC) is a complex process, combining the actual design work with experimental research.
The content of ROC is determined by the nature of the development object, its purpose, the way of manufacturing, etc. For this design object, several typical stages of work can be identified, for which a complete list of technical documentation is produced, which is the result of the work of designers. These stages of work are regulated by the Unified System of Design Documentation (ESKD), which operates in all industries. We give their composition and content.
Terms of reference are representatives of the marketing service of the customer and the enterprise. It reflects the tactical and technical requirements of the future product:
• conditions and mode of operation of the goods;
• enlarged basic technical parameters and characteristics, including connecting dimensions;
• the resource (lifetime) of the goods;
• Estimated output;
• safety of product operation and sanitary and hygienic standards;
• patent cleanliness;
• terms and conditions of storage;
• artistic and architectural solution (design);
• Transportability (packaging, packaging), etc.
Requirements of the technical assignment should be guided by the release of new competitive products. The head of the enterprise approves the terms of reference.
The technical proposal (advance design) contains calculations of technical parameters and economic efficiency, which justify the possibility and feasibility of developing a new product. Calculations are performed on several variants of product manufacturing, the optimal variant is analyzed and the optimal economic effect is chosen.
After agreeing with the marketing department, OSG, customer and other services, the technical proposal is approved by the head of the enterprise. The project is the basis for the subsequent stages of the design preparation of production.
The draft design is not performed on a specified scale, but with mandatory observance of all necessary proportions in the dimensions of the product. As a rule, a preliminary design is developed in several versions, product models (plastic, wood, etc.) are manufactured, which are discussed by a specially created commission. The Commission selects one option and approves it for further development, ie, for it drawings (drawings) of the main nodes and general view, kinematic, hydraulic and electrical diagrams are executed, drawings so that the outline design gives a complete picture of the device and the principles of operation New product. After the final approval and approval, the preliminary design is the basis for the development of the technical design.
The technical project is developed in strict accordance with the requirements of the standards. At this stage, various kinds of projection, sections are performed in order to get a complete picture of the device and the operation of the new product. As part of the technical design, drawings of the main units and assemblies are carried out with their calculations for strength, stiffness, stability and other strength characteristics, justifications are made for the selection of materials for the most critical parts. At this stage, instructions for the operation of the product (passport, technical description) and an explanatory note for the technical design are compiled.
Working design documentation is developed only after the approval of the technical design and only on its basis. It includes working drawings of all parts of the product (except for the normals), their necessary projections, views, sections, material, technical manufacturing conditions, etc. Such a set of information allows further development of the technological process of manufacturing parts, depending on the type of production.
On the basis of working drawings of parts in the experimental shop of WGCs, all parts of the product are manufactured; Taking into account custom-made components, units, rubber goods, cable-conductor products, as well as assembly and testing of the prototype.
Specification of the design of individual parts and the adjustment of the overall working project are carried out both during assembly and during testing of the prototype. If necessary, the installation lot of products is manufactured. Based on the results of the tests, a decision is taken to prepare for serial (mass) production of the goods, to refine it, or to stop further work.
Reproduction, storage, accounting of design documentation (originals, floppies, cripples, blueprints (copies) of all drawings) and the issuance of necessary copies to the workshops and departments of enterprises is carried out by a special bureau of technical documentation (BTC) of WGCs or archives. All the multiplied working drawings of the parts are received in the OSG for the development of technological processes and other stages of technological preparation of production.
The stages of the development of the terms of reference and the advance design are often called preparatory. Depending on the complexity of the products being developed, some stages may not be fulfilled (for example, a technical proposal) or be combined (for example, draft and technical projects, technical design, development of working documentation, etc.).
Working out the design of the product for manufacturability
This stage of work is aimed at increasing labor productivity, reducing costs and reducing the time for designing and manufacturing technological equipment.
Under the technological design of the construction is understood a set of features of the design of the product, which are manifested in the possibility of optimizing the costs of labor, materials and time in the technological preparation of production, manufacture and operation, in comparison with the corresponding indicators of the same type of product designs of the same purpose.
To assess the technological design of the product, the indicators characterizing the laboriousness of its manufacture in the norm-hours are determined; Material consumption (metal content) or mass of the product; Cost of manufacturing the product.
In the process of design development, the processability of the product is established by three factors: constructive continuity; Level of standardization and unification of parts; The level of applicability of materials.
The coefficient of constructive continuity (Кк п) determines the degree of use in the new design of parts borrowed from other products already mastered by production:
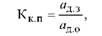
Where adz - the number of parts in a new product, borrowed from other products; Ado - the total number of parts in a new product.
Constructive continuity entails technological continuity, i.e., the possibility of maximizing the use of existing equipment, equipment and materials.
The coefficient of applicability of materials is determined by a similar formula and characterizes the difficulty in providing a new product with the necessary new raw materials, components and materials.
The coefficient of constructive standardization (Kst) shows the degree of application in the new design of standard parts:
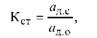
Where ad is the number of standardized parts in the new product.
The total coefficient of standardization and unification (K) for a new product can be estimated from the formula
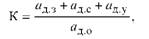
Where a is the number of unified parts in the new product.
Metrological examination of design documentation
Metrological expertise is necessary for the purpose of analyzing and evaluating technical decisions regarding the choice of parameters that are to be measured, establishing standards of accuracy and providing methods and means for measuring the development, manufacturing, testing, operation and repair of products.
As a result of the metrological examination, the documented conformity of the working measurements of the required accuracy must be ensured on the basis of correctly established accuracy standards, and recommendations are given regarding the possibilities of improving the methods and means of measurement and simplifying the control operations.
The main tasks of metrological examination of technical documentation at the working stages of its development are:
• Assessment of compliance with the technology established by standards in the field of metrology and measurement technology;
• Evaluation of the provision by the product design of the ability to control the necessary parameters (suitability of the design for monitoring);
• determination of the expediency of development, manufacture and application of non-standardized measuring instruments in the manufacture, testing, operation and repair of products;
• Establishment of conformity of indicators of accuracy of means and methods of measurement to requirements of optimum modes of technological processes and quality control of products.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.