home
 Management Management
 Organization of production - Kurochkin A.S. Organization of production - Kurochkin A.S.
|
Organization of production - Kurochkin A.S.
Methods of transition to the production of new products
In addition to the factors considered, the duration of the development period is also affected by the form of transition to the production of new products. There are two main forms of transition: with a stop and without stopping production. Each of these forms distinguishes between sequential, parallel and sequential methods.
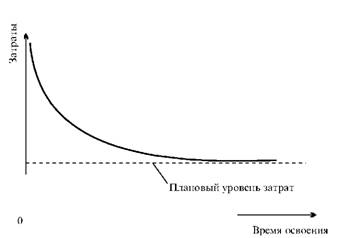
Fig. 28. Schedule of changes in costs at the stage of development of new products
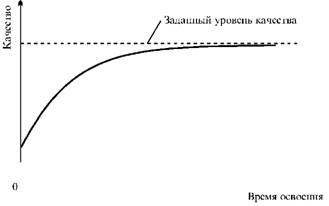
Fig. 29. Schedule of changes in the quality level of new products at the stage of development of new products
The choice of the method of transition essentially depends on such factors:
• technical level of the product being developed, its difference from the product being taken off;
• technological complexity of the new product;
• availability of reserve production facilities and capacities.
A consistent method of transition is characterized by the fact that the production of new products begins after the complete cessation of output, withdrawn from production. There are two variants of this method: interrupted-sequential and continuous-sequential.
In the intermittent-sequential method, after the release of the old product A has ceased, the work on re-planning and installation of the process equipment is first performed on the same production areas and, after their completion, the production of a new product B commences (figure 30, a). The duration of these works determines the time of stoppage of production ^ T, during which neither the old nor the new product is produced. According to economic indicators, this is the least effective variant of the transition, since during the time T the highest losses in the total output of products are observed.
With a continuously-sequential method of transition, the output of the product to be developed begins immediately after the output of the product is discontinued, ie, AT-0 (Fig. 30, b). In this case, there are also losses in the total output of products, but they can be reduced due to a sharp reduction in the period of development.
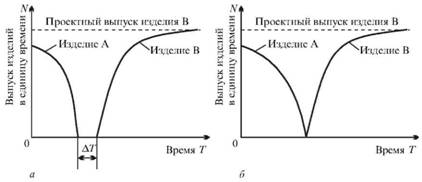
Fig. 30. Consistent method of transition to the release of new products:
A - intermittently-sequential; 6 - continuously-sequential
The parallel method of transition is characterized by the fact that simultaneously with the reduction in the volume of production of old products, the output of a new product increases (Figure 31). This method is most often
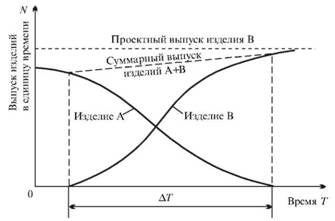
Fig. 31. The parallel method for switching to the production of new products is used in engineering. Its main advantage over the sequential method is that it is possible to significantly reduce the losses in the total output of products during the development of a new product.
A parallel-sequential method for switching to the production of new products assumes that the company has free capacities and production areas. The development of a new product begins on them: technological processes are perfected, qualification training of personnel is carried out, the first lots of new products are organized. In this initial period of development in the areas of the main production, the production of items subject to replacement continues (Figure 32). After the initial period of development is completed, a short-term stop occurs both in the main production and in additional sections (AT), during which the re-planning of the areas of the main production is carried out; Here, too, equipment is transferred from additional sites. After the completion of these works, new production is organized in the main production.
The parallel-sequential method is widely used in mass production with the development of new products, which differ significantly in design from the one being removed, and allows to ensure high rates of increase in the output of new products after a brief stoppage of the main production.
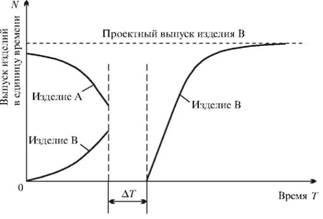
Fig. 32. Parallel-sequential method of transition to new products
Test questions and tasks
1. Objectives of technical preparation for the production of new products for enterprises operating in the market.
2. Stages of design preparation of production and their features.
3. What is the difference between the stages of technological preparation for different types of production?
4. What indicators assess the choice of technology options and how are they calculated?
5. What parameters determine the functional units of the enterprise at the stage of organizational and economic preparation of production?
6. The basic directions of acceleration of technological preparation of manufacture to development of new production.
7. Describe the periods of development of industrial production of new products.
8. Analyze the change in costs at different stages of production preparation and development of new products using a specific example.
9. Advantages and disadvantages of existing methods of transition to production of new types of products. What factors influence the choice of this or that method?


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.