home
 Management Management
 The organization of production - AS Kurochkin The organization of production - AS Kurochkin
|
The organization of production - AS Kurochkin
5.2. System Logistics Production
The functions and structure of the material and technical supply service
Supply of raw materials enterprises, the main and auxiliary materials, fuel and other types of material and technical resources implemented by the Division Logistics (DL).
The functions of the DL include:
• planning needs of the enterprise in the material and technical resources required for the functioning of the primary and secondary industries, as well as for reconstruction and technical re-equipment of the enterprise;
• Operational activities for the implementation of procurement plans - market research vendor market for specific types of resources, contracting, implementation of material resources of contracts with suppliers;
• acceptance, placement, storage, preparation for release and release of inputs shops and services of the enterprise;
• Establishment in conjunction with the planning and economic, technical and financial departments of the enterprise-based differentiated norms of stocks of material and technical resources and to bring these standards to warehouse employees; regulation of the size of stocks and the control of their status;
• participation in the development of organizational and technical measures to save material and technical resources, the replacement of scarce raw materials and less scarce;
• organization of the control over the expenditure of material and technical resources of shops and services for their intended purpose;
• operative account receipts of material and technical resources for the company, they leave the shops and services, status of inventories.
The organizational structure of the department of logistics depends on the type of production, its scope, the range of consumption of raw materials, the degree of co-operation with suppliers and forms of enterprise supply.
For small businesses supply functions are performed by individual employees or a group of production department of the company. In the medium and large enterprises, these functions are performed by departments of logistics.
Institution-building enterprises supplying services is diverse. In each case, it varies depending on the size and type of production, volume and range of consumable materials and products, the level of specialization and cooperation, the availability of transport routes and supply and marketing network of bases in the area of the territorial location of enterprises, and other factors.
Most companies supply service presented the department (management) Logistics. As a rule, it consists of a planned group (bureau); material groups, specialized by types of materials; Dispatching Unit (Office); warehouses material (Fig. 33). Guide service on a medium-sized enterprises entrusted to the director of production, and on the large - Director of Purchasing and Supply (Director for Commerce).
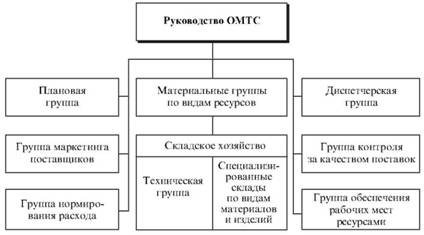
Fig. 33. The organizational structure of the Department of Logistics
In recent years, the practice of the organization of logistics enterprises shows that in the DL includes the following group of marketing specialists resource providers; rationing the consumption of materials; monitoring the quality and quantity of deliveries; providing jobs resources.
Group marketing resource providers
Depending on the size of the enterprise, each such group of experts can be an independent agency or other part of the Bureau (Group) responsible for the specific issue or subject. For example, resource providers Marketing Bureau shared or resource groups (equipment, tooling, raw materials, components) or on the marketing functions (information management, study of suppliers of image, study the competitiveness of suppliers and their products, prices, etc..). It is obvious that the formation of the Bureau of substantive basis required experts owning all marketing functions. In the formation of the Bureau on a functional basis specialists should be well versed in the peculiarities of all types of resources used in the enterprise.
Group of rationing consumption of materials
Bureau (Group) rationing the consumption of materials has the following main functions:
• developing methods to optimize the use of resources in an enterprise;
• develops standards consumption of material and energy resources by major objects of the company;
• develops the material balances.
Norms of consumption of materials used in the company are divided into summary and specified. Summary of the application rates are developed for each product or unit volume work on the aggregated nomenclature of materials and used for the preparation of annual accounts and applications. The specified application rates are developed for each item, the product and the unit volume of work in an expanded range of materials and are used in the calculation of the needs and development of material and technical supply of the enterprise plans, calculating operational departments supply plans and the preparation of materials in the production of release limits.
The most important indicator of the use of material resources is material utilization (Ki m), which is defined by the formula
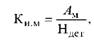
where Am - useful (net) amount of material on the workpiece, kg; Ndet - established material flow rate to the workpiece, kg;
Similarly, use of the material is determined by the ratio of actual expenditure on his part (product). relations planned
(Regulatory) and the actual coefficients indicate the use of materials in the existing reserves of their economic spending.
The higher the ratio the use of materials, t. E., The closer its value is to one, the better the material is used. On increasing the utilization rate is influenced by:
• improving the structure of the materials used, which helps to reduce waste;
• the use of a raw material that is similar in scope and size to produce from his parts and products;
• introduction of progressive technological processes.
Group control over the quality and quantity of deliveries
The quality of the delivered goods shall udovoletvoryat requirements specified in the contract of supply. The audit of the compliance and control group engaged in the quality and quantity of supply.
Methods to ensure the quality of its products are classified as follows:
on acceptance of deliveries of parties:
a) continuous monitoring;
b) sampling:
• acceptance sampling supplies batches by attributes;
• continuous sampling by attributes;
• acceptance sampling by attributes skip-lot;
• acceptance sampling by attributes;
• audit sampling; by acceptance control:
• testing of the installed system supplier and methods to ensure the quality of operations;
• testing provider used methods of control over the quality of purchased goods;
• consideration and determination to improve the quality of the goods of a particular supplier;
• comparative evaluation of the quality of products from different vendors.
Quality control of the goods supplied and the timing of orders is carried out in enterprises regardless of their size and ownership.
Group provide job resources places
Providing material resources of production facilities and other parts of business units involves the following functions:
• establishment of quantitative and qualitative targets for supply - limiting;
• Preparation of material resources to productive use;
• vacation and delivery of material resources to supply the service depots to place direct consumption or warehouse management;
• Operational control of the supply;
• accounting and control of the use of material resources in the production units.
At the enterprise are two fundamentally different ways of production logistics:
• passive - receiving materials from warehouses workshops as necessary;
• active - centralized (advance) delivery of materials from warehouses to shops.
The first way - passive - is applied at the enterprises of individual and small-scale industries and enterprises with frequently changing production program, ie where it is difficult to determine what kind of material and in what time frame will need to shop... In addition, this method is applied in all enterprises for repair and maintenance needs. Issuance of materials is made either by a one-time requirements, or the limit on the map.
The disadvantage of this method of procurement is that the materials are released from the warehouse in small quantities, which makes efficient use of storage mechanisms and improve productivity of warehouse workers, and deliver these materials from the warehouse to the shops consumers on their own, ie. E. Labor and transport funds are used irrationally, increasing the cost of shipping materials.
The second way - active - applied in enterprises with a stable program, thread-mass and high-volume production. At the same time stocks advance prepare materials to be sent to the shop; therefore, better internal transport is loaded. In addition, warehouse, performing schedule delivery of materials, plant leads to the timely acceptance of these materials and thus contributes to the rhythmic manufacturing process. Schedule feed material is transferred to the workshop and the logistics department. On the basis of the schedule is filled up of card supply of materials to the shop for hours.
In active mode supply shops available transport-but-dispatch group supply department or warehouse facilities on a daily basis provides a certain number of vehicles (cars, electric cars, etc.), Which are served by regular workers, stevedores and freight forwarders supply department, engaged in the loading and delivery of materials shops .


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.