home
 Economy Economy
 Business Economics - Pokropivny SF Business Economics - Pokropivny SF
|
Business Economics - Pokropivny SF
Chapter 11. Organization of production
Key concepts and terms
Manufacturing process; technological process; operation; type of production; production cycle; ways of combining operations; a non-threaded products; mass production; production line; the concentration of production; specialization of production; co-operation activities; combining; diversification; conversion
11.1. The structure and principles of the process organizatsiiproizvodstvennogo
The structure of the production process. The production process - a set of interrelated activities of people, means of labor and nature required for the manufacture of products. The main elements of the manufacturing process is the process of labor as a conscious human activities, objects and environments of Labour (Fig. 11.1).
This resource components of the manufacturing process, which requires a certain expenditure. In addition, many industries use natural processes (biological, chemical processes in the agricultural and agro-industrial production, drying, cooling components after heat treatment, etc.). Natural processes takes time, and the resources are consumed only in case of artificial intensification of these processes.
The main component of the production process is a process - a set of actions to change the status and definition of the objects of labor. The enterprises implemented a variety of manufacturing processes. They are divided on several grounds: the destination, the time course of degree of automation (Table 11.1.).
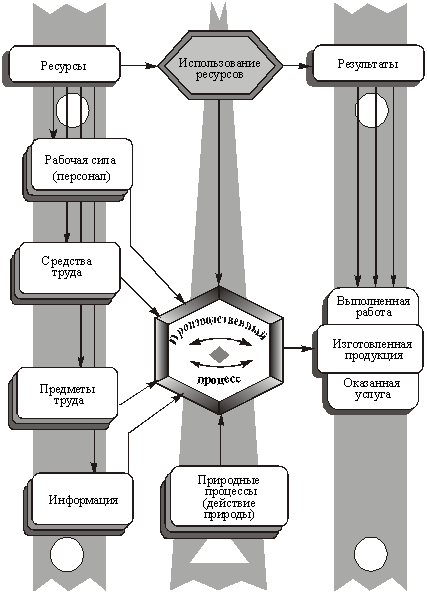
Fig. 11.1. The elements (resources) and process rezultatyproizvodstvennogo
Table 11.1
CLASSIFICATION PROIZVODSTVENNYHPROTSESSOV by separate characters
| Classification sign | Types proizvodstvennyhprotsessov |
The essential characteristic of |
|
|
Processes of direct manufacturing of production. In many industries release stage: the procurement, manufacturing and assembly |
|
manufacturing processes in the production plant needed for the normal exercise of the fundamental processes. By supporting the work of repair are usually related, instrumental, power farms |
|
|
They provide normal conditions for the implementation of primary and secondary processes. These include storage and transportation processes |
|
|
|
They are characterized by cycles associated with the production of a certain type of product piece (machines, appliances, clothing, footwear) |
|
The processes of production, which has no specific sustainable volume and form (liquid, bulk, gaseous substances) and therefore does not require cycling |
|
|
|
Carried out directly by the worker, the physical effort which are the main source of energy |
|
Processes performed by the employee using machines |
|
|
Processes performed by the employee using machines |
|
|
Exercise machine without the employee's pre-designed program |
By appointment manufacturing processes are divided into main, auxiliary and service. The main processes - is the process of direct production of the main products of the enterprise, which defines its production profile, specialization and is marketed as a commodity for sale.
The main processes are divided into stages: the procurement, processing, manufacturer (assembly). Together they form the main production. Auxiliary processes include manufacturing of products used at the plant to ensure the normal flow of basic processes. They are grouped according to their purpose, forming such subsidiary production as repair, tool, energy and others. Operating processes provide normal conditions for the implementation of the main and auxiliary works. These include warehousing, transportation processes, and so on. N.
By the time the flow of manufacturing processes are divided into discrete (discontinuous) and continuous. Discrete processes inherent cyclicality associated with the manufacture of certain types of products, which are calculated in units (machines, appliances, clothing and under.). Continuous processes are inherent in the production of products not having established the amount and form (bulk, liquid, gaseous). Therefore, their occurrence does not require a cyclical process.
According to the degree of automation distinguish manual, mechanized, automated and automatic processes. Manual processes are carried out directly with the employee (workers, employees, professional), physical strength which is the main source of energy. Mechanized worker processes run with the help of machines. The employee controls the machines, and directly performs only auxiliary operations. Automated processes are carried out under the supervision of staff cars. Over the last may be some auxiliary operations. Automatic processes are carried out without the participation of the employee cars and to the developed program.
The basic structural unit of the production process is an operation that is finished its part of the process, which is performed at one workplace, on the subject of the most labor without changeover. Among all the technological operations specifically isolated, the totality of which constitutes the technological process.
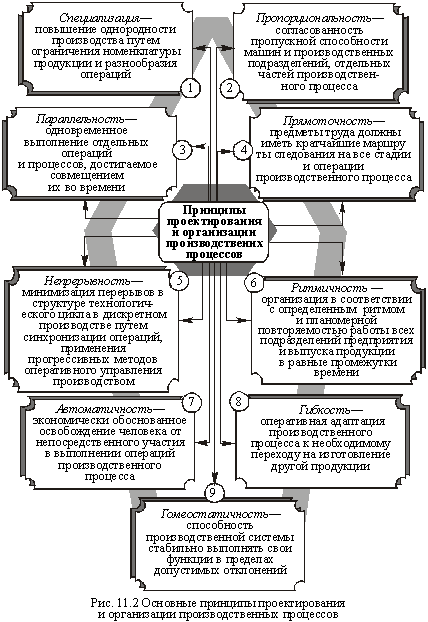
Principles of organization of the production process. The manufacturing process and its individual operations must be rationally organized in time and space. To do this, the design of new products need to adhere to certain principles. The main ones are listed in Fig. 11.2.
- The principle of specialization means limiting the diversity of the elements of the production process, in particular a decrease in the range of products manufactured in each area of the company, as well as different types of production operations carried out in the workplace.
By increasing the uniformity of production, specialization of simplifying its organization and creates preconditions for its automation, resulting in better use of resources of the enterprise, improved product quality, reduced costs.
The level of expertise in-plant depends essentially on the structural, technological and organizational unification. Unification - is bringing the product, its production methods or elements to form a single system. Unification can reduce the range of parts and components, it is reasonable to limit the variety of production methods, types and brands of equipment, m arshruty intrashop (mezhtsevyh) displacement of parts, and so on. N.
Compliance with the principle of specialization significantly affect the implementation of other principles of rational organization of the production process.
The principle of proportionality requires the coordination capacity of all parts of the production process, the entire interconnected system units and machines. Proportionality is reached when the cumulative performance of technologically related units of production is proportional to the volume of work performed. This corresponds to the condition
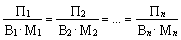 (11.1)
(11.1)
where P, V, M - in each unit, respectively the amount of work, the performance of the workplace, the number of jobs;
n - number of technologically interconnected units.
Violation of this principle leads to the emergence of "bottlenecks" or incomplete download individual units. In enterprises with complex structures difficult to reach full production capacity of the proportionality of individual units (brigades, sites, shops, production). She periodically violated by the development of new products, reduce their unequal rates of labor input in different units, etc. The emergence of imbalances -.. A natural result of the development of production and operation in a dynamic environment. However, they need to anticipate and minimize planned.
- The principle of parallelism provides simultaneous execution of certain operations and processes. Compliance with this principle is particularly important in the manufacture of complex products, compiled from many parts, components, assemblies, serial production of which would require an excessively long operating time. Parallelism is achieved by rational dissection of products into its constituent parts, combining the execution time of various operations, simultaneous manufacturing of different parts. Parallel execution of works in the workplace is provided mnogoinstrumentalnoy workpieces, combining time to perform basic and auxiliary operations.
- once-through principle means that the objects of labor in the processing should move the shortest way at all stages and operations of the production process (without counter and reverse motion). To comply with this principle, shops, stations, jobs (as far as possible) are placed on the downstream side. Supporting the production, service, storage, in turn, arrange as close as possible to the units they serve.
- The principle of continuity requires that the intervals between adjacent technological operations have been minimal or completely absent. To the greatest extent this principle is implemented in continuous production - chemical, metallurgical, power, etc. In discrete manufacturing, where the process has a wide differentiation of fully interoperable eliminate interruptions can not be both technical and organizational reasons.. Under such conditions, an important task is to minimize interruptions in the production cycle time by synchronizing operations structure, the use of advanced methods of operations management. The continuity of the production process need to complement the continuous operation of equipment and workers.
- rhythm principle consists in that the work of all departments and the output should be carried out on a certain rhythm, repeating systematically. In realizing this principle in the same time intervals produced an increasingly uniform or equal, the number of products, providing the same uniform loading jobs. Rhythmic work can make full use of the production capacity of the company and its divisions.
- The principle of automaticity economically justified liberation of man from direct involvement in the implementation of production operations. Particularly relevant is the implementation of this principle in industries with heavy and harmful working conditions. Automate not only production processes, but also other spheres of human activity including management.
- Principle of flexibility means that the production process must quickly adapt to changing organizational and technical conditions relating to the transition to the production of other products or modification of products. The flexibility of the production process makes it possible to develop new products quickly and cost-effectively. The value of the principle of flexibility, especially increases in accelerating scientific and technological progress as the production facilities are often changed.
Flexible manufacturing can quickly adapt to changing market conjuncture, which increases its competitiveness. The flexibility of the manufacturing process is achieved universalization tools, automation equipment and processing methods, the introduction of CNC machine tools, flexible manufacturing systems.
- homeostasis principle consists in the fact that the production system has been able to consistently carry out its functions within the tolerance and counter the influence of dysfunctional. This is achieved by providing technical and organizational mechanisms of self-regulation and stabilization. By organizational stabilization systems belong to the system of operational planning and production control, preventive maintenance of equipment, safety stock, and so on. N.
The principles of rational organization of the production process are closely linked and complement each other to varying degrees are implemented in practice. When designing the production process, its organization, it is necessary to take into account these principles, but the optimal organizational and technical solutions chosen by the criterion of economic efficiency.


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.