home
 Economy Economy
 Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF
|
Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF
14.5 Standardization and certification of products (services)
Modern business conditions force each enterprise to introduce an effective control mechanism for managing product quality and strictly adhere to its requirements. The defining elements of this specific management, which have the most significant impact on the process of constant provision of production and supply of the market with competitive products, are standardization and certification of products.
Standardization of products
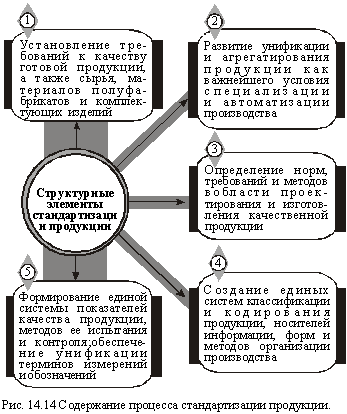
By standardization is understood the establishment of uniform rules with the aim of streamlining activities in a particular industry. As applied to the product, standardization covers several structural elements (Figure 14.14).
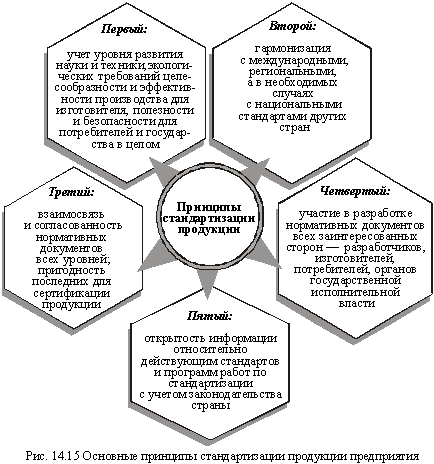
Certain principles must be observed in the standardization process. Among the latter, the main ones are those listed in Fig. 14.15.
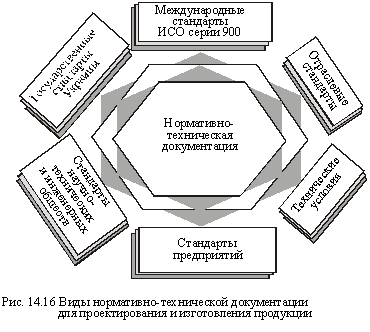
The results of standardization are reflected in the special normative and technical documentation. Its main types are standards and technical conditions - documents that contain quality standards and methods for achieving them (a set of quality indicators, the level of each of them, methods and means of measurement, testing, labeling, packaging, transportation and storage of products) that are mandatory for producers. Normally, technical documentation used at enterprises covers certain categories of standards that differ in the degree of rigidity of the requirements for products and the multiplicity of standardization objects (Figure 14.16).
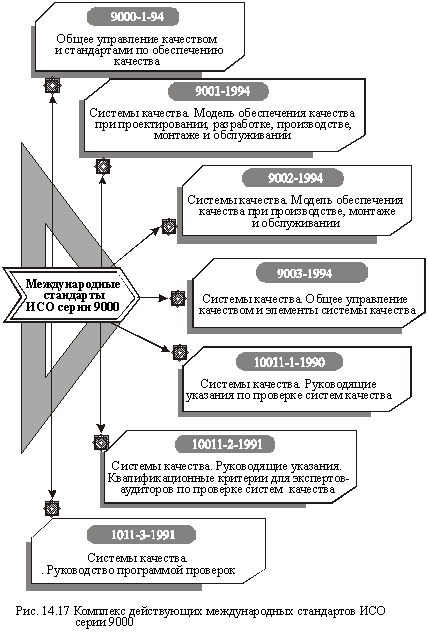
The most stringent requirements to the quality of products are the international standards developed by the International Organization for Standardization - ISO they use for certification of products for export to other countries and sales on the world market. Currently, ISO 9000 standards exist and are being applied. A list of these standards is shown in Fig. 14.17.
State standards of Ukraine are established on:
- Products for general industrial applications (bearings, tools, fasteners, etc.);
- Inter-industry products;
- Products for the population and the national economy;
- Organizational-methodical and general technical objects (scientific and technical terminology, classification and coding of technical, economic and social information, information technologies, technological documentation, organization of works on standardization and metrology, reference data on the properties of materials and substances);
- Elements of national economic objects of state significance (transport, communications, energy systems, defense, the surrounding environment, the banking and financial system, etc.);
- Test methods.
They contain mandatory and recommendatory requirements. Mandatory requirements include those that guarantee the safety of products for life, health and property of citizens, its compatibility, interchangeability, protection. All other requirements are of an advisory nature.
Industry standards develop products for which there are no national standards of Ukraine or concerning which it is required to supplement and increase the requirements of existing state standards. The standards of scientific and technical and engineering societies are developed in the case of the need to disseminate the results of fundamental and applied research obtained in certain branches of knowledge or spheres of professional interests. This category of normative documents can be used on the basis of voluntary consent of relevant stakeholders.
Technical conditions (TU) contain requirements regulating the relationship between the supplier (developer, producer) and the consumer (customer) of the products. They are called upon to regulate norms and requirements for products for which there are no state or industry standards. The specifications are developed on the order of a separate enterprise, as well as for products first mastered by production.
The company's standards are singled out as a separate category conditionally (without a legal basis). Their enterprises create on their own initiative to specify the requirements for products and production itself. The objects of standardization at the enterprises may be individual parts, units, assembly units, equipment and tools of own production, certain standards in the sphere of designing and manufacturing products, organization and management of production, etc. Such standards are also used to create an internal quality management system and Products.
Standards and specifications are documents of a dynamic nature. They need to be periodically reviewed and refined taking into account the innovative processes and new requirements of consumers for the designed and manufactured products.
Modern directions of improving standardization consist in the development of state and international standards not for each specific product, but for a group of homogeneous products, and for a limited number of (the most significant) indicators. This makes it possible to significantly reduce the number of existing standards, simplify their content and reduce the cost of the entire standardization process.
Certification of products and quality systems
When an enterprise conducts an active foreign economic activity, the certification of products becomes the most important element of production management in general and the quality management system in particular . Each type of goods that the company wants to sell on the world market should be certified, ie, have a document certifying a high level of its quality, compliance with the requirements of international standards ISO series 9000. The experience of foreign commercial activity acquired by our enterprises testifies that the so-called Non-certified products are estimated to be 3-4 times cheaper in the world market, therefore, it is actually sold for a pittance.
In Ukraine, as in many other countries, they produce mandatory and voluntary certification . Mandatory certification is carried out exclusively within the state management system of business entities, covers the inspection and testing of products in order to determine its characteristics (indicators) and further technical supervision of certified products. Voluntary certification is carried out on the initiative of the business entities themselves (on a contractual basis).
Business entities (producers, suppliers, contractors and sellers of products subject to mandatory certification) must:
- In the established manner and within a specified period, to carry out certification of the relevant facilities;
- To ensure the production of products, observing the requirements of the normative document, according to which it is certified;
- To sell products only if there is a certificate;
- Terminate the sale of certified products if it is found to be inconsistent with the requirements of a certain regulatory document or the certificate has expired.
The organizational basis for certification of products produced by the enterprise is the network of state testing centers (GIC) for the most important types of products for production, technical and cultural use. A wide network of such centers has been established in many industrialized countries. In recent years, international certification systems have also been formed. Activities to establish such systems are coordinated by a special certification committee - CERTICO , which is part of ISO.
This committee developed:
- Rules and procedure for certification of products;
- The criteria for accreditation of testing centers (laboratories);
- Conditions for entry into the international certification system (the availability of regulatory and technical documentation containing requirements for certification products, a high level of metrological support for production, the functioning of a special system for supervision of the activities of testing centers and product quality).
Several countries already have accredited testing centers in CERTICO and recognized by the world community, which issue certificates for certain types of products. In particular, in the US there are centers for testing tractors and agricultural machinery, in France - cars, Czechia and Slovakia - electrical equipment and medical equipment.
In early 1993, Ukraine became a member of ISO and the International Electrotechnical Commission - IES. This gives it the right, along with 90 other countries of the world, to participate in the activities of more than 1000 international working bodies of technical committees for standardization and certification and use more than 12 thousand international standards.
To obtain the greatest possible success and create an image of a reliable partner in the external market, it is desirable for enterprises to create and certify their own quality systems . In accordance with the international standard ISO 8402 "Quality. Vocabulary "A quality system is a set of organizational structure, responsibilities, procedures, processes and resources that ensure the overall management of the quality of manufactured and produced products. The corresponding level of such a system is guaranteed by a certificate that is issued for a certain period of time - one year, two years, etc. The national certification body has the right to issue a certificate for a quality system; If necessary, he is given the opportunity to delegate such a function to another organization accredited for this purpose.
To evaluate the quality system and obtain a certificate, it is allowed to involve any foreign firm that is engaged in certification. The "weight" of the certificate and the level of trust in it depend on the image of the organization that issued the document.
At the enterprises of Ukraine, such quality systems still need to be created. They must necessarily provide for integrated quality management, which requires teamwork and joint efforts. In this regard, we can identify the main principles of the formation of a quality system.
- Preparation of all categories of personnel of the highest professional level in all categories; (People, not machines, provide the necessary quality);
- Immediate interest of the first manager and the entire management of the enterprise in a permanent positive solution to the problems of ensuring the quality of products; Subordination of the organizational structure of the system to the main goals and objectives of the enterprise (for example, the combination of the posts of the deputy director of the enterprise on quality issues and the head of the technical control department is in practice not practical, since technical control is not the most important in the system);
- Management of product quality with the participation of all employees without exception; The current distribution of responsibilities between departments to their managers; Involvement of workers and daily work in this direction through circles of quality (based on the experience of Japan, the United States), etc.
Very important and extremely necessary is also the active support by the state of the initiative and efforts of the enterprise and organization in the development, implementation and certification of quality systems of products, their entry into the world market.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.