home
 Economy Economy
 Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF
|
Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF
16.5. Prices for products (services): essential characteristics, types, methods of establishment and regulation
General characteristics of prices, types of prices
In market conditions of management, the key factor that actively influences the development of social production and the standard of living of the population is price, that is, the monetary expression of the value of the commodity (products, services). It always fluctuates around the price of production (converted form of the value of a unit of commodity, equal to the sum of production costs and average profit) and reflects the level of socially necessary labor costs.
The prices applied in a market economy carry out three main functions: metering, measuring, distributing and stimulating .
- Accounting and measurement function of the price is that it acts as a means of recording and measuring the costs of social labor for the production of certain types of products or for the provision of a variety of services.
- The distribution function consists in the fact that with the help of prices deviating from value, a redistribution of a part of the incomes of primary economic entities and the population is carried out.
- The stimulating function of the price is used to motivate the increase in the efficiency of management, ensure the necessary profitability (profitability) for each normally operating producer, intermediary and direct seller of goods for production and consumer purposes.
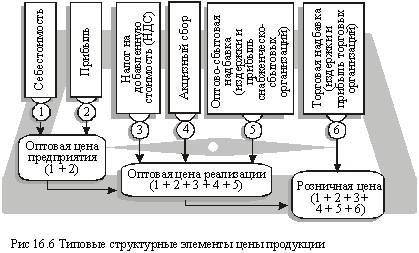
The price of a unit of output (a separate service) is formed from the corresponding components characterizing the structure of certain types of prices, which are used by various economic entities. Typical price structures are shown in Fig. 16.6.
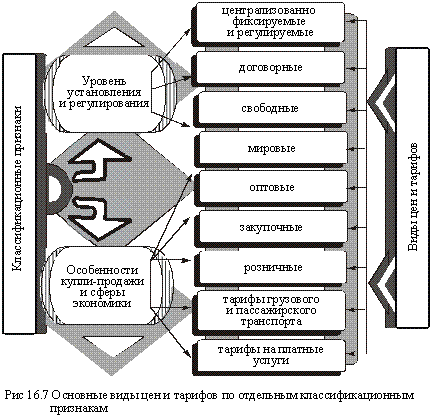
In the management system, many types of prices are used, allocated according to different classification characteristics or without such characteristics. The main types of prices and tariffs, which are grouped according to different classification characteristics, are shown in Fig. 16.7.
According to the classification criterion "The level of establishment and regulation" distinguish between centrally fixed , contractual and free prices.
- Centrally fixed prices are set by the state: on resources that affect the overall level and dynamics of prices; For goods and services of decisive social importance; On products, the production of which is concentrated in enterprises (in organizations) that occupy a monopoly position in the market.
- The level of contractual prices is formed on the basis of an agreement between the producer (seller) and the consumer (buyer) and relates to a particular consignment of goods.
- Free prices are the prices determined by the enterprise (organization) independently. However, the state has a certain effect on contractual and free prices, pursuing an antimonopoly policy, regulating taxation and lending terms for certain groups of business entities.
Depending on the specifics of the process of buying and selling and the sphere of the economy, there are world, wholesale, procurement and retail prices, as well as tariffs for the transportation of goods and passengers, the provision of a variety of paid services.
- World prices are a monetary expression of the international value of goods sold on the world market. They are determined: for some goods - the level of prices of the exporting country; For others - by the prices of exchanges and auctions; For many products - the prices of the world's leading firms.
- Wholesale (holiday) prices for products of industrial and technical use and consumer goods are established on the basis of: actual costs of production (ie, cost) of products; Profits of the enterprise (organization); Value of the value-added tax (VAT); The amount of excise (for goods subject to excise duty); The amount of the license fee (for alcohol products).
- Procurement prices are used by supply and marketing, procuring organizations, wholesale intermediary forms, wholesale trade enterprises (organizations) and other legal entities that carry out trading activities in accordance with their charter. They include the wholesale (selling) price of the manufacturer, VAT, excise and license fees, the costs of these enterprises (organizations) for the purchase, storage, transportation and sale, as well as the profits necessary for normal operations.
- Retail prices are determined independently by trading enterprises, catering enterprises and other legal entities that sell goods or provide services to the population, in accordance with market conditions, the quality of goods (services) and the level of wholesale prices.
- A separate group of prices is made up of various tariffs . Tariffs of freight and passenger transport - a fee for the transport of goods and passengers, which is collected by transport enterprises from shippers and the public. Tariffs for paid services characterize the amount of payment for services in the sphere of consumer services, banks and communications, legal services, etc.
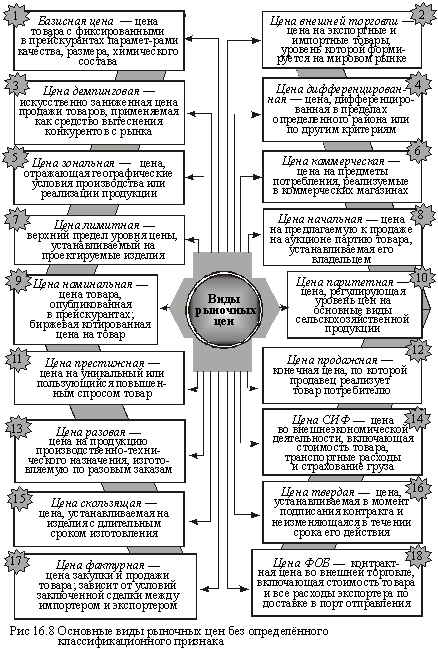
In the modern practice of management, market prices are also applied, which are allocated without a specific classification criterion. The main ones (with a brief intrinsic characteristic) are shown in Fig. 16.8.
Modern pricing provides a system of price franking . Franco (ital.franko, lit. - free) is the type of a foreign trade purchase agreement where the price of the goods includes the costs of its insurance and delivery to the place specified in the contract.
It is customary to distinguish between the prices of the "free station of departure" and "the French station of destination". In the conditions of setting the wholesale price of the "franco-dispatch station", the cost of delivering the products from the departure station to the place of consumption is borne by the buyer of the goods; So the shipping costs the seller does not include in the price. The wholesale price of the "franco-destination station" includes the transportation costs that are reimbursed by the wholesale supply organization or the product manufacturers.
General Specific Pricing Factors
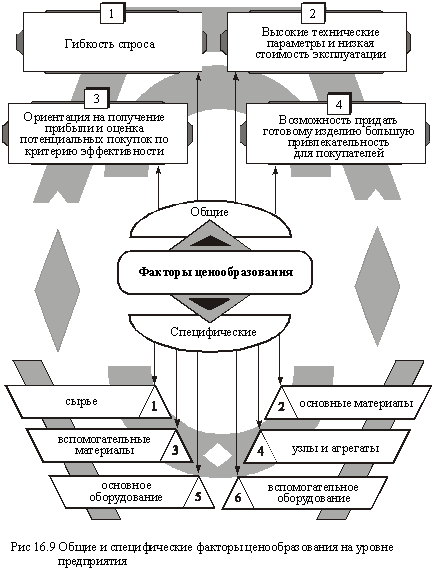
The whole set of factors that somehow affect the pricing process for diversified products (services) is divided into two groups: general and specific (Figure 16.9).
Common factors determining prices for goods are the following:
Elasticity of demand, which affects the price level directly - with the growth of prices, the demand for a certain product decreases and vice versa; High technical parameters and low operating costs; Level of after-sales service. It is clear that affordable prices, consistent with the quality of the product, will always be attractive to potential buyers.
Objectively, there are specific pricing factors for the main types of production and technical products.
- Raw materials, as is known, are subjected to only such treatment that facilitates its use or transportation. Prices for it are set taking into account the requirements of standards and volume, demand and supply. It is the availability of approved standards that is the main factor in pricing for basic materials. The establishment of prices for ancillary materials that perform almost the same functions and, therefore, have a stable demand, are based on the level of demand, quality indicators and volumes of production.
- In connection with the desire of buyers to limit the number of suppliers of prices for units and units as much as possible, they are installed (all other things being equal) taking into account the image of the company's products on the market and with the aim of stimulating the sale of own goods at a bargain price.
- Prices for the main equipment takes into account its versatility or vice versa - specialization. The higher the specialization of equipment, the stricter the requirements for both operational parameters and price. The price of a piece of ancillary equipment is usually lower than the base one. Moreover, provided that the volume of production and sales of such equipment increases, it becomes possible to further reduce the price.
Methods of pricing for products (services)
In the market conditions of managing various methods of pricing can be applied. The main ones are shown in Fig. 16.10.
- The calculation of the price for the "average costs plus profits" method is the simplest and most widely used. In accordance with it, the price (C) is determined by the formula
(16.19) We have the following result:
Where С 3 - average costs (cost price);
P - the amount of profit in the price, which is set by the enterprise (organization) or limits the state as the marginal level of profitability of products (services).
- The calculation of the price based on the target (fixed) profit is considered a variant of the method of calculating the price on the basis of average costs (cost price). Its peculiarity lies in the fact that the price is strictly dependent on the total amount of profit that the enterprise expects to receive from the sale of a certain quantity of products. Under the condition of linear dynamics of dependent values, the price is established using formula
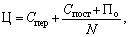 (16.20)
(16.20)
Where С per - variable costs per unit of output (service);
With the post. - constant costs for this product (service) for a certain period (quarter, year).
By - the total amount of profit that can be obtained from the sale of products (services) for the same period;
N - the volume of sales of products (sales of services) in physical terms.
- The price setting on the basis of the subjective value of the goods is carried out taking into account the potential (actually identified) demand for this product on the market.
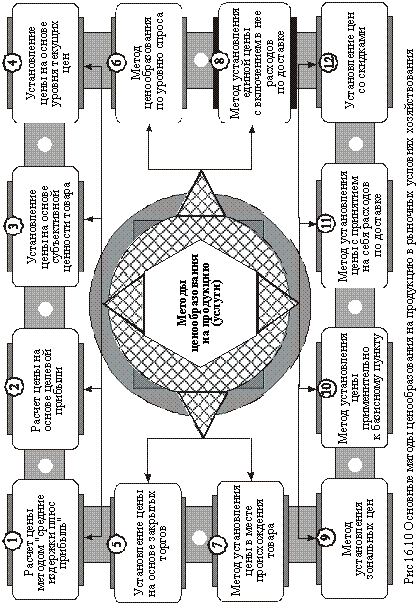
- The pricing method " according to the level of current prices" ("on the level of competition") is that the price is considered as a function of prices for similar products of competitors. Depending on the characteristics of the product and the type of market (monopoly, oligopoly), this pricing method has various modifications (setting prices primarily at or below the current market price, setting prices for a specific product, taking into account prices for similar products of competitors and the ratio of the parameters of these products ).
- Pricing based on closed bidding is a variation of the "current price level" method and is used to obtain an order for the production of certain products (bargaining for a lucrative contract).
- The pricing method "by the level of demand" provides for the establishment of prices through the trial sale of goods in various segments of the market. This takes into account the terms of sale, market conditions, related services; The consequence of this in different market segments for the same goods prices can be different.
- The method of establishing prices in the place of origin is reduced to the fact that the goods are transferred by the transport organization on the terms of the franco-car. After that, all rights to the goods and responsibility for it pass to the recipient (the customer).
- The method of establishing a single price with the inclusion of delivery costs means the relevant action of the enterprise (organization) to include the same amount of transportation costs in the price, regardless of the remoteness of the buyer (customer).
- The application of the method of establishing zonal prices is that an enterprise (firm) allocates several zones, within which uniform prices are established depending on the level of transport costs.
- The method of setting prices for a basis item is characterized by the fact that the seller (firm) chooses a specific region (city, region) as the base and charges all customers (customers) transportation costs in an amount equal to the cost of delivery to the area (city, region) From where the goods are actually shipped.
- The method of establishing prices with incurring delivery costs means that the enterprise (organization) incurs, in part or in full, the actual costs of delivery in order to stimulate the receipt of orders from customers (customers).
- When establishing a discount price, the seller establishes a certain discount from the initial price, taking into account the advance payment of bills, the order of a large batch of products or off-season purchases of it, etc. This allows the seller enterprise to maintain a more stable level of production during the year.
The choice of the pricing method and the establishment in accordance with it of a certain price level is the initial stage in the development of the pricing strategy and tactics of the enterprise (organization). In the future, the price is constantly adjusted, being a mechanism for flexible response to the changing market conditions and improving the strategy of the enterprise (organization).
Questions for self-study in depth
- Methodological aspects of determining the composition of costs included in the cost price.
- Dependence of total costs and unit cost of production on production volume.
- The method of express analysis on the system "costs - volume of production - profit".
- Localization of costs by their origin and responsibility centers.
- Methods of drawing up estimates of production, depending on the stage of planning and the size of the enterprise.
- The factoring of the cost of production and the scope of its application in market conditions.
- Improvement of the composition of cost items for the calculation of the cost of certain products in industry.
- The direction of improving the distribution of indirect costs in the calculation process.
- Forecasting the cost price of new products at the stages of their development and production development.
- The price as an economic and financial lever of management of production (activity) in market conditions of management.
- Objectivity of application of various kinds of the prices (tariffs) on production (services) in a modern system of managing.
- Possible methods of pricing in a market economy. Rationale and choice of methods for establishing prices for products (services).


Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.