home
 Economy Economy
 Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF
|
Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF
Chapter 17. Financial and economic results and efficiency of activities
Key concepts and terms
Financial activities; Financing activities; Financial planning; profit; gross profit; Operating profit; Marginal profit; net profit; Financial value of the firm; solvency; Efficiency of production (activity); Social effectiveness; Animated effect; Performance indicators; Factors of efficiency growth .
17.1. Contents and forms of financial activity of the enterprise (organization)
Characteristics of financial activities
The operation of the enterprise is accompanied by a continuous circulation of funds, carried out in the form of resource costs and income generation, their distribution and use. At the same time, sources of funds, directions and forms of financing are determined, the structure of capital is optimized, settlements are made with suppliers of material and technical resources, receivers of goods, state bodies (payment of taxes), personnel of the enterprise, etc. All these monetary relations constitute the content of the financial activity of the enterprise . It is in providing financing that the main essence of financial activity is.
The main tasks of financial activity of any business are:
- The choice of the optimal forms of financing, the structure of the capital of the enterprise and the directions of its use with a view to ensuring consistently high profitability;
- With the balance in time of receipts and expenditures of payment means;
- Maintaining proper liquidity and timeliness of settlements.
In accordance with its sources, the financing of enterprises is internal and external . Internal financing is carried out at the expense of funds received from the activities of the enterprise itself: profit, depreciation, revenue from the sale or lease of property. External financing uses funds not related to the enterprise: contributions of owners to the authorized capital (directly and in the form of purchased or shares), credit, debtors' obligations, government subsidies, etc.
It is also necessary to distinguish between financing from own and attracted funds. The attracted funds include those that must be returned, that is, a loan or other debt obligations. The rest of the funds are treated as equity. At the same time, each firm striving to effectively manage, objectively should provide the optimal (economically expedient) ratio of its own and attracted capital.
An important form of financing is credit - the paid provision of money or other valuables in debt for a certain time. The attraction of credit funds expands the financial capacity of the enterprise, but at the same time creates the risk associated with the need to repay debts in the future and pay interest for using the funds raised. At present, loans in non-monetary form are widely used: commodity credit, rent and its variety - leasing .
Commodity loan is a short-term loan that one enterprise provides to another in the form of goods through deferred payment for the delivered products (supplier credit). With the commodity form of the loan, the debtor can formalize its obligation in the form of a bill that gives the right to its owner to receive the amount specified in this document within the prescribed period. Commodity credit is used primarily as a means of expanding the scope of the market and increasing the volume of sales of products.
A special form of long-term credit is rent - contractual urgent paid possession and use of property. The Lessor provides the tenant with certain property for a stipulated period for a fee acceptable to both parties.
A common form of leasing in the world practice is leasing, when the lessor - the leasing company buys the rental objects (first of all the equipment) from the manufacturing enterprises and leases them on certain terms. After the expiration of the lease, its facilities (depending on the terms of the contract) or returned to the lessor, or leased for a new period or redeemed by the lessee.
Planning of financial activities
An important financial management tool for an enterprise is a financial plan. The main goal of drawing up a financial plan is to reconcile revenues and expenses in the planning period. In the long-term financial plan, the principal issues of financing the activities and development of the enterprise (organization) are solved. These issues include, first of all, financing of capital investments, repayment of debts, payment of interest on debt obligations, etc. Current financial plans for the year (quarter, month) are developed in more detail by types of income and expenses, taking into account their calendar dynamics.
The financial plan of the enterprise (organization) is compiled in the form of a balance of revenues and expenses . In the income structure, the main revenues are from stable own sources - profit and depreciation.
To the irregular own sources of income belong to the issue and sale of shares, proceeds from the sale of unnecessary assets, etc. The difference between the financial planned needs and own funds is covered by borrowed funds in the form of loans, bond issues, leasing, etc.
One of the forms of attracting funds is the accounts payable, which for its relative stability was called sustainable liabilities . To it carry a passing debt on wages, deductions for social needs, a reserve of future expenses, etc.
This minimum debt is formed by the average daily accrued expenses for certain of their elements and the number of days from the beginning of the month until the moment of payment. For example, a constant minimum wage arrears for an enterprise that has a quarterly wage fund of 4,500,000 hryvnias, and wages paid to employees on the 5th day of each month, will be 200,000 hryvnia. 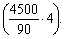 The financial plan does not include the total amount of this debt, but its change (increase or decrease) in the planning period.
The financial plan does not include the total amount of this debt, but its change (increase or decrease) in the planning period.
The expenditure part of the balance sheet of incomes and expenses includes planned directions of means: for payment of taxes; Replenishment of the reserve fund; The formation of investment resources (including the replenishment of working capital); Payment of remuneration to staff based on the results of work for the year; Payment of dividends, etc.
An important form of financial planning is the preparation of the operational balance (budget) of cash receipts and expenditures. The simplified form of such a balance is presented in Table. 17.1.
Table 17.1
CONDITIONAL BALANCE (BUDGET) OF CASH FLOWS OF ENTERPRISES FOR THE FIRST QUARTER OF THE CURRENT YEAR, ths. UAH.
| Month | The rest of the month begins |
Receipt |
Payments |
The remainder of the end of the month |
Deviations (+, -) |
|
per month |
A common |
|||||
January |
50 |
450 |
420 |
80 |
+30 |
+80 |
February |
80 |
380 |
400 |
60 |
-20 |
+60 |
March |
60 |
390 |
380 |
70 |
10 |
+70 |
The amounts of receipts and payments, of course, do not coincide, which is due to both the operational economic activity and the investment activity of the enterprise.
The data given in Table 17.1. Testify that within three months of a quarter the enterprise has a surplus of money resources. In this case, it is advisable to place free money in a profitable asset, that is, invest. In the absence of such funds, it becomes necessary to obtain a bank loan.
Prospective current plans need to be constantly adjusted taking into account the actual financial condition and specified indicators of the company's development.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.