home
 Economy Economy
 Business Economics - Pokropivny SF Business Economics - Pokropivny SF
|
Business Economics - Pokropivny SF
17.2. Creation and use of profit
Essence and profit indicators
Profit - is part of the revenue that remains after the recovery of all costs of production and commercial activities of the company. Describing the excess of income over expenses (expenses), income expresses the purpose of business and is taken as the main indicator of its effectiveness (efficiency).
Profit is the main source of funding for development of the enterprise, improve its material and technical base to ensure all forms of investment. All activities of the company sent out to ensure profit growth, or at least stabilize it at a certain level.
Depending on the formation and distribution secrete several kinds of profit. First of all, distinguish between the total profit and profit after tax (net profit). Total (book) profit - all profits of the enterprise, obtained from all directions of its activity to its taxation and distribution. .. Profit after taxation, ie profit actually made available to the company, has a common name in Russian literature - the net profit.
In foreign economic theory and entrepreneurship are commonly used concepts gross, operating margin and earnings.
Gross profit - the difference between revenue and operating costs (cost of production, with a specific calculation on incomplete cost). This includes the actual income and so-called non-productive (administrative, commercial) costs. Operating income, which is often referred to as profit, equal in magnitude to the gross margin less non-operating expenses. Marginal profit characterizes the volume of revenue from sales minus variable costs. It includes the actual profits and fixed costs. Accordingly, such gain coincides with the largest gross profit with the proviso that only performed by calculation of the variable costs.
Sources of income and its calculus
The company's profit is generated from the following sources: a) the sale (sale) of products (services); b) the sale of other assets; c) non-sale transactions. Gain on sale of products (operations) is the principal term of the total profits, because it is, reflects the mission and company profile. It is defined as the difference between the proceeds from the sale of goods (excluding value added tax and excise duty) and its total cost.
In the case of calculation on the part of the incomplete cost costs, which is not included in production costs, is attributed to a specific period and when determining the gain (Pr) is excluded from revenues, that is,
Pr = Bp - Wed - Sn.s.p, (17.1)
where Bp - proceeds from the sale of products;
Wed - cost of goods sold (sold) products from incomplete costs;
Sn.s.p - costs that are not included in production costs, and assigned to a specific period.
This so-called direct method of calculating profit, which is recognized as the main (basic). Along with them, there is an analytical method, according to which the projected income is determined correcting its base (actual) value of taking into account the impact of certain factors in the billing period, for example, changes in the volume of production and sales of products, its structure, the cost of products and prices. This method can be used in a relatively high proportion of products of the same type in its general scope.
Gain on sale of property, for which the enterprise for one reason or another become unnecessary, include gains from the sale of fixed assets (tangible assets), intangible assets, securities of other companies. Its value is determined as the difference between sale price and net book value of the object sold, taking into account the costs of implementation (dismantling, transport, payment of agency services).
Profit from non-sale operations - is the profit from participations in joint ventures, property lease (leasing), dividends on securities, the income from the ownership of debt obligations, royalties, income from economic sanctions (fines).
This scheme of calculating the value of the total profit for the sources of its formation is essential for analysis and economic decision-making. But we must bear in mind that the total profit is subject nalogooblozheniya.V therefore state authorities regulate the method of determining the taxable profits in the regulations. In particular, according to the Law of Ukraine "On taxation of income enterprises" (1997) taxable income (PNO) is calculated according to the formula
PNO = Dve - (Zo + AO), (17.2)
where Dv - gross (total) income for a certain period;
Zo - total costs for the same period;
JSC - the amount of depreciation of the value of assets subject to amortization.
The main component of income is the proceeds from the sale of products. The income also includes gains from property sales and non-sales operations. The total costs - is primarily the cost of products sold, as well as losses from the sale of property because it exceeded its carrying amount with respect to the proceeds from the sale of assets. Depreciation allocated from the total amount of expenses, because their calculation and use is controlled by public authorities in a specific order.
Use of profits
The financial policy of the company occupies an important place distribution and use of profits as the main source of financing investment needs and meet the economic interests of the owners (investors). The concept of using business profits is shown in Fig. 17.1
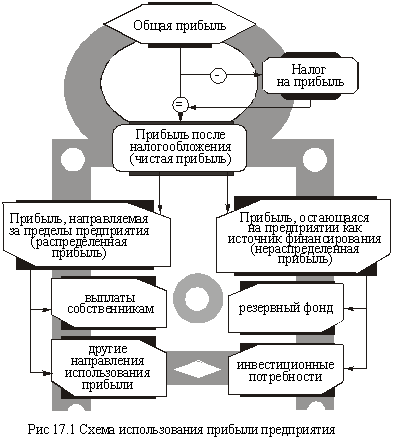
Of the total income tax paid in accordance with the conditions laid down by the legislation on the taxation of business profits. The profit remaining after tax (net profit), arrives at the complete disposal of the enterprise and is used in the manner prescribed by its charter and the decisions of its owners.
The principal (main) use trends suggest dividing profits into two parts: 1) Earnings available outside the enterprise, called the distributed income (distributions to owners of corporate rights of the enterprise personnel as a result of work on social support); 2) profit remaining at the plant and used as a source of development finance (retained earnings). The latter is directed to the creation of a reserve and investment funds. The reserve fund is a financial compensator possible deviations from the normal turnover of funds, the source cover the additional resource requirements. Its formation is a must for business companies, rental companies, co-operatives.
This general scheme of profit distribution should be more specific in enterprises with various legal forms, that is primarily concerned with joint-stock companies (enterprises). As is known, the owners receive shares of the corporate profits as dividends (income investors on the invested capital). On joint-stock company dividends may be regarded as a fee for raised from the sale of shares capital.
Distribution of profits to pay dividends, and investing is a difficult financial problem, which is essentially ambiguous and affect the financial stability and prospects for the company. Focus sufficient amount of profit for dividend payments and a high level of such increase demand for shares and increase their market rate. However, it limits its own source of funding complicates the solution of problems of perspective development of the enterprise.
It is clear that low dividends lead to opposite results. In these circumstances, the joint-stock company (the company) is forced to choose a dividend policy that would meet the specific conditions of its activities. Possible dividend policy (dividend payment procedure) in a particular company are presented in Fig. 17.2.
Each of these options has its own advantages and disadvantages, and is used generally, is not constant, and within a certain time period due to the economic and financial condition conjuncture enterprise.
When distributing profit enterprises dividend percentage value (d) defined by the formula
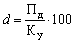 (17.3)
(17.3)
where the front - part of the profit allocated for payment of dividends;
Ku - the authorized capital (fund) of the enterprise.
The absolute amount of dividends per share (D), respectively, will be
D = Pd / N and (17.4)
and where N - number of shares that forms the value of the authorized capital (number of shares sold).
Part of the profit used for dividend payment shall be determined in accordance with the selected option of the dividend policy. The experience of foreign companies and successfully operating domestic enterprises shows that the share of the dividend amounts in net income ranges from 30-70%. If it is less than 30%, the payments are considered to be too low, and when the relative size of their 70% - too high.


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.