home
 Economy Economy
 Business Economics - Pokropivny SF Business Economics - Pokropivny SF
|
Business Economics - Pokropivny SF
17.3. Evaluation of the financial and economic sostoyaniyapredpriyatiya (organization)
The essence of evaluation and information base
Financial and economic state of the enterprise (organization) is characterized by the level of his (its) profitability and capital turnover, financial stability and the dynamics of the structure of funding sources, the ability to pay on debt.
Proper assessment of the financial results of operations and financial and economic condition of the enterprise in modern conditions of managing is very important for its management (administration), as well as for investors, partners, creditors, government agencies. Financial and economic state of the enterprise is almost always interested in and its competitors, but in the opposite aspect - they are interested in (quite naturally) to weaken positions of competitors in the market.
To assess the economic and financial condition of the enterprise (organization) need appropriate information base, and above all income statement and balance sheet - a synthetic document on the composition of assets of the enterprise (organization) and the sources of their formation in the form of money on a specified date. The simplified form of the balance, entered into force in Ukraine since January 1, 2000 and meets the international standards of accounting business entities is given in Table. 17.2.
Table 17.2
BALANCE enterprise (organization) FOR PREPARING FOR THE ______________ (in thousand. UAH .; conditional numbers)
| Assets | sum |
liability |
sum |
I. Non-current assets |
I. Equity |
||
1. Intangible assets: |
1. Share capital |
8000 |
|
- Residual value |
220 |
2. Additional capital |
- |
- Primary costs |
320 |
3. Reserve capital |
2000 |
- wear |
100 |
4. Retained earnings |
4500 |
2. Construction in progress |
|||
3. Fixed Assets |
|||
- Residual value |
11000 |
||
- Primary costs |
15000 |
||
- wear |
4000 |
||
4. Long-term financial investments |
|||
5. Other non-current assets |
|||
Total for Section I. |
11220 |
Total for Section I. |
14500 |
II. current assets |
II. Ensuring follow-payments and payments |
- |
|
1. Reserves: |
|||
- productive reserves |
2200 |
||
- unfinished production |
3000 |
||
- finished products |
1500 |
III. long term duties |
|
2. Notes Receivable |
- |
||
3. Accounts receivable for goods and services |
2100 |
1. Long-term loans |
4000 |
4. Accounts receivable |
- |
2. Other long-term liabilities |
- |
5. Current financial investments |
1700 |
||
6. Cash and cash equivalents |
1300 |
||
7. Other current assets |
- |
||
Total for Section II |
11800 |
Total for Section III |
4000 |
III. Prepaid expenses |
400 |
IV. Current responsibility |
|
1. Short-term loans |
1520 |
||
2. Promissory notes issued |
- |
||
3. Accounts payable for goods and services |
2200 |
||
4. payables |
1200 |
||
5. Other current liabilities |
- |
||
Total for Section IV |
4920 |
||
V. Deferred income |
|||
Balance |
23420 |
Balance |
23420 |
The relationships between the individual groups of assets and balance sheet liabilities have significant economic value and are used for the assessment and diagnosis of the financial condition of economic entities.
Assessment of financial and economic situation at a certain fixed date based on the analysis of official documents, in particular the balance sheet (the organization). For this purpose certain groups and specific design for each group (Fig. 17.3).
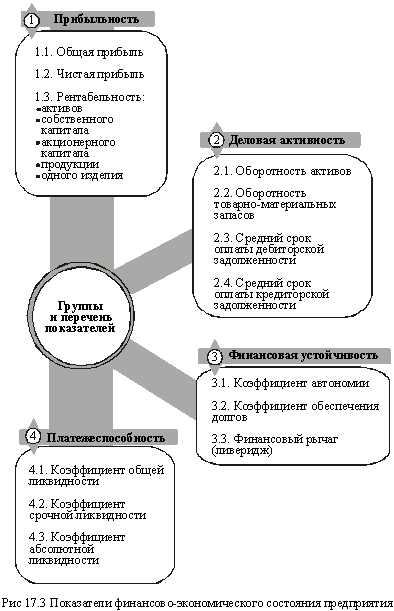
Evaluation of profitability and activity
The profitability of companies is measured by two indicators - profit and profitability. Profit expresses the absolute effect of excluding the resources used. Therefore, to analyze and supplement indicator of profitability.
Profitability - is the relative measure of the efficiency of the enterprise, which in general terms is calculated as the ratio of profits to costs (resources). Profitability modification takes several forms, depending on exactly which resources and profits (costs) are used in the calculations.
First of all, distinguish the profitability of invested resources (capital) and the profitability of production. Return on invested resources (capital) is determined in several versions: the return on assets, return on equity, return on equity.
Return on assets (ROA) characterizes the efficiency of the available assets of the enterprise and shall be calculated by the formula
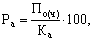 (17.5)
(17.5)
where (h) - total (net) profit of the company for the year;
Ka - the average amount of assets on the annual balance sheet.
This figure is calculated based on the total (before tax) and net (after tax) profit. Common methodological passage in this case does not exist. Therefore, you must indicate in the calculation which is profit taken.
Index total return on assets can be broken if the company carries out various activities (for diversification). In this case, along with the profitability of assets is determined by the profitability of certain activities (eg, profitability, service, business, and others.).
Return on equity (Rs.k) reflects the efficiency of the assets created at their own expense:
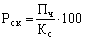 (17.6)
(17.6)
where P h - net profit of the company;
Ks - equity.
Return on equity (Ra.k) indicates the upper limit of the dividend on shares and calculated by the formula
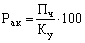
where Ku - the authorized capital (nominal value of the shares sold).
This indicator can also be defined as the return on equity, generated only from the usual (ordinary) shares. In this case, do not include dividends on preferred shares and the authorized capital of the rule nominal value of these shares.
Profitability of products (P) characterizes the efficiency of its production and marketing costs. It defines the ratio of profits from sales of products (Pr.p) to its total cost over the same period (Sr.p), t. E.
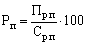 (17.8)
(17.8)
Product Profitability can also be calculated as the ratio of profit from sales to the total volume. It is in this form, this indicator is used (calculated) in the international practice of management.
In multiproduct manufacturing and cost-effectiveness of its individual species is determined, along with the efficiency of all production. Profitability of products (Pi) is calculated by the following formula
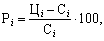 (17.9)
(17.9)
where C i, C i - respectively, the price and the cost price of i-th product.
Business activity of the company is quite a broad concept and includes many aspects of its operations. Specific indicators in this case serve as indicators of current assets and inventories, the value of receivables and payables.
Current assets (n a) - a measure of the number of revolutions of the assets for a certain period (mostly one year), that is,
and n = V / Ra, (17.10)
where B - revenues from all activities of the enterprise for a certain period;
Ka - the average value of assets over the same period.
Under these conditions, the average duration of one revolution (t a) will be
and t = Dk / n and (17.11)
where Dk - number of calendar days in the period for which is determined by the werewolf.
Revolving inventory (n tm.z) expresses the number of revolutions for a given period:
tm.z n = Cp / Ms, (17.12)
where Cp - the full cost of sales for a certain period;
Ms - mean value of the stocks in monetary terms.
enterprise activity in settlements with partners is characterized by average payment terms of receivables and payables.
The average term of payment of trade receivables of enterprise (t o.d.z) determined by the formula
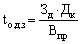 (17.13)
(17.13)
where the rear - receivables (receivables buyers);
Dk - number of calendar days in the period for which the calculated index (year - 360, quarter -90);
Fwd - the volume of sales of products for the billing period.
During the period t o.d.z payment requirements for enterprise customers are converted into money. It is clear that the reduction of this period is a cost-effective, and elongation (compared with fixed-term or last year) - undesirable and needs determine the causes of the latter.
The average term of payment of accounts payable to suppliers (t o.k.z) is determined from the relationship:
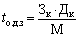 (17.13)
(17.13)
where Sk - value of trade payables;
M - the volume of purchases of raw materials and materials for the billing period in monetary terms.
Reducing the time of payment of accounts payable, ceteris paribus can not be regarded as a positive development for the company, as it is related to the mobilization of additional funds. An increase in the debt payment period may be due to various reasons: deterioration of the payments to contractors, a lack of funds from enterprises, delaying payment for the use of accounts payable as a source of funding, etc.
Assessment of financial stability and solvency
Financial sustainability of the enterprise is characterized by the ratio of own and attracted (borrowed) capital. For this purpose, a variety of indicators, which are called coefficients. Among them are the most common factors of autonomy and ensuring debt.
Coefficient of autonomy (Ka) is determined by dividing the equity capital on the final figure (total) Balance of the enterprise:
Ka = Kc / Kb (17.15)
where Kc - equity company;
KB - the result of the balance sheet as of a certain date.
According to Table. 17.2, e.g.,
ka = 14 500/23 420 = 0.62
This means that the assets of the company by 62% provided their own means. The rest (38%) financed by debt. This value ratio is acceptable - the debts are fully covered by equity. If ka <0.5, it increases the risk of non-payment of debts, and hence the concern of creditors. Increasing the value of the coefficient of autonomy leads to increased financial independence and reduce the risk of violations of the entity's financial stability.
Ratio of secured debt (kod) is a modification of the first indicator and is defined as the ratio of equity and debt capital
ko.d = Kc / Kd.o, (17.16)
where Kd.o - debt (debt capital). Thus, in accordance with the balance sheet data (tab. 17.2)
ko.d = 14 500/8920 = 1,625
Consequently, the shareholders' equity exceeds the debts 1,625 times. Normal is considered to be a situation where kod 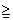 1.
1.
It is necessary to take into account the fact that the analytical evaluation of financial condition on the basis of such factors is not always unambiguous. Of course, the reduction in the share of debt in total capital strengthens the financial independence of the company. However, at the same time narrowing the choice of funding sources and the possibility of increasing its efficiency.
Under certain circumstances advantageous to borrow. In this case is the effect of the so-called financial leverage (liveridzha), which is expressed in terms of debt-to-equity ratio.
When the fee for a loan is less than the return on assets in view of taxation, increased debt (increase in the ratio Kd.o / Kc) leads to an increase in return on equity. Hence, the involvement of credit in this case is the financial leverage (liveridzhem) increase the efficiency of the enterprise.
The solvency of the company, ie. E. Its ability to settle its debts, is determined by the liquidity ratios. They show how the short-term Liabilities Twa covered by liquid assets. Since the current assets have different liquidity, to the extent determined by the number of liquidity ratios - total, immediate and absolute.
Ratio total liquidity (ko.l) - the ratio of current assets (Section II of the asset balance) to short-term liabilities (liabilities section IV):
ko.l = Ko.a / Kk.z, (17.17)
where Ko.a - current assets of the company;
Kk.z - short-term debt of the company.
According to the balance sheet data (tab. 17.2)
ko.l = 12 200/4920 = 2.48
This means that the working capital of the company exceeds the short-term debt of approximately 2.5 times. If ko.l <2, then the company is considered to be the low pay. When excessively high value of his (ko.l> 3-4), there may be doubts about the efficiency of use of circulating assets. For optimal value ko.l significantly affect the share of inventories in current assets. For businesses with small stocks of this kind and promptly paid Receivables obligations would be acceptable lower level of the ratio of current assets and current liabilities (ko.l <2) and, on the contrary, in enterprises, in current assets which are large proportion of inventories is the ratio should be maintained at a higher level.
Quick ratio (ks.l) is calculated as the ratio of current assets higher (immediate) liquidity to short-term liabilities, ie
ks.l = Ks.l / Kk.z, (17.18)
where ks.l - high-current assets (immediate) liquidity, which includes current assets less inventories.
In our example (tab. 17.2)
ks.r = 5100/4920 = 1.04
This value ks.l is normal and indicates the possibility of timely payment of debt. If ks.l <1, then the company's solvency is low.
Absolute liquidity ratio (ka.l) - is the ratio of the absolute liquid assets to short-term liabilities:
ka.l = Ka.l / Kk.z, (17.19)
where ka.l - absolutely liquid assets of the company (cash and cash equivalents).
According to Table. 17.2.
ka.l = 3000/4920 = 0.61
Normal can be considered a situation where ka.l 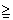 0.5.
0.5.
The level of liquidity of the enterprise depends on its profitability, but the unique connection between these indicators traced only in the planning period, where high profitability is a prerequisite for adequate liquidity. In the short term this is not a direct link. A company with good profitability may have a low liquidity due to large payments to the owners, the reliability of the debtors, etc. Therefore, to ensure satisfactory liquidity of the enterprise requires a certain amount of administrative effort and to optimize the financial and economic decisions.


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.