|
 |
Few aquariums full of plants, remain free from algae. To fish in most cases does not matter. In the background: Eichhornia azurea. |
 |
Gorgeous floral composition, centered on the tiger Nymphaea (Nymphaea lotus). In the foreground - the plants of different species with high stem. They require constant pruning. For such exposure should be a lot of space! |
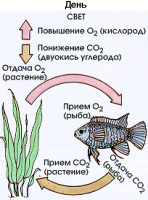
The appearance of the aquarium plants is determined. And then conclusion is that plants - is primarily a decorative element. To have not developed such a representation, we need some information about the biological relationships. Aquatic plants and fish inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide. Of course, they can not break down the water molecules - H 2 O; they can only be used for breathing substances from air dissolved in the water. But the amount of these substances may vary. The fish need more oxygen, and they give up more carbon dioxide than the plants. This disparity in compensated respiratory plant assimilation processes: under the action of light energy plants convert inorganic substances from soil and water into organic matter (protein, starch, sugar). These plants are distinguished from animals. In the process of assimilation of the plant requires more carbon dioxide than it exhales, and at the same time free of oxygen is larger than it needs to breathe. And because the fish exhale more carbon dioxide than the plants, this "extra" carbon dioxide is beneficial to the process of assimilation of the plant, and at the same time the excess formed in the process of assimilation of oxygen is good for the fish. Thus, fish and plants are complementary. Theoretically, they live in a biological balance. Only at night, when due to lack of light suspended assimilation, dissimilation process plant produces oxygen and does not require carbon dioxide and exhales it, with the surplus accumulated in the bicarbonate. However, the plant's need for oxygen is so low that fish under normal conditions in a sleepy state is not affected. The negative impact may have only overpopulation fish tank and a surplus of plants without supplemental oxygen. The oxygen content in water is particularly low, and the carbon dioxide content in water is high especially about 9 o'clock in the morning. It is logical that at this time the lowest level reached and the pH (acidity), but at the beginning of the process of assimilation, he rises again (the rhythm of the chemistry of the water). For the amount of oxygen entering the water is crucial to the overall surface of the aquatic plants. The vastness of it, the more oxygen the plants emit. It should be noted that a more extensive surface do not differ broadleaf plants, but on the contrary, a plant with many thin cirrus leaves - such as cabomba, yarrow, Eger, Java moss and Indian water fern. Catching the placement of plants in the aquarium should be aware of lighting conditions. In the part of the tank that is illuminated it is best to place the plants, which require a lot of light (due to the thin pinnate leaves) and grow rapidly. They thus will block the light from the other, more small plants. Those places in the aquarium, because of the shadow of this or because of decorative elements are not subject to such an apparent light irradiation, it is necessary to plant the plants, at least in the sense of intricate lighting needs. Plants with delicate feathery leaves almost always require a lot of light and can not tolerate "algal blooms."
 |
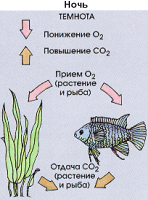 |
| The process of photosynthesis: assimilation and dissimilation day night. The figure on the right: the early morning of oxygen (O 2) is reduced, but the amount of carbon dioxide (CO 2) increases. Only after a few hours will occur assimilation process, the oxygen content is increased according to the number of plants. It is pointless and even dangerous to leave on overnight installation fertilizer CO2. Continuous regulation much more useful. |
Another important task performed by aquatic plants, is water purification. Unlike many terrestrial plants, water inhabitants have the ability to absorb minerals not only back, but also special cell on the leaves. Thus, they take water from the organic compound (aspartic acid, threonine, etc. guanine.) To use them for their own development. It turns out that the digestion of floating waste neighbors are just for the benefit of plants and do not have to first pass conversion way into minerals. Moreover, harmful bacteria are deprived of the nutrient medium and prevents their multiplication, as well as poisoning and water turbidity. However, and here the ratio of the number of fish and plants in the tank plays an important role. The more plants per fish falls, the water is purer. Formed with a smaller amount of mud particles are decomposed by bacteria, destroyers and absorbed by plant roots. The overabundance of dirt particles always indicative of too many fish that does not allow to achieve biological balance, which was mentioned above. On the other hand, there are so many fish, happy digging in the dirt, and therefore in need of a small amount of it. In this case, the fish in the aquarium can be and more. But for them the best crumb peat mud. Many types of plants require certain nutrients. It is not objectionable for most aquarists, and just because they prefer to see in your home pond plants do not like one another, and the combination of different shape and color types. Thus, plants can be found among those that optimally match their own requirements nutrients available to them.
 |
 |
| Dutch aquariums attractive original combination of different groups of plants. They can not and should not become the reproduction of natural habitats. |
Type and amount of landscaping plants in the aquarium, due primarily to the ratio of the plant-fish. Large, agile fish, especially if a lot of them need a lot of oxygen. This means that they require more and plants than small fish, especially if they are small. But at the same time the volume of gardening depends on the type of fish. Among them there are those who are suitable thickets (labyrinth fish). But for the inhabitants of the open waters in need of space for swimming, should be densely planted only distant corners, and at the side walls and the rear of the aquarium need to place the plants in separate groups. Thus it is necessary to choose plants that produce a lot of oxygen. Many fish bushes with thin cirrus or broad leaves are necessary as a substrate for eggs or as a shelter. Labyrinth like to postpone their cemented saliva nests on floating plants. And for angelfish, eagerly tearing broad leaves, very fit eel, sagittarii or Echinodorus. For schooling fish with light signals requires a shady location in the back of the densely planted tank plants. They are well combined with plants that prefer shade (crypts) or those which still develop even with moderate light (Echinodorus). If fish strongly break the roots, the plant is best placed in pots or keep afloat; If the fish are digging the ground (carp), it is necessary to abandon the plant with fine pinnate leaves (yarrow), because they are easily contaminated. Cichlids and klinopyatnistyh barbs, as well as a number of other fish species, do not neglect the soft greens, can not be placed in a tank with delicate plants (yarrow, cabomba) - unless, of course, you are not going to provide them with food so expensive! As, probably, it was clear from the above, the abundance of plants with a small number of fish, strong light and inadequate ventilation can sometimes be harmful: due to a lack of CO 2 bicarbonates water fall so that the leaves formed limescale deposits and they become to the touch rough, as it were sprinkled with sand (biogenic removal of lime). But this deficiency has recently been possible to fill and without questionable use of mineral water, that is, using a diffusion device for fertilizing with carbon monoxide. All aquatic plants can easily absorb carbon monoxide (CO 2), when it arrives in gaseous form. Assimilation chemically bound from carbonates or bicarbonates respectively carbon monoxide usually weak and irregular. But diffusers provide plants with carbon dioxide gas in sufficient quantity in this form first developed especially for aquariums. We do not advise you to sit near any plants indiscriminately. Some of their views need to be combined into groups, and then to separate them from each other with stones and driftwood. Planted aquarium, the plants should not be placed too close to each other. Plants continue to evolve, and their fast-growing species may be only a few weeks to increase strongly (Vallisneria, sagittariya, Eger). In a small aquarium should be only 2 - 3 species, and more - proportionally more. For very large aquarium plants before purchase is recommended to take a plan developed by a specialist in underwater gardens, so you buy the right amount of each type of plant. With your underwater garden terraces, place bog plants as high as possible, so that they soon seemed out of the water and could blossom. Of course, this is possible if the tank upper lid is not closed and hanging lamps illuminated. Different kinds of mosses and plants (Java moss Vesicularia dubyana and Java fern Microsorium rteroptus) can be used to cover the snags. For this purpose, thin feathery moss (and larger plants such as ferns, only the roots) is carefully placed in the narrow cracks of wood. The connections that they are stronger, it is possible even before the growth of a thin elastic wrap. At least once a year densely overgrown aquarium should be treated as treated garden. This is too big or too fat plants are cut, so that they did not take each other's light and space, gradually starting to suffer from this. All the sick and weak plants should be removed. Because at a certain time, the growth is stopped, it is then, in a period of rest, especially the need to closely monitor. to the accumulation of dirt and other waste not intended for aquarium corners: the plants will not be able to process this material so fast, as they usually do. Due to this, formed pockets, completely devoid of oxygen. For any size of aquarium should not forget about the problem of compatibility of plants planted. This view is often repeated, but it does not become the alphabet aquarium! But in fact, many plants do not tolerate each other, which leads to damage of the weaker species. So, you can not keep in the same aquarium Cryptocoryne, eel and sagittarii. Similarly, the floating plants harms condensation moisture (it is necessary to help Plexiglas frame to increase the space between the water surface and luminaire housing).
How to plant? Before planting, each plant should be cleaned of clinging to him filamentous algae, snails eggs, rotten areas, etc. After that, it takes about 20 minutes to disinfect in pink (to wine-red) solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate). It is also recommended bath (5 to 10 minutes) with a solution of alum (1 teaspoon / 1 liter water) or rinsing with hydrogen peroxide (1 teaspoon / 1 liter water). Then the plant should be carefully rinsed. The roots can be slightly undercut to awaken them to the speedy growth. After that, it is necessary to fill the reservoir washed soil to a height of about 10 cm and cover with water (5 - 10 cm). Start placing the plants should be from the back wall of the aquarium: they put the highest of them, and the observation side as possible leaving free or distributing it along those species that are small or form a ground cover. The roots should be placed in accordance with their natural growth. Cryptocorynes and eel take root straight down. The index and middle fingers need to do the proper hole in the soil and place the plant in it - a little deeper than the root of the neck, although the root has to be straightened. Then trample the soil lightly and gently pull the plant up to root for seemed neck. Thus, even thin branching roots will be located directly in the ground. At the root of the neck Cryptocorynes may even put out a little from the ground. For each plant must account for 5 - 6 square centimeters of the bottom area, but also the distance between each instance it depends upon the size and future growth. Increasingly plants such as S. grif fithi, C or C siliata beckettii and the distance between them should be not less than 15 cm. Aponogetona and Echinodorus roots flat, they go down by just a few centimeters and are distributed mainly horizontally. They need to make an elongated fingers and not very deep hole, place a fan in her roots and again sprinkle with a mixture of dirt. The distance between the small specimens should be 8-10 cm, and between the larger (in a large aquarium) 15-30 cm Some types aponogetona is 20 -. 40 leaves, and they need plenty of free space on all sides (!).
Water plants, which absorb the substance they need directly from the water by means of special organs of their leaves, should be planted in the ground in the form of cuttings, without roots, after removing the leaves from the stem of the two lower nodes. Flat stones retain the cuttings, so they do not pop up until take root. Creeping plants should be planted 4 - 6 pieces together, like bushes, otherwise they are pretty pathetic. But each of them must be located at a distance of 1 - 2 cm from each other (especially with respect to cabomba). Plants do not grow in size, too, planted next to bushes. Plants with horizontal branching rhizome (eg, sweet flag) should be placed under a bias to a part, albeit shoots protruding from the soil. Water plants, which absorb the substance they need from the soil solely by the roots, as well as those that are difficult to "work" the roots, but the need for nutrients (aponogeton, Echinodorus, Cryptocoryne), should be placed in the ground in a flat dish or pot. These bowls can be filled with a mixture of earth, two-thirds consisting of clay and peat aquarium. By the way, recently went on sale and special premixed for aquarium. In no case can not use prepared soil mixture for flowers: it is impossible to control what fertilizers are added, and they can easily turn into hotbeds of putrefaction. The high bowls or pots, protruding above the ground, you need to lay the stones so that they do not spoil the general form of the aquarium, reminiscent of nature. The same method should be used in aquariums, where they will live burrowing ground cichlids. Among other things, potting culture has the advantage that when cleaning the bottom ground receptacles can simply be removed from the tank, and then put again without damaging the roots. The most favorable time for planting - spring. Young specimens originate mostly from greenhouses, where they are used to correct the change of seasons. In the spring the young plants at these ends rest period (November to January) and they start to let the new shoots.
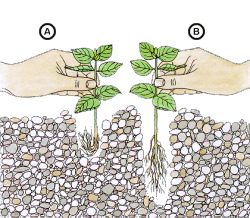 |
Many amateurs make mistakes when planting plants in the aquarium: The roots must not be bent (a), and right (b) for all of its processes placed in the ground. The best thing to do first hole deeper, put the plant, and then gently pull it up. |
Breeding of aquarium plants
Plant Breeding in the aquarium occurs most often vegetatively: suckers and sprouts, cuttings, and dividing plants. Scion is necessary only to separate from the mother plant, where they formed a sufficient number of roots. Cuttings can be extracted by separating the branches or shortening the main stem. Some species form roots without landing in the ground, so that they are sufficient to fix the glass pin or flat stones on the ground and wait until they take root. Divide plants are best done in spring. Plants forming winter buds fall collected, placed in a flat container and sand with small amount of water and allowed to reach winter frost. Around the middle of February, these can be transferred to a room where there is an aquarium, so that they gradually get used to the higher temperature. After that, they can be planted in the aquarium, where under the influence of hot water and lighting, they will soon be allowed shoots. Most aquarists resort to these simple ways of vegetative reproduction, as they are applicable to almost all water plants and not too difficult.
|
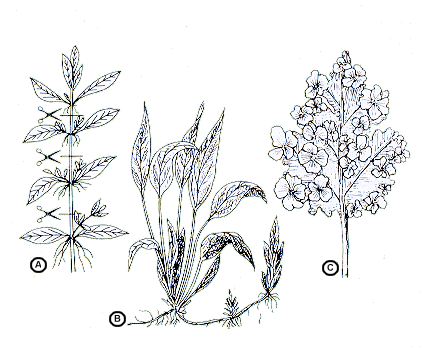
| There are two types of plant propagation: seed and vegetative. The latter may occur in many ways, as you can see below: (a) the plants with erect stem enough to cut off a part between two nodes to get a sapling, and after its establishment - a new plant; (B) shows the spines here with young seedlings. After some time it will be possible to cut the umbilical cord linking them to the mother plant, and then they become fully samostoyatelny.Na right figure (c) it is evident that on the record sheet of floating plants (here: Cetatopteris pteridoides), especially on its edges, formed subsidiary plants ; over time, they are separated from the mother plant and start an independent life on the water surface. |
plant Requirements
 |
Magnificent habitats of plants produced by various sources in the highlands of Sri Lanka. Above the surface of the water can be recognized lush thickets Limnophila indica. In the foreground Alocasia macrorrhiza. |
 |
The bed of the rivers in the south of Sri Lanka: Aponogeton rigidifolius spread its shoots over water mirror quiet backwater. In the background, a group - Lagenandra ovata. |
Many aquarists are afraid of planting a beautiful and large plants. Often the cause is gained bitter experience, when you start to remember again and again "in vain thrown out money," or repeating that "this will not work again, nothing." However, setting the stage for a new aquarium, you can try to put it in plants without fish! After all, the first few weeks after planting in the aquarium plants suffer badly and do not go into growth. Often they do not have exactly matched nutrients and (or) water indicators (still) wrong. Here we must all check and try, and here's why: no treatment without a diagnosis. Just in case, if the plants do not grow at normal rates of water - plus a strong lighting, plus CO 2 fertilization - you can imagine the disease. But as a rule, plant requirements are satisfied, and these few "gifts". Most often, they absorb nutrients the surface of the leaves, but do not understand it as a generalization: not every plant takes root only in order to gain a foothold in the soil. The plants with strong root system - just remember the Amazonian Echinodorus (Echinodorus), Crinum (Crinum), aponogeton (Aronogeton) and different species and varieties of water lilies (Nymphaea) - developing better if in sand or gravel to mix the so-called soil additives (they are sold in specialized stores). Unverified additives should, on the contrary, the soil removed from the aquarium. These include first and foremost all the earthen mixture of colors, that is, those that are intended for filling in the balcony boxes, etc. They are supersaturated fertilizer! The overabundance of fertilizer is just as harmful as it is their absence. If too many fish aquarium (as is often the case), the content generated as a result of the nitrogen cycle of the final products of decomposition or transformation respectively - nitrates - becomes so great that the plant can not recycle them. That is why you need to regularly perform a partial replacement of water, do not forget that along with the allotted water and leave all the fertilizer contained therein. Therefore, before the change of water is necessary for some time to stop fertilizing fertilizers. It is useful to know what the content of nitrates in your tap water; it is enough to call the waterworks. When the tank is equipped with properly inside it can arise several temperature zones. This can not be tolerated. For example, if you try to avoid too much water movement, since because of it can be displaced in the carbon dioxide entering the aquarium, the aquarium, where in the corner provide heat one or more heating elements may be formed area with water of different temperatures. Most plants do not like the one hand, the temperature difference, on the other - a constant overheating. In addition, no assurance can be unheated floor (especially in cool place) that the plants do not "freeze the legs." In tropical waters the bottom can not be cold, so it should not be so, and the aquarium. It is necessary to pay attention to one feature of the so-called "bulb plants": unlike all the other inhabitants of the aquarium green they need a period of rest. When you buy tuberous, they no longer are young plants. Actually, in most cases, and not sold from the plant stems, tubers viz. If you want to enjoy these plants for a long time, then take care of them in accordance with their nature. You should know the fact that they are highly dependent on natural living conditions of their tropical homeland. And those are not as constant as assumed in our latitudes. Dryness and floods follow each other, for the hot days come cool nights, and during the rainy season very strongly fluctuating water indicators. According to these conditions, such plants can not stand the constant heat of aquarium water; from time to time they need rest, with self-report such time as their foliage wilts. To support the process of their life, it is necessary at the outset seat tubers of these plants (different kinds aponogetona) in a pot. They are placed in the bottom soil during their stay in the tank, and with the beginning of a period of rest is removed. Pot culture to give after flat bowl to the tubers were covered with the water for only a few centimeters. The water temperature at the same time reduced to about 15 ° C. After that, the plant shoots die. But the owner of them should not be frightened, and to increase the temperature: Only this can cause tubers real harm. In this state, outside the aquarium, tubers should be in average at least two, but no more than four months. Then the pot of culture can again be placed in the aquarium ground: time for "addictive" will take a little bit.
fertilizers
No one is surprised that the fish have to be fed. But then the plants just need food, which in a normal aquarium they fully can not receive. Hence, one who is particularly important plant growth and the beauty of its underwater garden, to do something more than just planting and waiting. Fertilizing plants with nutrients depends on the type of lighting: light provides energy, if it has the correct spectrum and intensity appropriate; it also promotes healthy metabolism and sufficient assimilation in plants. The faster the metabolism, the higher the need for a natural plant nutrients. Nutrients that can and should be fed plants are different. In the first place, of course, is to ensure the plants with carbon in the form of CO 2. Fertilizers proposed plants in small doses for successful development are mineral nature: this calcium, magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, nitrogen and iron. Especially important iron fertilization, although in the past few years effective it was difficult to conduct, and brings a lot of problems. The content of iron, wearing chemical symbol Fe, the aquarium water is determined using a special test (Fe-test). One of the consequences of iron deficiency may be a discoloration of leaf chlorosis. It is not always discoloration of leaves shows exactly chlorosis; often we can talk about lack of content of other substances, magnesium or manganese. Iron from the water <s are usually removed at waterworks.
However, in tropical waters around it contains, moreover quite often in high concentration. Native to many aquarium plants (Cryptocoryne) water is rich in oxygen and weak alkaline reaction: it is released in the form of iron oxide hydrate and ferric phosphate, what can be seen in the brown deposits on the bottom. Is chlorotic symptom of failure, you can check, as already mentioned, with the help of a special test. After that you should decide whether iron fertilization is needed and in what quantities. When the iron in the water too much, its compounds can settle on the gills of fish in the form of brown plaque, hindering their breathing. If there is discoloration and yellowing of the leaves, and if this set of iron deficiency, plant lover should intervene. Iron as a fertilizer is produced in various forms, for example, in powder form - so it dissolves rapidly in water, with stabilizers do not give it to precipitate. Synthetic organic substances strongly bind iron so that oxygen can oxidize and it is easily assimilated by plants. Other manufacturers offer the nutrients in liquid form - is, for example, Duplaplant tool for daily feeding "Dupla" company; they can sprinkle the aquarium water using dosing nasosik the same firm. "Tinze" firm Filter system (Osmolator) also provides for dosage of fertilizer. In recent years, the CO 2 fertilization has become a "miracle cure" for beautiful and well functioning aquarium, planted plants. Commercial offers everything needed for this installation. Firstly, this diffuser through which CO 2 in gaseous form (carbon dioxide) enters (diffuses) into the aquarium water in solution and further acts as a carbon dioxide. But with one problem can not be solved diffuser, because depending on the size of the aquarium is consumed more or less the amount of CO 2. This gas must be contained in a special vessel. But there is no point at the CO 2 fertilizer use cans with carbon dioxide, for siphon - it would be too expensive! By itself, the gas is cheap, but only need to add it to the very numbers that are required to the plant! And how much gas they need? The answer to this question depends on the tank volume (liters of water), light intensity, water hardness (harder than it is, the higher the demand for gas) and the density of plantations. As an average we can take 2-3 grams of CO 2 per day at the volume of 100 liters, and water of medium hardness. Accordingly, for aquariums up to 500 liters is enough for 10-15 grams of gas. The most well thought out in this sense, "Dupla" firm products: they release the six cylinders of different sizes (160, 300, 500, 1500, 3000 and 6000 g). It is easy to calculate the average gas consumption: if we start from the 15 grams per day, it means that the cylinder with 1500 g will be enough for 100 days. In Germany, after the empty bottle for a full exchange usually in a special paragraph.
 |
You can either mount the installation, the metering of CO 2, and adjust its automatic operation. |
The equipment consists of a cylinder pressure gauge and pressure relief valve. Anyone who would like to especially fine-tune the supply of CO 2, it can be done with a long-acting regulator: it constantly adjusts and automatically sets the pH by accurate dosing of CO 2. Another part of the system (used in conjunction with an adjustable constant) can be a solenoid valve by which (a timer) may suspend supply of CO 2 at night, when the process plant assimilation stops. It should be pointed to the fact that the aquarium water enriched with CO 2, should not be that strong movements that produce filter pumps: running water to quickly push out carbon dioxide. Assimilation, that is, the formation of organic substances (carbohydrates) of carbon dioxide, air and water, depending on the input light energy. Usually, this energy comes from the sun. But in an aquarium sunlight replace the lamp to give the plants the possibility of formation of carbohydrates (sugar, starch, cellulose, and others.); This process is called photosynthesis. Thus, light and carbon dioxide should be considered as interconnected complex, because the absorption of carbon dioxide by plants have light reaction. If water is hard, because it contains a lot of lime, the lime addition required enhanced CO 2, since it binds with lime. But carbon dioxide - is not only a valuable nutritious product for the plant, and - at too high a dose - poison for fish, resulting in difficulty of breathing. Poisoning with carbon dioxide is only possible at a low pH, as carbon dioxide in the acidic environment lowers the pH below 7.0. This requires a concentration of about 150 mg / L. If this happens, intensive aeration of the aquarium water (expulsion of carbon dioxide) to quickly remedy the situation. To bind carbon dioxide in water, carbonate hardness is required at least 2 ° dKN,
Depending on the structure and characteristics of the underwater leaves and marsh plants can be divided into seven groups:
1. plants with ribbon-like or thread-like leaves;
2. The gross or mohopodobnymi;
3. with petiolate;
4. tonkoperistymi;
5. floating on the surface and the water column;
6. with floating leaves;
7. marsh plants
 |
 |
Flower
Limnophila
aquatica |
Flower
Lobelia cardinales |
 |
Flower
A.senegalensis |
Group 1: Good oxygen producers. Prefer bright place. Among them there are species that form a ground cover. Appendages to attach to the ground stud or glass stones. Since most of these plants also requires nutrition through the roots need a potting culture. The rhizomes can be divided. Eel and sagittarii not be placed together with Cryptocorynes!
Group 2: Good oxygen producers. They are used for laying eggs and form a perfect shelter. Because these plants absorb substances necessary for them only through the pores, it can be fastened to the ground glass stud or flat stones, as long as they will not be allowed Tapered rhizoids. Propagate by cuttings or sprouts. Recommended light place.
Group 3: These plants prefer dim lights and soft water. Depending on the type of culture it may be recommended in pots. Cryptocorynes not be placed together with eel and sagittariyami!
Group 4: The most active oxygen producers; some of them (cabomba) require very soft water and intense lighting. They are used for spawning and as a shelter. Since the roots they only need an anchor, they should be planted in groups and fastened to the ground. Propagated by cuttings.
Group 5: They are used for laying eggs. Requires a lot of light. Floating plants can be covered with only one third of the total surface of the aquarium. They need constant air supply and often sensitive to moisture condensation. Upper glass should not be.
Group 6: It is advisable to plant out the plants in pots or bowls. They need a strong overhead illumination.
Group 7: Well suited for aquariums, where the bottom is laid terraces: it gives them the opportunity to grow and above the water surface. As seen on The above classification (by groups), the plant can be viewed from different perspectives.
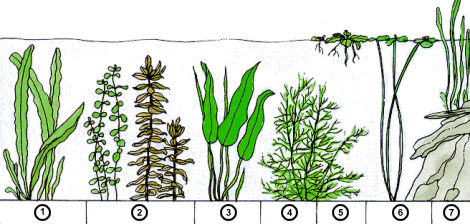 |
The types of water plants:
1 plant with ribbon-like or filamentous; 2-gross or mohopodobnymi; 3 with petiolate; 4 tonkoperistymi with leaves; 5 floating on the surface and the water column; 6 plants with floating leaves; 7-marsh plants |
|
|


 created to find ...
created to find ...



Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.